Industry
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A pair of bills has been passed in Congress that will see America's Homeland Security and cybersecurity engineers working together for the betterment of the cybersecurity situation prevalent in the world today. The interesting distinction to be made here is to notice that Homeland Security will be working with private sector cybersecurity firms. Private security network engineers are understanding more about automation, control and SCADA systems than engineers within the American government. The U.S. actively wants to avoid entire substations being taken down by hackers ; a scenario which has actually happened in countries like the Ukraine. The second bill passed was an act named the Rapid Innovation Act which would see the American government making funds available to research and development for emerging technologies. Smells like the Internet of Things.
Congressman John Ratcliffe said: "With these growing cyber threats posing significant danger to our homeland and infrastructure, it is critical that our government keep pace by actively working with the private sector to find solutions to protect our network."
 Australian tech companies are also seeing the adoption of private network security firms. NEC Australia says that it will be building an AU$4.38 million Global Security Intel Centre (GSIC) that will police the Internet of Things to add an extra layer of cybersecurity to countries or companies that want in. With 50 billion devices connected to the internet by 2020, cybersecurity is one of the most important industries to either study in or invest in.
Australian tech companies are also seeing the adoption of private network security firms. NEC Australia says that it will be building an AU$4.38 million Global Security Intel Centre (GSIC) that will police the Internet of Things to add an extra layer of cybersecurity to countries or companies that want in. With 50 billion devices connected to the internet by 2020, cybersecurity is one of the most important industries to either study in or invest in.
One of the biggest targets for cybersecurity is currently banking. Recently, in May, a gang of Japanese criminals made off with $13 million in cash over three hours. They used counterfeit credit cards from a well-known South African bank and were able to steal the money through cybersecurity loopholes. The heist had South Africa's central bank warning local banks to invest into cybersecurity. This is not an isolated incident, these sorts of cybersecurity stories are happening globally.
An insider source said: "They were smart in selecting Japan. They found a badly protected ATM network in a low-risk country, guessing that the fraud analytics software would not automatically block the transactions."
Leonhard Weese, a contributor for Forbes, thinks authenticating users and encryption is the answer to protecting the banks. What kind of system could possible authenticate a user and ensure a level of unbreakable encryption? Bitcoin, of course.
He writes:
Bitcoin uses a method, widely available for decades, called "assymetric encryption", to authenticate the owners of keys. These keys are a pair of mathematically linked numbers. One functions like a key and is private, ergo never leaving the owner's computer. The other can be understood as a lock. It can be safely handed around and publicized without risking a loss of these funds.
Source: The Hill / Forbes
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Elon Musk has fingers in many pies and those pies have been producing major engineering marvels lately. It's difficult to ignore the engineering endeavors he associates himself with because they are so current and so 'now'. From securing a high-speed tube train to developing the next battery-powered cars to landing a rocket, the list truly does go on.
Musk also has his money in an artificial intelligence company named OpenAI. You guessed it, they develop artificial intelligence. They are actively working on a robot that would assist with "basic housework". The company won't be manufacturing the robot but they will be concerning themselves with the artificial intelligence that would understand what housework is to begin with. The robot that they will most probably test the AI with would be similar to BRETT. The robot is Berkley University's Robot for the Elimination of Tedious Tasks.
Berkely's robot reportedly has the ability to perform housework duties and continue learning about how to do them more efficiently. Through trial and error, the robot eliminates any room for error once it has learned a lesson from grappling with different tasks.
So, will we be communicating with our household robots in our mother tongue and expecting them to reply to us? OpenAI says this will be possible. In a statement, they said: "Today, there are promising algorithms for supervised language tasks such as question answering, syntactic parsing, and machine translation but there aren't any for more advanced linguistic goals, such as the ability to carry a conversation, the ability to fully understand a document, and the ability to follow complex instructions such as natural language."
Further afield, in other Elon Musk news. Tesla, who Musk is the CEO of, is going to buying a company called Solar City. The CEO of Solar City is Elon Musk. The company's modus operandi is in the name, really. They focus on solar power systems for homes, businesses and governments.
"The SolarCity team has built its company into the clear solar industry leader in the residential, commercial and industrial market, with significant scale and growing customer penetration," Tesla Motors wrote in a press statement. The company says they are excited to be a company that offers end-to-end clean energy products. "This would start with the car that you drive and the energy that you use to charge it, and would extend to how everything else in your home or business is powered."
Talking about Tesla Motors, Elon Musk has confirmed that their much-anticipated Model S vehicle will also be able to survive a swim. He said in a tweet: "We *def* don't recommend this, but Model S floats well enough to turn into a boat for short periods of time. Thrust via wheel rotation."
Musk felt he had to address the situation after a video out of Kazhakstan showed that the vehicle had powered through at least a meter of water:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
This Thursday Britain will make a decision. The decision is whether to leave the European Union or remain in the position they currently fulfill. As the day draws closer, engineering experts have unequivocally supported a 'STAY' vote. Experts say that if Britain does leave the European Union, they might be cutting off their noses to spite their face, especially in engineering industries. And the warnings keep streaming in.
"The fact that we source talent from the best universities in continental Europe is to the benefit of the UK economy because they help us to design infrastructure in the country," said Chief Executive of WS Atkins Plc, Uwe Krueger, speaking to Reuters News Agency.
 We have already reported what leaving the EU means for civil engineering due to already spiraling figures in the industry. The data done by market analysts shows that civil engineering activity in the country had slowed down. The Brexit vote has notoriously damaged steel workers' outputs significantly.
We have already reported what leaving the EU means for civil engineering due to already spiraling figures in the industry. The data done by market analysts shows that civil engineering activity in the country had slowed down. The Brexit vote has notoriously damaged steel workers' outputs significantly.
However, now experts like Krueger are warning that A-grade engineering graduates will be last in line when it comes to engineering talent. Rolls-Royce is another engineering company that has said it would be better for their interests if Britain remained in the EU. The company drafted a formal letter that said their stance is that they want to remain 'IN'. Chief executive, Warren East, has been quoted saying that their new engine testing plant could be in danger of losing profits if Britain exit the EU.
He was quoted from a BBC Radio interview: "We're making investment decisions all of the time about where to place different parts of our operation, and uncertainty created by Brexit puts a lot of those decisions on hold and that pause is something that our US competitors don't have to cope with. That's why it's not good for us."
It's not only Britain's own industries that might struggle to recover from the lack of investment after a hypothetical 'OUT' vote. According to the Wall Street Journal, German exports estimations will have to be tweaked if Britain exit the EU.
The president of the Federation of German Wholesale, Foreign Trade, and Services, Anton F. Börner said: "Brexit leads to insecurity and a loss of trust over the years. This is poison for the economy in the UK and in all of Europe."
The fact of the matter is, the polls have been 50/50 in the lead up to the referendum and only by Thursday will we know whether or not to keep focused on how a Brexit could affect engineering in the UK.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Cybersecurity for Automation, Control and SCADA systems is becoming one of the most important fields of study in the world today. The industrial world is moving towards Industrie 4.0 and the internet of things, interconnecting entire industrial companies and syncing them to cloud-based solutions. Cyber-criminals are actively making hundreds of thousands of dollars every single day from holding the data from these industries ransom.IBM Security has released a report of how much hacking is costing the cyber security industry. The report revealed that a major data breach could see companies parting with $4 million per data breach.
Globally, cyber crime is accounting for $400 billion per year, according to British insurance company, Lloyd. The United States government has secured $14 billion to combat cyber security attacks in the country that could save the data of countless companies. Studying toward a cyber security qualification could see an engineer or IT specialist making a pretty penny with ensuring that  industries remain safe from cyber crime. We recently reported that cybersecurity education in the United States specifically is not up to scratch. Hopefully, the money budgeted will go towards the educating of cyber security professionals.
industries remain safe from cyber crime. We recently reported that cybersecurity education in the United States specifically is not up to scratch. Hopefully, the money budgeted will go towards the educating of cyber security professionals.
"Cybersecurity incidents continue to grow in both volume and sophistication, with 64 percent more security incidents reported in 2015 than in 2014," said Amanda Carl, IBM's corporate communications officer.
Their report further indicated that noticing a breach could take up to 201 days and the containment of a breach could take up to 70 days, on average.
IBM's CEO and President Ginni Rommety said: "We believe that data is the phenomenon of our time. It is the world's new natural resource. It is is the new basis of competitive advantage, and it is transforming every profession and industry. If all of this is true - even inevitable - then cyber crime, by definition, is the greatest threat to every profession, every industry, every company in the world."
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, said that his institution sees 10 to 20 attempts at infiltrating their online systems every week. He confirmed this in his YouTube series, the Engineering News Network. He goes on to explain that industrial networks are vulnerable and expressed dismay surrounding the shortage of cyber security experts. He said: "Industrial networks for your PLCs and other hardware used to be proprietary. Now, they're open with ethernet,TCPIP and of course, are a whole lot more vulnerable to hacking. We all access the cloud now, which means that your information has to traverse a very public network, so it raises your profile in terms of attacks. We need to design - into everything we do, both individually and holistically - some sort of cyber security. So, concepts such as security in depth, you need to understand and apply to your systems"
The IBM report further indicated that companies who invested into cyber security companies to prevent or remedy cyber crime have saved the companies $400,000. IBM found that data breaches that were remedied in 100 days only cost companies $3.23 million. Data breaches discovered before 100 days only cost $1 million.
The real question is: Is $14 billion enough investment into the research of cyber security, that claims $400 billion of damage every year? Let us know in our comments section.
Source: IBM
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Researchers at the Massachusetts Insitute of Technology have tackled one of the biggest questions plaguing the engineering industry: Where are all the women? The last two years have been landmark years for universities that have prioritised closing the gender gap that exists in the engineering world. Some universities ensure to have at least 30 percent female attendance in their engineering courses. Some universities have even ensured that half of the classes are female. However, aside of the strides being made in getting women into engineering, MIT has found that some issues arise once they have arrived in the industry, as well. The researchers took a look at why women leave engineering.
We recently reported that Engineers Australia's study into gender gaps in engineering said that less than 1% of Australian women past the age of 50 years old are currently working in the industry. Meaning, the other women who used to work in the industry had all left the industry before the age of 50. According to the Telegraph, only 9% of the United Kingdoms' engineering workforce is female. Furthermore, Jobsite's study into female engineering saw that there are three times the number of female engineers in the 20-24 age bracket than there are in the 40-44 bracket.
 Susan Silbey, a Professor of Humanities, Sociology and Anthropology at MIT with regards to the engineering industry, said: "It turns out gender makes a big difference. It's a cultural phenomenon." The paper she co-authored is titled: Persistence is Cultural: Professional Socialization and the Reproduction of Sex Segregation. The report focuses on engineering relatively closely, revealing that women become "disillusioned with their career prospects" once they aim to achieve big goals in the engineering industry.
Susan Silbey, a Professor of Humanities, Sociology and Anthropology at MIT with regards to the engineering industry, said: "It turns out gender makes a big difference. It's a cultural phenomenon." The paper she co-authored is titled: Persistence is Cultural: Professional Socialization and the Reproduction of Sex Segregation. The report focuses on engineering relatively closely, revealing that women become "disillusioned with their career prospects" once they aim to achieve big goals in the engineering industry.
They also crunched the numbers and unveiled their results in the report:
- Women account for 20 percent of undergraduate engineering degrees
- 13% of the engineering workforce is female (U.S.)
The research included the study of 40 undergraduate engineering students who wrote in diaries twice every month. They had 3,000 diary entries to peruse and generate data from. What they found is that when female engineers are involved with team-based activities outside of the lecture halls, gender stereotypes run rampant.
One of the diaries that detailed a robot-designing brainstorming session, showed what kind of gender discrimination occurred: "...two girls in a group had been working on the robot we were building in that class for hours, and the guys in their group came in and within minutes had sentenced them to doing menial tasks while the guys went and had all the fun in the machine shop. We heard the girls complaining about it..."
Source: MIT News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The International Energy Agency has released their report on liquefied natural gas and how the market is growing. The report, titled 2016 Medium-Term Gas Market Report, says that investment into LNG will grow the market by 45% between 2015 to 2021. Australia will be a big producer, along with the United States, however after Shell's announcement of a slow-down on a lot of projects, the market is looking volatile. The report also stated that global natural gas demand would increase by 1.5% annually, which is an estimation that differs from the previous measurement of 2% growth. One of the bigger importers of LNG, with a huge increase in demand, is China.
 China's demand for LNG would grow by 15% between 2016 to 2021, this according to a report compiled by TechSci. The report was titled 'China LNG Market Demand & Supply Analysis, By End-User, By LNG Terminals Forecast and Opportunities, 2011-2021'
China's demand for LNG would grow by 15% between 2016 to 2021, this according to a report compiled by TechSci. The report was titled 'China LNG Market Demand & Supply Analysis, By End-User, By LNG Terminals Forecast and Opportunities, 2011-2021'
"Government of China prioritized expansion of natural gas based power plants, on account of growing air pollution and rising greenhouse gas emissions. This is boosting installation of new natural gas-based power plants along with LNG terminals, especially in Guangdong and Shangai provinces of the country. In order to reduce coal consumption, Beijing has already replaced four major coal power plants with natural gas. In the coming years, the government is planning to replace all coal-based power plants in the country with natural gas based power plants. This shift towards natural gas based power plants is forecast to propel growth in natural gas exploration and production, as well as augment China's LNG imports in the coming years," said Mr. Karan Chechi, Research Director with Techsci Research.
China is the third biggest importer of LNG in the world, behind Japan and Korea, says TechSci.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Fortune 500 list for 2016 has been released. The list details 500 companies that make up two-thirds of the United States' gross domestic product. The companies posted $12 trillion in revenues and $840 billion in profits, according to Fortune. However, due to a volatile construction and oil year, how are engineering companies coping?
The top 10 on the Fortune 500 should give you a pretty good idea of where the top-paid engineers are working:
- Walmart
- Exxon Mobil
- Apple
- Berkshire Hathaway
- McKesson
- UnitedHealth Group
- CVS Health
- General Motors
- Ford Motor
- AT&T
 Most notably, Exxon Mobil and Apple are very close to the top. Oil and gas and electronics seem to be ruling the roost right now. Also, those are two companies that are going to be spending money on renewable energy and the creation of new branches within their companies.
Most notably, Exxon Mobil and Apple are very close to the top. Oil and gas and electronics seem to be ruling the roost right now. Also, those are two companies that are going to be spending money on renewable energy and the creation of new branches within their companies.
However, last year, engineering companies who have a keen focus on construction in the makeup of their companies went up on the Fortune 500 list in a successful 2015. The guys over at Construction Dive compiled a list of which engineering companies had made it to the Fortune 500 and stayed there over the years:
| Company name | Revenue | Profits | Number of employees | Rank of last year | Years on Fortune 500 list |
| Jacobs Engineering Group | $12.115 billion (down 4.6%) | $303 million (down by 7.7%) | 56,950 | 239 (up 4 spots) | 16 |
| Peter Kiewet Sons' | $8.992 billion (down 12.4%) | $251 million (down 28.3%) | 22,000 | 286 (drop of 28 spots) | 17 |
| Quanta Services | $7.632 billion (down 2.8%) | $311 million (up 4.8%) | 24,500 | 361 (up 9 spots) | 4 |
| EMCOR Group | $6.723 billion (4.3%) | $172 million (up 2.1%) | 29,000 | 421 (up 40 spots) | 16 |
| CH2M Hill | $5.362 billion (down 1.0%) | $80 million (unchanged) | 22,000 | 480 (up 2 spots) | 8 |
The company that jumped up a staggering 40 spots was EMCOR Group. With sixteen years on the Fortune 500 list, the company improved their revenue and profits in 2015.
The company that gained the second most ground was Quanta Services, which went up 9 spots compared to the previous year. They are based in Houston, Texas and capitalize on the oil industries that are prevalent in the area. The shareholders said that the "drop in revenue" they experience was caused by the current demand for oil, which they could not control.
2016 should be an interesting year for these companies due to construction slow-downs on new orders. U.S. construction is posting its lowest numbers in five years. With construction and oil struggling to recover in 2016, we could see these companies post even lower results. However, ExxonMobil seems to be coping in the tougher industry, being second on the top ten list of Fortune 500. What is apparent is that companies like EMCOR and CH2M are very close to losing out on their Fortuen 500 status as engineering companies with focus on construction and engineering.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Research and Markets, who claim to be the world's largest market research store have conducted fresh research on the global gas turbine market, making projections for 2016 all the way up to 2020. The research has been published in a 106-page journal titled Global Gas Turbine Market 2016-2020. Gas turbine engineering will still be lucrative for the next 4 years due to the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of gas turbines. The researchers foresee a CAGR of 3.49%.
 The report portrays the market in a positive light due to the push for renewable energies occurring in the world today. The researchers think that governments will invest more money into the gas turbine market in an attempt to integrate renewable energy technologies and to cut emissions.
The report portrays the market in a positive light due to the push for renewable energies occurring in the world today. The researchers think that governments will invest more money into the gas turbine market in an attempt to integrate renewable energy technologies and to cut emissions.
Anju Ajaykumar, a lead analyst at Technavio, talking about the report, said: "Worldwide, power generation is undergoing a transformation from centralized systems to integrated networks due to growing reliance on distributed power generation systems. Distributed power technologies are less than 100MW in size with the standard size being less than 50MW, which is the limit permitted by distribution systems at distribution voltages."
The research underlines which markets are directly affecting the rise in the need for gas turbines:
- Power generation 70.39%
- Mobility 17.18%
- Oil and gas 6.07%
- Others 6.35%
"Gas turbines are an essential part of distributed power technologies product portfolio along with diesel and gas reciprocating engines, solar panels, fuel cells, and small wind turbines. Thus, growth of distributed power systems will translate to an increased demand for gas turbines during the forecast period," Ajaykumar concluded.
Back in 2012, General Electrical debuted 60 Hz gas turbines named FlexEfficiency and since then have seen new orders flying in. Toshiba has recently asked GE's Power Services to retrofit steam turbines in their steel manufacturing facilities in South Korea. The power plant would recycle the steel facility's blast furnace gas and use that to fuel boilers to create steam. The method is an environmentally conscious method, the company says no harmful gases will enter the atmosphere. When launched, GE said their gas turbines would avoid up to 56,000 metric tons of carbon emissions per year.
Siemens - who also have a range of gas turbines - were contacted by Israel to install two natural-gas fired turbines in a power plant. They will be installing their SGT-800 industrial gas turbines which have a capacity of 70MW each. They will also be installing one in Malaysia.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Royal Dutch Shell will be investing less into LNG starting this year. The intention to slow down on investment into liquefied natural gasses will continue towards 2020, insiders in the company have confirmed.
"Integrated gas, which was previously a growth priority for Shell, has reached critical mass following the BG acquisition...particularly in Australia. The pace of new investment will slow here," said Shell chief executive Ben Van Beurden.
 Shell bought rival BG Group (a group known for its LNG sales) for $50 billion. After the purchase, Shell said it would "limit spending" on new projects. There is an impending $40 billion project in Canada that still needs to happen, however, analysts are saying it could be postponed.
Shell bought rival BG Group (a group known for its LNG sales) for $50 billion. After the purchase, Shell said it would "limit spending" on new projects. There is an impending $40 billion project in Canada that still needs to happen, however, analysts are saying it could be postponed.
Shell will be exiting 5 to 10 countries to further cut spending, under the oil crisis the world currently finds itself in. They are now moving closer and closer to shale oil and gas production and renewable energies. This would leave Australia - now one of the biggest LNG producers - without major investment in LNG.
"There is a view that says if we wait, we don't have to do anything because the demand of the developing world will grow...and if we turn off coal power stations, gas demand will go up, and next year's conference will be a rosy one. Well, nothing could be further from the truth. Simply surviving is not an option...we must change to grasp the opportunity in front of us," said Woodside Petroleum chief Peter Coleman, talking to a crowd at the Australian Petroleum Production and Exploration Association in Woodside.
"LNG is still a segment that strongly supports reinvestment. But LNG moves in fits and starts and it demands investment in big lumps," Van Beurden said.
Coleman further berated the Australian LNG industry for investing into the wrong areas. LNG projects topped $200 billion in investment in the last ten years. He said: "While we may wax lyrical about the $200 billion, it actually started as $100 billion. We shouldn't be proud of the $200 billion. We didn't deliver on our promise, we've delivered a very expensive energy source."
Source: The Australian / Reuters
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Australian construction had a slow May, according to the Performance of Construction Index. The country dropped 4.1 points down to 46.7. A good construction month is usually past the 50 point mark. The measurements are done by an Australian company known as the Ai Group (Australia Industry).
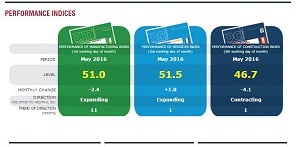
Ai Group, however, did indicate that apartment building and commercial construction was the hardest hit with losses in the research. The group confirmed that the lack of new orders has caused the fall, and it is the most significant fall since February 2015. Australia joins Britain who is also struggling to improve the number of orders in construction.
Ai Group did, however, confirm that manufacturing in May was down by 2.4 points but remained above the 50 point comfortability barrier.
Britain
Interestingly, British manufacturing might be improving despite subpar construction numbers due to the impending EU Referendum. It is a slow improvement due to the numbers that turned for the worst during the first quarter of the year.
EEF chief economist, Lee Hopley, spoke to Reuters, saying: "While all of this suggests that manufacturing is coming out of the mire of the past 18 months, even a decent six months in the latter part of the year will still leave output broadly flat over 2016 as a whole. If however a vote to leave the EU, we can expect a very significant period of political and economic uncertainty which will see the sector facing uncharted waters for some time to come."
So, if Britain exits the EU it would damage the improvement that manufacturing is currently seeing. If true, this would mean even more losses of jobs in the manufacturing industry which has already lost 385,500 since 2008, a study confirmed.
Source: The Australian / Reuters
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Engineering companies sometimes lose their staff to other engineering companies. We've seen it happen frequently inside the engineering teams of Apple and Tesla, where engineers resign and move on to 'greener pastures'. A recent management change within Cisco Systems Inc. - who are wanting to become the leaders in Internet of Things technology - has made four of its top engineers resign from the company. Mario Mazzola, Prem Jain. Luca Cafiero and Soni Jiandani were supposedly the research and development dream team for Cisco but have now decided to part ways with the company.

The group was in charge of the design of products that Cisco recently bought into called "spin-in" products that saw the engineers getting big paycheck raises based on technology they sold to the company. A former executive at Cisco the engineers saying: "Mario is the soul. Luca is the brain. Prem is the heart. And Soni is the mouth." Some went as far as to say that the group ARE Cisco, due to the amount of tech they had built for the company and the amount of tech the company bought from them. However, they do hold office job positions at Cisco as well.
The engineers had a rare deal with Cisco. Their involvement in Cisco involved creating a start-up company, developing hardware and software and then selling it to Cisco and making a lot of profit. This is the idea behind the "spin-in" technologies. Budding engineers, take note.
Business Insider recapped the amount of money Cisco paid every time the group of engineers built a start-up company and then sold the technology they built :
- $750 million in 2001 for storage networking switches under company name Andiamo Systems
- $678 million for a "new kind of server" technology in 2008 under company name Nouva Systems.
- $863 million for a "core networking product" under company name Insieme Networks.
The four's positions in the company were shuffled just as June started. They were given advisory positions in the company by CEO Chuck Robbins in an internal memo.
However, it's all over now. The four have resigned from Cisco and are probably on their way to sipping on cocktails on their yachts, due to being multimillionaires as a result of Cisco's investment into their technology. However, if this isn't an engineering success story, we don't know what is.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
India
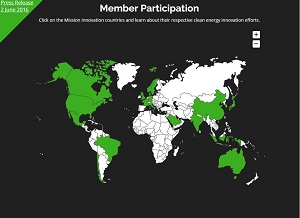
India is hiking their investment into renewable energy from its current $72 million to a handsome $145 million over the next five years. They are currently participating in what is called the Mission Innovation. A movement that holds countries accountable in terms of accelerating global clean energy. To see which countries have pledged their support for eliminating greenhouse gases, see the photo attached to the left of the article.
"Mission Innovation is the noblest mission which will help humanity. This has also touched the heart and soul of our Prime Minister. With super-efficient air conditioners, we can reduce the energy demand from 60 Giga Watts of energy to 40GW, a saving of 30 per cent. This translates to cost savings in consumer energy bills of $2.8 billion and GHG reductions of 20 million tons of C02 equivalent," said Union Minister for Science and Technology Hars Vardhan.
Australia
In Australia, the Greens party has launched a clean energy policy that will see solar technology being fairly priced so consumers can access it. Their policy would ensure $192 million would be funded for installing photovoltaic cells in schools as a "right to solar" so that schools can be powered by renewable energy. The solar policy is being considered brave by some critics, in a situation where Australia is trying to lead the charge for solar expansion.
The Greens are also trying to prevent any fees or charges that the government would try to impose due to the usage of solar technology. Their policy guards homes and businesses from fees "likely to be imposed by electricity networks clawing back their diminishing revenues as our electricity system decentralises and consumers become empowered."
The party is currently trying to move Australia into a country powered by 100% renewable energy by 2030.
Source: Mission Innovation / The Guardian
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial automation is slowly making humans redundant. We have recently seen Foxconn (an electronics manufacturer) let go of 60,000 human workers due to their assembly line becoming fully automated. We are seeing restaurant industries replacing their waiters, waitresses and their kitchen staff for robots in fast food companies in the United States and China. Robots can do almost everything a human can, just more efficiently and around the clock for twenty-four hours a day.
At a town hall in Elkhart, Indiana in the United States on the 1st June 2016, Barack Obama spoke about jobs losses in manufacturing due to automation after a steel worker pointed out that jobs were not being made in available in the area anymore. Here are some of the excerpts of what Obama said, minus the references to what his campaign achieved throughout the years:
If you look at just the auto-industry as an example, they've had record sales and hired back more people over the last five years than they had for a very long, long time.
We actually make more stuff, have a bigger manufacturing base today than we've had in most of our [the United States of America] history. Part of the problems have to do with jobs going overseas...Part of it has had to do with automation.
You go into an auto-factory today, that used to have 10,000 people and now they have 1,000 people making the same number of cars or more. What that means is, even though we are making the same amount of stuff in our manufacturing sector, we're employing fewer people.
Now, the good news is, that there are entire new industries that are starting to pop up.
But, for those folks who have lost their job right now because a plant went down to Mexico, that isn't going to make you feel better. What we have to do is make sure that folks are trained for the jobs that are coming in now, because some of those jobs of the past are just not going to come back.
But, I gotta tell you that the days when you just being willing able to work hard and you can walk into a plant and suddenly there's going to be a job for you thirty years of forty years, that's just not going to be there for our kids. Because, more and more, that stuff's gonna be automated. And if you go into a factory that kid is going to need to know computers, or is gonna need to know some science and some math because they're not gonna be picking anything up they're just going to be working on a keyboard.

The robot revolution is being observed all around the world. The worry is that once robots are doing most of the repetitive tasks that humans have been making their livings on, there will be a group of humans that are out of work, are ill-equipped to go into another job and as a result, cannot get a job. The hopeful few want to try and get governments to introduce a universal basic income. Being paid for being human.
A referendum was voted on in Switzerland yesterday that attempted to secure the universal basic income. 77% of voters opposed the plan, whilst 23% supported the proposed law. The proposed income would have been $2,555 per month to every adult human whether work was done or not. Swiss campaigners have been conducting peaceful protests down streets in Switzerland to ask for the universal basic income.
A campaigner for basic income, Che Wagner, spoke to the BBC, saying: "We want to introduce a basic income for you, human beings because we don't wanna grab your work and make you suffer but we want to make you free. In Switzerland for example, over fifty percent of total work that is done is unpaid, it's care work, it's at home, it's in different communities so that work would be more valued with a basic income."
According to the BBC, Finland will be conducting a trial of universal basic income on 8,000 low-income participants to measure the feasibility of giving every human a leisure wage.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
If you haven't seen the new Michael Moore documentary 'Where Do We Invade Next?' then make sure you give it a watch this weekend. The documentary centers around what policies countries around the world enjoy that America may benefit from. One of the countries focused on in the documentary is Norway. Moore shows that Norway does not endlessly punish its criminals and rather tries to legitimately reintroduce them into society, the maximum prison sentence in the country is 21 years. What was apparent through the documentary is that Norway is led by a progressive thinking government that gives its citizens the best they can offer.
 Now, Norway may change the way they power cars as well. News company CNBC spied a headline from a Norwegian newspaper named: Dagens Næringsliv. The headline translates to: "Stop sales of diesel and gasoline vehicles in 2025. It is understood that four political parties are joining hands to support the prohibition of cars powered by diesel and gasoline. If the sales of gasoline and diesel powered vehicles are banned it would be a world first and a shocking move from Norway considering that the country is one of the largest exporters of oil.
Now, Norway may change the way they power cars as well. News company CNBC spied a headline from a Norwegian newspaper named: Dagens Næringsliv. The headline translates to: "Stop sales of diesel and gasoline vehicles in 2025. It is understood that four political parties are joining hands to support the prohibition of cars powered by diesel and gasoline. If the sales of gasoline and diesel powered vehicles are banned it would be a world first and a shocking move from Norway considering that the country is one of the largest exporters of oil.
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, tweeted as if the law is a done deal: "Just heard that Norway will ban new sales of fuel cars in 2025. What an amazingly awesome country. You guys rock!!"
According to Electrek, Norway also holds the "highest percentage of electric vehicle market share of any country" meaning that banning the gas-powered vehicles will not be difficult for the country, however, they might want to cause a domino effect where other governments follow suit. CNBC confirms that Norway has the smallest driving population in Europe, with only 150,000 cars being sold in 2015.
The official draft document is named the 2018-2029 National Transport Plan and will make a case for completely eliminating emissions by vehicles by 2025.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Paris is under water and the situation seems to be worsening. Today the French government has confirmed the closing of the Louvre in Paris. The staff will move selected works to higher ground in the gallery to ensure that the water causes no damage. The floods were caused by extended rainfall in the area and the weather service has warned that the rain won't slow down over the weekend. 25,000 people will be left without power. Germany has also been hit hard after constant rainfall had caused up to 5 deaths and left several people missing. Europe is becoming commonplace for floods in recent times making civil engineers wonder what is to be done. Flash flooding is something that engineers are researching so that damage to property and valuables is far less than it is in the world today.
 Flash floods are also occurring in the U.S. in Texas. Analysts are saying that the flooding could continue for weeks to come. The flood has already claimed the lives of five soldiers and another four are missing in what is being considered historic floods for the state.
Flash floods are also occurring in the U.S. in Texas. Analysts are saying that the flooding could continue for weeks to come. The flood has already claimed the lives of five soldiers and another four are missing in what is being considered historic floods for the state.
An engineer foresees more floods in the future and wants to help with a new app that could benefit the entire world. A professor of civil engineering at the University of Texas at Arlington, D.J. Seo, has coded a new app named iSeeFlood. The app would assist in real-time reporting of flash flooding that could inform motorists and household owners that water could be rising wherever they are. On top of the user generated data, Seo's team have installed wireless sensors that will model urban water systems with Collaborative Adaptive Sensing of the Atmosphere which will also alert the engineers if water levels rise to the point of flash flooding.
"We will integrate the information that people send us using the app and the data from the sensors and the CASA system with flash flood forecasting models...Urbanization means we have changing land surface conditions such as increasing impervious land cover, which changes how rain may be running off and accumulating," said Seo.
The CASA systems are a relatively new technology but will be invaluable to severe weather warnings that could lead to flash floods. The technology works by scanning areas prone to heavy storm systems so that predictions can be made on how severe the storms are going to be due to atmospheric pressure.
Researchers hope the technology will be proven successful so that countries all around the world can warn their citizens that severe storms might cause flash floods. The technology could prevent deaths and save valuable property due to fair warning that storms are on their way.

- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Additive manufacturing is being used in many engineering industries, and there are still improvements being made in the way 3D printers do what they do. The University of Oklahoma has a lab where the latest in 3D printing technology is being used. Bizzell Memorial Library Innovation @ the Edge is the pride and joy of the budding engineers who would come and print their projects on the 3D printers. It is not uncommon for universities to have 3D printers on hand for engineers to test out.
"In places like car factories, they already use it to make models. In the future, it will come more into homes. If you have an idea for what want, you don't have to wait for someone to go and make it. It's getting to a level where everyone can use it," said Joris Juru, a junior computer engineering major. Juru wants to make 3D printing faster and points out that printer software is becoming more industry specific.
For example, an industry-specific 3D printing technology has been used at Airbus. They have just successfully printed a drone at an aerospace expo in Berlin. Donning the name "Thor", Airbus's drone is 4 metres long and has a 4-meter wingspan and weighs 55lbs.
One of the more interesting advancements in the 3D printing world comes out of Cornell University. They have been working with faster printing systems and have noticed that they could alter 3D prints whilst they were printing. They started to experiment with "edits" during the printing process and found that they were successful with a Wireprint 3D printer. The printer they used is different from a conventional printer but the research could prove useful even to the current 3D printers.
"On the fly print allows the user to check the design in a real usage context and to continue to design and print afterwards," the researchers said in their video. First prints are sometimes failed prints, therefore, this new method by Cornell University could refine the first print processes of a project.
The printer can begin on a project whilst the designer continues to design the rest of the project on the software. The researchers said: "[The on the fly printing] opens new opportunities for rapid prototyping and has great potential to improve the overall quality of the design process."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The UK construction industry continues to slip as the looming Brexit vote draws nearer. The 25th of June will be the deciding day to whether or not Britain stay with the European Union or opts out. Since the vote was announced, engineers have been keeping their eyes on the Markit/CIPS construction purchasing managers' index (PMI). The theory is that due to the looming vote no one will be investing in the construction industry, and those critics would be right.
 The PMI data made available indicates that the manufacturing sector did see some improvement, however, the construction industry is at a three-year-low. The numbers in the index went down from 52 in April, to 51.2 in May. June could be seeing a further slip in numbers due to the vote. A senior economist at Markit, Tim Moore, told The Telegraph: "My data signalled the worst month for commercial building since June 2013, while residential work and civil engineering activity both saw a renewed loss of momentum. Survey respondents noted that the forthcoming EU referendum has disrupted new order flows and the timing of client decision making in particular."
The PMI data made available indicates that the manufacturing sector did see some improvement, however, the construction industry is at a three-year-low. The numbers in the index went down from 52 in April, to 51.2 in May. June could be seeing a further slip in numbers due to the vote. A senior economist at Markit, Tim Moore, told The Telegraph: "My data signalled the worst month for commercial building since June 2013, while residential work and civil engineering activity both saw a renewed loss of momentum. Survey respondents noted that the forthcoming EU referendum has disrupted new order flows and the timing of client decision making in particular."
The neighbours across the pond are also interested in what is going to happen on the 25th. Donald Trump said that he would be visiting the UK the day the referendum happens. Trump has invested in the civil engineering endeavours in the UK, notably buying the Turnberry Hotel that has just been opened to guests. Trump says that Britain should leave the EU, which he confirmed in an interview with Fox, where he said: "I know Great Britain very well. I know the country very well. I have a lot of investments there. I would say that they're better off without it [the EU]. But I want them to make their own decision." He also said that the UK would not be in the back of the line for trade deals if he were president. President Obama notoriously said that Britain would be at the back of the line in trade deals if they opted to leave the European Union.
The Guardian caught up with the chief UK and European from IHS Global Insight, Howard Archer. He said: "The government will be particularly disappointed to see housebuilding growth could only edge up for the third month running in May and is around its lowest levels since early 2013, given that it is looking to address the UK's accurate housing shortage."
Other analysts are saying even if Britain remains in the EU, the damage has been done and the slow-down will continue. "The official data clearly shows that public sector construction is squeezed, while the revival in housebuilding has run into skilled labour shortages," said Samuel Tombs, chief UK economist at Pantehon Macroeconomics.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The CEO of Amazon, Jeff Bezos, has said that the industrial economy is key to expanding into space.In an interview at the Code Conference in California, he spoke about Blue Origin, the SpaceX competitor company that he is a part of, and why Mars is the next frontier. He also said the answer to energy is in space and industry would move into space instead of staying on earth. Ready to become astronauts, engineers?
Bezos spoke candidly to an interviewer overseen by a large audience. He said: "Energy is limited here. In at least a few hundred years...all of our heavy industry will be moved off-planet. Earth will be zoned residential and light industrial. You shouldn't be doing heavy energy on earth. We can build gigantic chip factories in space. We don't have to build them here."
Then Bezos referenced solar energy and the future it has: "The Earth shades itself...in space you can get solar power 24/7. The problem with other planets...people will visit Mars, and we settle Mars, and people should because it's cool, but for heavy industry, I would actually put it in space." He does have a point, however. If enough solar panels can be put into space - and in perfect positionings - 24/7 solar power could be a possibility. Engineers, get to work!
It's not just you...it does sound like Jeff Bezos is rambling. However, this is just Bezos talking candidly about things that Elon Musk is trying to do and hoping he can be in that golden circle of engineers that are pushing our world forward..
Meanwhile, SpaceX and Elon Musk have successfully landed another Falcon (which can be seen here) on a barge and have reiterated that they plan on getting to Mars as soon as 2018. Tech Insider has put a good video on YouTube, showing the exact type of rocket that SpaceX wants to send to Mars.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Apple Inc has opened a new store in San Francisco's Union Square and are following in the footsteps of Ikea, Walmart and others that will be running their stores on completely renewable energy. The store would be their flagship store which will be showcasing the Apple brand. The store spent $23.6 million on the new store's construction.

"The store is powered by 100 percent renewable energy, including power produced by photovoltaic panels integrated into the building's roof," said the press release from Apple announcing the opening of the store. Photovoltaic panels that are integrated into the roof instead of being positioned on top of it are called Building Integrated Solar Photovoltaic (BIPV). However, a writer for Electrek thinks Apple is up to something else based on the photovoltaic panels that have been put up at the new flagship store. It was the pricing that intrigued the writer. He pointed out that, according to Buildzoom, the photovoltaic array that was integrated into the roof cost Apple $800,000 and would push out 50kW of solar energy. Why would they need that much energy connected to one store? His question is: "What did they build?"
The discrepancy - to the curious few - of this new flagship construction is that a normal 50,000W solar system retails for $150,000, however, Apple used $800,000. Some analysts say that Apple could be selling the power they generate in their new flagship store back to the grid to assist with renewable energy that can be then sold to customers through utilities or will eventually sell their own energy to consumers. Based on the cost-effective construction of the building - or at least that's what it looks like - the hefty price tag on the photovoltaic system they are using is either a case of over-reporting how much was spent for tax purposes or they have built something cool.
Did you know?: The City of San Francisco had made it law that any construction under ten stories has to have photovoltaic panels connected to it. This would make them the first state in the United States to implement such a law, and it will be fully implemented in 2017.
Regardless, the new flagship store is a wonderfully minimalistic look at a company that continues to engineer some of the most sought after products:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Computex 2016 has kicked off in Taiwan and who better to kick the show off than Taiwanese company ASUS? Throughout the week, companies will deliver keynotes and show off advances in consumer technology. A recurring theme from most of the companies showing off their new devices is virtual reality, but another subject is coming up quite a lot; home robots.

ASUS has unveiled Zenbo , their answer to the home robot. A potbellied, two wheeler, vacuum-like robot with a head that juts outwards with a screen for a face. It will cost $599. ASUS chairman, Jonney Shih, said: "For decades, humans have dreamed of owning such a companion: one that is smart, dear to our hearts, and always at our disposal. Our ambition is to enable robotic computing for every household."
What will this robot assist with in the house? Obviously not coffee making. But its other uses include:
- Being a fun and educational playmate for children
- It can assist the elderly with keeping up to date with meetings they may have or things they need to remember
- It can take photos
- "I am a robot of many talents, I can sing and dance," Zenbo said.
- Can assist you with tasks around the house
- It can even turn on your lights and turn your TV off
Here is the very strange video from ASUS that shows why exactly you might need the Zenbo robot. It's a mini-movie but it's worth seeing what kind of uses this little robot might have:
How many minutes did you manage to watch?
Meanwhile...
SoftBank, the company behind the Pepper robot that a host of companies are wanting to partner with, has added a strange line to their user agreement. "The policy owner must not perform any sexual act on the robot or engage in other indecent behaviour." The warning is probably necessary.
The Pepper robot will also support the Android operating system now that the SDK (Software Developer Kit) has been released. You can obtain the SDK from the Pepper Partnership Program so you can get started on developing apps for Pepper.
Nonetheless, Pizza Hut has also ordered themselves a Pepper robot that will be taking food orders, with the collaboration of MasterCard's MasterPass. In Japan, the Pepper robot is being used as a coffee machine salesman in one of Nestle's branches. What a time to be alive.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Computex 2016 has kicked off in Taiwan that will see keynotes from several companies including ASUS, Intel, Microsoft and more. The big thing at the conference this year? The Internet of Things and how it is changing computing.
First of all, Intel is sacking 12,000 employees in their industry due to what the New York Times is called the "PC Demand Plummet". Intel is restructuring their company to not only limit themselves to semiconductors but try and compete as a multifaceted tech company. One of the focuses is interconnecting objects together with the Internet of Things.
Brian Krzanich, Intel's chief executive, alluded to the fact that ignoring the IoT industry wouldn't be wise due to the number of connected devices rising to 50 billion by 2020.
"We think this is going to grow to 50 billion devices and trillions of dollars of economic impact. It will change the way we live and work. As we go out talking, we see more companies investing in it. We are making a transformation from a PC-oriented company to one that powers things that are connected to the cloud and everything necessary to make that happen," said Doug Davis, the senior vice president of Internet of Things at Intel, talking to Venture Beat. "We've seen how the markets have evolved. We now use data to control things. There's an opportunity to extract that data and make use of it. We call this phase, like connecting wind energy farms, 'connecting the unconnected'.
To see some of the Internet-of-Things-connected devices that Intel is bringing out, watch this video from CNet. This is footage from Computex 2016:
Intel is also working towards completely wireless PCs as well. These have chips inside of them that would allow wireless charging of laptops and wireless data sending over connected WiFi networks. They are also working on self-driving cars, but more specifically the screens that will deliver infotainment on the inside of self-driving cars, but nothing they can show off just yet. Once again, all of these things will be connected to the Internet of Things.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
German researchers from the Leibniz University of Hannover are conducting research into how to make a robot feel pain. Perplexingly, the researchers have been working with Kuka robots and programming some reactions to pain-inducing scenarios into robots. This disregards the entire premise of why robots would be employed. Do we not install robots in factories because unlike humans they cannot get tired and they cannot feel pain? Regardless, the researchers are making a case for installing an "artificial robot nervous system" into robots.
"Pain is a system that protects us. When we evade from a source of pain, it helps us not get hurt," said Johannes Kuehn, one of the engineers attached to the research. They have shown the research to panels of experts at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) that is taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.
The other engineer working alongside Keuhn is Professor Sami Haddadin. He said, "A robot needs to be able to detect and classify unforeseen physical states and disturbances, rate the potential damage they may cause to it, and initiate appropriate countermeasures, i.e, reflexes."
Reportedly, the researchers used a "nervous robot-tissue model" that was inspired by "human skin structure" that would be able to sense temperature and pressure. The engineers programmed the robot to have heat and pressure thresholds that if met, would then attempt to avoid whatever the engineers were throwing at it. The robot also sends out pain information for the engineers to peruse, when something infringed on its pressure thresholds.
As the researchers talk it starts to make more sense. Essentially, they don't want the robot to feel pain but rather to have reflexes to something that threatens their hardware as if they were feeling pain. So if the robot senses that it is in a room that is on fire and it has the ability to move out of the room instead of getting 'hurt', then it should be able to do that. However, perhaps robot helpers around the house should be given the ability to feel some sorts of 'pain' but industrial robots should have to tough it out. Yes? Maybe? No?
Stanford University engineers have also been experimenting with technology that would allow a robot to avoid a collision with something else. This particular avoidance system was programmed five years ago but will be invaluable research for years to come due to the increase of robot workers replacing factory workers in the world today:
Source: IEEE Spectrum
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Is Canada in trouble of losing their status as an energy superpower? Were they ever considered an energy superpower to start with? Well, they would like to think so. However, the Canadian government has a draft report doing the rounds that indicates that the country is scared of the impending move away from fossil fuels in the world today due to the amount of money they may be losing.
The Canadian government used a company named Policy Horizons Canada, a strategic foresight organization, to measure what impact the change in the global energy landscape will have on their country.
 "The world's energy is transforming rapidly as the cost of renewable-based electricity, particularly from wind and solar, declines to become competitive with or lower than the price of electricity generated by fossil fuel and nuclear power plants," the beginning of the executive summary of the report read. "The price of batteries is falling precipitously leading to their application at local and grid-level scales in the power supply system as well as facilitating significant electrification of transportation. The shift to an electricity-dominated global energy mix will be accelerated as decreasing costs combine with increasing government and private developing countries where the need for additional energy capacity is greatest."
"The world's energy is transforming rapidly as the cost of renewable-based electricity, particularly from wind and solar, declines to become competitive with or lower than the price of electricity generated by fossil fuel and nuclear power plants," the beginning of the executive summary of the report read. "The price of batteries is falling precipitously leading to their application at local and grid-level scales in the power supply system as well as facilitating significant electrification of transportation. The shift to an electricity-dominated global energy mix will be accelerated as decreasing costs combine with increasing government and private developing countries where the need for additional energy capacity is greatest."
Policy Horizons says there are three things forcing the hand of government to change from fossil fuels:
- Cost Reduction: Renewable energies becoming cheaper as a result of technology advancements
- Digital Economy
- Climate Change and Air: Developing nations embracing renewable energy to meet economic and development goals.
The Canadian government is now fully aware of the challenges that lie ahead, and really every government that is seeing the rise of renewable energies should be reading Canada's governmental report and making the relevant changes to their energy policies. Canda sees the impending doom of competition for energy markets and knows the best techbokogy is waht will win the hearts of consumers.
"Minerals and metals such as lithium and rare earths could replace oil, gas and coal as strategic resources based on their use in the batteries, electronics and photovoltaic cells of the emerging energy ecosystem," the Policy Changes section of the report said.
The foresight company said that storage solutions were "emerging and evolving" faster than the government thought they would. Enery storage really is the 'great disruption' the analysts have been talking about. The opening of Tesla's Gigafactory (and facilities of the same nature) is of particular interest to the Canadian government who sees lithium-ion slowly taking over. "Utility-scale energy storage techbologies are available now and may be a cheaper alternative to peaking power plants as well as new transmission lines by allowing public utilities to position battery plants near high demand areas like cities and industries and improve load-balancing while reducing GHG emissions," the company wrote.
They conclude the report by saying: "It is increasingly plausible to foresee a future in which cheap renewable electricity becomes the world's primary power source and fossil fuels are relegated to a minority status."
The full draft report can be read: HERE
Original source: CBC News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
And now for something completely different. Here's a scenario that you may never have thought of but engineers have had to grapple with. A woman loses a limb and gets a prosthetic limb to replace it. She gets invited to a wedding that requires formal wear. How does the woman wear high-heels to this event? This is the big question that Johns Hopkins University students want to answer. A team of engineers recruited some physician students and prosthetics experts and got to work. What they produced was a solution named Prominence. The first prosthetic foot that is custom designed to fit into high-heels of up to four inches high.
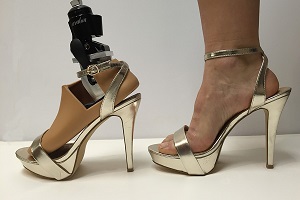
"High heels have become an integral part of the female lifestyle in modern society, permeating through all aspects of life -- professional and social," said the students from the Whiting School of Engineering. "For female veterans of the U.S. armed services with lower limb amputations, that seemingly innocuous, but so pervasive, and decidedly feminine part of their lives is gone."
The researchers say that 2,100 American women have lost their leg or a foot in military service and wanted to give the women a chance to reexperience the feelings of going to a formal event and wearing the same clothes as able-bodied people did. The prosthetic feet that are currently available on the market are actually built for men's shoes without a woman's desire to wear a high-heel ever considered.
Here were some of the challenges that the engineering students faced when having to design a prosthetic foot that would also be able to contort itself so that it could fit into a heel without causing the wearer displeasure:
- A foot that is adjustable without a tool to help it adjust for different heel heights
- Ensure that it does not slip once adjusted
- Weighs less than three pounds so that it is not too heavy
"An adjustable ankle is useful in contexts even beyond high heels. Ballet, flats, sneakers, boots, and high heels especially, all vary in height, so an adjustable ankle opens up opportunities to wear a variety of shoes," said Alexandra Capellini, one of the students who had lost her leg to bone cancer who was participating in the study.
- A 28-layer carbon fiber foot plate was tested successfully
- There is still work to do, but they are closer to a working prototype
Nathan Scott, a senior lecturer in the Whiting's School's Department of Mechanical Engineering who is the advisor of the ongoing project, said: "I think the final prototype produced showed the way forward. As usual, we just need to go around the design and prototyping loop one more time."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A Canadian plant might hold the future of carbon emissions and what we could do with them. The hope is that we could remove carbon from the air everyone is breathing right now in a process called 'direct air capture'. The company has been actively working on the process for four years now. The company leading the direct air capture process is a company named Carbon Engineering Ltd. The company has gotten backing from Bill Gates, oil billionaire Murray Edwards and other deep-pocketed investors. What they are working on would equate to snatching carbon emissions from cars, planes and other small-emitting devices and reclaiming the carbon so that it does not further poison the atmosphere. The idea is that once the carbon has been captured, it can be repurposed into carbon fuels.
"What we're doing is opening up, in a more serious way, a pathway to synthetic fuels from air. That's something that people get excited about," said David Keith, Carbon Engineering Ltd's founder. That was a quote from the Globe and Mail - in Canada - from January 2016. What strides has the company made in the last five months? Let's find out.
The company is a finalist in Virgin's Earth Challenge, where if they won, they would earn $25 million for the facility. The competition is dedicated to removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. This would assist the facility in further purchasing the tools they need to build their Prototype Air Contactor. The prototypes remove carbon emissions from vehicles that emit carbon into the air.
Christophe Jospe, a chief strategist for the Center for Negative Carbon Emissions (CNCE) writing for Virgin Earth's competition recapped the importance of Carbon Engineering Ltd's plight and highlighted its importance in our world today:
- Their process is feasible and makes economic sense
- Air capture (technologically removing CO2 from air) is a crucial technology to get to a carbon neutral future and beyond; and
- The world is starting to wake up to the fact that we cannot continue to treat the atmosphere as a dump for fossil based CO2, and there will be more policies and incentives to reflect that reality.
- Christophe Jospe, Virgin Earth
The company has continued its work in trying to repurpose the carbon into fuel so that they can power buses in the town they operate in, Squamish, British Columbia. Geoff Holmes, Carbon Engineer's business development manager said: "It would basically be a closed circle. You're capturing CO2 from the air, turning it into fuel, the car burns it, and it goes back into the air."
Will the world latch on to the idea or are there other ways we can eliminate carbon altogether that could be more profitable than direct air capture? The engineers are hard at work to try and make it happen. What will the next innovation in greenhouse gas reduction be? Check the video below for how the direct air capture facility from Carbon Engineering actually works.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The robot takeover continues. Industrial automation and the Industrial Internet of Things are the keywords that you should be following in the year 2016 because there will be news about them every day. Recently, Adidas opened a fully automated branch in Germany and is now making pairs of shoes in a fully automated process. Seemingly, Foxconn, the company behind supplying Apple and Samsung to the world, is doing the same thing.
According to the South China Morning Post, the $4 billion that was pumped into Foxconn has been used on buying automated industrial gear.
"The Foxconn factory has reduced its employee strength from 110,000 to 50,000 thanks to the introduction of robots. It has tasted success in reduction of labour costs. More companies are likely to follow suit," said the Department of Publicity head Xu Yulian.

The reason they replaced their workforce? Foxconn did not mince their words. In a statement, the group said: "We are applying robotics engineering and other innovative manufacturing technologies to replace repetitive tasks previously done by employees, and through training, also enable our employees to focus on higher value-added elements in the manufacturing process, such as research and development, process control and quality control. We will continue to harness automation and manpower in manufacturing operations and we expect to maintain our significant workforce in China." 60,000 employees are a lot of employees to lose at once.
The news out of Foxconn resonates with what the former CEO of McDonalds Ed Rensi said, albeit more harshly, this week: "I was at the National Restaurant Show yesterday and if you look at the robotic devices that are coming into the restaurant industry -- it's cheaper to buy a $35,000 robotic arm than it is to hire an employee who's inefficient making $15 an hour bagging French fries -- it's nonsense and it's very destructive and it's inflationary and it's going to cause a job loss across [the United States] like you're not going to believe."
It shouldn't be long before we see the next company slicing its employee strength in half and replacing them with automated industrial robots. There are fresh revelations in the robot industry every single week.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Facebook and Microsoft have become the new favorite tag team of the internet. The two companies have joined hands and have built a new fiber optic cable that will be laid in the Atlantic Ocean. The project's name is Marea, and will stretch beyond 4,000 miles, sandwiched between Virginia and Spain. The cable has eight pairs of fiber optic strands making the cable the "highest capacity link across the Atlantic".

Najam Ahmed, Facebook's vice president of network engineering, said: "If you look at the cable systems across the Atlantic, a majority land in the Northeast somewhere. This gives us so many more options." This project would bode well for both Microsoft and Facebook due to the oncoming competition that Google poses as their own internet service provider.
Facebook and Microsoft made an announcement together, saying that the undersea cable would lower costs, jack up bandwidth speeds and inject the strength needed to handle the loads of data that are being used around the world. They also highlighted cloud-storage on a large scale would be accommodated and the more personal internet usage like putting pictures up on social media.
Affording trans-Atlantic undersea cabling has enabled American tech companies to jump into the internet service providing game and the world will see more of this as innovation in the industry occurs. Facebook is also working on hardware to connect to their internet solutions and have shown promise in that area this year. They need lightning-quick internet to power their virtual realm, or at least that's the rumor.
Just how fast will the cable be transferring data? Here's the fact:
- Bandwidth transfers of up to 160 terabits per second
- This would make the cable one of the largest, fastest transatlantic cables in the world
Construction will begin in August and will allegedly take a year to complete. Engineers from Spain's Telefónica SA will be assisting with the project. Facebook engineers say that other companies are set to utilize the area for internet cabling as well but they would be the first to do so.
To understand how undersea cables are laid and what kind of engineering occurs before laying cable, SEACOM explains:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The ego has landed. Dr. Ben Choi, an associate professor of computer science at Louisiana Tech University claims that he has...in his possession...the new technology...that will revolutionize the computing industry...forever. No, really. USA Today affiliate, the News Star, has reported that Choi possesses new hardware that will redefine what we know about the computer engineering industry as we know it. So, expect a big announcement soon...maybe.
 Choi will deliver a keynote at the International Conference on Measurement Instrumentation and Electronics taking place in June. He will allegedly display the changes to the methods pertaining to the "foundational architecture" and designing of computers. He has reportedly changed the way computers compute. The computers of the future, as according to Choi, will not use binary but rather make use of "multiple values" which would lead to quicker computing. In the industry, this is normally associated with quantum computing, but perhaps Choi has other plans of how this achievable. He will be relaying information about the data transfer between processors, the speed of microprocessors and increasing the capacity of memory.
Choi will deliver a keynote at the International Conference on Measurement Instrumentation and Electronics taking place in June. He will allegedly display the changes to the methods pertaining to the "foundational architecture" and designing of computers. He has reportedly changed the way computers compute. The computers of the future, as according to Choi, will not use binary but rather make use of "multiple values" which would lead to quicker computing. In the industry, this is normally associated with quantum computing, but perhaps Choi has other plans of how this achievable. He will be relaying information about the data transfer between processors, the speed of microprocessors and increasing the capacity of memory.
"Advances in the foundational design of the computer are needed in business and research applications as well as at the foundation of cyber security efforts across the nation. Dr. Choi's invention to present at the upcoming conference has, increases interest in this foundational architecture," said Dr. Galen Turner, director of computer science, cyber engineering, electrical engineering and electrical engineering technology at Louisiana Tech.
Choi will be releasing a journal with a published report on the future of computing. He says: "If this is successful, computers in the future will be based on our technology." A lot of confidence being exuded here. Choi is currently focusing on Humanoid Robots, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Intelligent Agents, Semantic Web, Data Mining, Fuzzy Systems and Parallel Computing, according to News Star, so we'd imagine what he has been studying might factor into this new computing revolution he is going to deliver a keynote on.
Choi's revelations would have to be particularly strong in a climate where quantum computing is becoming even more popular. Or, Choi is actually working on the first quantum computer that can be purchased. Here's a quick lesson of what quantum computing is, as explained by the Prime Minister of Canada:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Chevron Corporation wants to eliminate any chance of being hacked by cyber criminals. They are currently working on "air-gap critical" systems to stay off of the internet whenever possible to minimize the opportunities for cyber criminals to infiltrate. They're hoping through this systems won't be taken down by targeted attacks, such as what happened in the Ukraine Power Plant attack in 2015.
 Dr. Byron K. Wallace, Chevron's cyber security process control network vulnerability assessor spoke at The Automation Conference 2016. He said: "We go to a bit of an extreme. It's not a one for all model...the core functions are the same, but the application is different industry to industry." Their answer to not being hacked is ensuring that they securely protect their process control networks by keeping them as far away from the internet as possible.
Dr. Byron K. Wallace, Chevron's cyber security process control network vulnerability assessor spoke at The Automation Conference 2016. He said: "We go to a bit of an extreme. It's not a one for all model...the core functions are the same, but the application is different industry to industry." Their answer to not being hacked is ensuring that they securely protect their process control networks by keeping them as far away from the internet as possible.
Chevron also seems to be blaming cyber threats as a possible explanation as to why their first quarter resulted in a $725 million loss in the first quarter of 2016. The company names certain hard facts that have been leading to less than desirable losses in 2016:
- Changing crude oil prices
- The competitiveness of alternate energy sources or product substitutes
- They note that potential cyber threats and terrorist acts could hurt them further, hence the push for air-gap systems that avoid the internet
To further add to their woes an pressures this year, Chevron shareholders have voted to continue the search for new oil fields, despite the global encouragement to stop using fossil fuels. The shareholders rejected climate change stress tests to measure what the continued impact of their business will be on the global climate. Their reasoning was that the climate measurement that occurs in the world today is untrustworthy. Whilst this happens, Chevron will cut 10% of its workforce and spend 25% less of their spending budget, according to the Wall Street Journal.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Adidas is ready to move their manufacturing duties over to the robots and back to Germany. It was 20 years ago that Adidas stopped producing their clothing in Germany and moved their manufacturing plants to Asia. Now they have set up their much-anticipated 'Speed Factory'. They will start large-scale manufacturing in 2017 and will build another factory in the United States.
The announcements come after Adidas tested the Speed Factory after they indicated they would be moving back to Germany last year. It must have gone well because now they are fully removing themselves from Asia. The company says that the German and American plants will be producing half a million pairs of shoes per year, each. According to Fortune, the company produces 301 million pairs of shoes as it is with physical labour.
"The current model in our industry is very much based on sourcing products from countries where our consumers are typically not based. By the time the consumer gets the products, the actual order placed by the retail partner was many months ago. We're trying to bring our products closer to where our consumer is, cutting out the phase where the product needs to be transported. Ideally, retailers will be able to place orders based on current trends, and we won't need to keep huge warehouses of products just in case. Our goal is not full automation. There are highly skilled employees working in these facilities" says Katja Schreiber, Adidas Group's senior director of corporate communications. She is assuring the worried employees that their jobs are safe...for now.
That's not the only manufacturing Adidas has successfully experimented with. They've also delved into additive manufacturing. Yes, that's right. Adidas (and their competitors Nike) have been 3D printing shoes. Hewlett Packard has announced that Nike will be using one of their HP Multi Jet fusion 3D printing solutions for large-scale manufacturing. HP claims their 3D processing station is the cleanest, most efficient, low-cost answer to printing. The printers will preview what the future of printing shoes might look like, due to the printer being able to run at 10 times the speeds of 3D printers on the market today.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Inflatable habitats are the next big thing in space. As we reported back in March, aerospace engineers at NASA are set to inflate a module made out of kevlar-like material that will serve as another room on the International Space Station. The room is called BEAM, otherwise known as The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module. It cost around $17.8 million to build and is being inflated, tomorrow, the 26th of May. The success of the mission could see more inflatable habitats being designed for spacecraft.

The engineers behind the project took to social media side Reddit to answer some of the public's burning questions ahead of the expansion which will be streamed live on NASA's website at 5:30 a.m. ET. Here are some of the highlights of what was asked to the engineers and what their answers were:
Q: How do you handle radiation? I image that an expandable structure must be initially compact, making it difficult to have good radiation shielding and be safe for human usage.
A: Radiation protection is indeed critical for astronauts on the Space Station and eventually traveling to Mars. As a technology demonstrator, BEAM will be fully instrumented with a variety of sensors by the Space Station crew after deployment and ingress, including thermal, debris impact, and radiation sensors. In addition, there are already sensors on the aft bulkhead that will measure dynamics loads during deployment this Thursday. Data from the sensors inside BEAM will be downloads by engineers on the ground throughout the 2-year mission on the Space Station. This data will be invaluable for the viability and design of future expandable habitats. Radiation can behave differently when passing through multiple fabric layers vs. metallic shells. It remains to be seen how BEAM's radiation protection will compare to standard metallic modules, but that is a big part of the reason for doing this tech demo, paving the way for the use of expandable structures in future exploration missions
- Steve Munday, NASA BEAM Deputy Manager
Q: For deep space missions, how do you envision your inflatable habitats protecting astronauts from radiation and how, if at all, will the gas(es) used to inflate the structure vary based on application? Are there any plans on eventually incorporating self-healing polymers in your future designs so as to make your structures more robust in the unlikely event of a minor puncture?
A: Inflatables have protection in terms of MMOD (Micrometeorite and orbital debris) and thermal protection ad has a robust MMOD and thermal protection design. BEAM demonstration will provide us data on radiation protection. The gas used to inflate the structure if it is used for habitats has to be 21% Oxygen breathing air. Self-healing polymers are very advanced materials with low TRL (Technology readiness level) but will be used for future designs of inflatables. If successful, they can provide a huge benefit
- Rajib Dasgupta, NASA BEAM Project Manager
The benefits of expandables? Dasgupta explains that they can be used for deep space habitats on Mars as well. He says they can transport them in a packed state and then expand them on Mars, which is a huge benefit, so that little houses can be erected on the surface of Mars. The data of the expansion happening on the 26th will give the engineers enough data to further establish their Martian intensions.
Q: Has any thought gone into how to safely decommission the BEAM module once it has reached its end-of-life? Are there any special considerations to take as compared to the standard modules?
A: The end of mission plan is to jettison BEAM from below the Space Station using the robotic arm. BEAM will naturally drift away from the Space Station and re-enter the earth's atmosphere about a year later. NASA engineers have analyzed this reentry and determined it will pose an extremely low risk to people on the ground. Remember that most of BEAM is made of fabric materials that will burn up quickly during reentry. The metallic parts of BEAM (for example, the two bulkheads on either end) are made of aluminum which should also burn up during entry. Even in a worst case scenario in which most or all of these bulkheads make it all the way to the ground, there is an extremely low risk of falling near anyone according to conservative computer model analysis.
The rest of the Space Station also will reenter the earth's atmosphere after the end of its usable lifetime, but it will be a controlled, guided entry, meaning it will be targeted to enter above an ocean, far from populated areas. BEAM has no propulsion or guidance capability, but still poses an extremely low risk to us on the ground.
- Steve Munday, NASA BEAM Deputy Manager
The engineers explain that BEAM will utilize 8 air tanks that will inflate the balloon to its full expansion, however, some air from the Space Station is used for the initial phase of expansion happening tomorrow. The two big takeaways from the Q&A session was the possible uses for these sorts of inflatable habitats on other planets and how that would work. Not surprising if considering that the engineers are a collection of NASA and Bigelow engineers that have been assisted by SpaceX engineers. It is set to be a very interesting time in their histories as they continue to build up to an eventual Mars mission.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A group of engineers from New Zealand have started a small start-up company named Invert Robotics. Their specialty? Robots that inspect industrial facilities. The engineers, originally from the University of Canterbury, patented the world's first climbing robot. The robot (pictured in the video below) can check industrial tanks for cracks, whilst an inspector controls it from a remote location. This means health and safety inspectors don't have to put their health or lives in danger. In turn, identifying unstable structures within industrial tanks will ensure that a business preserves the health, safety, and wellbeing of its employees
The robot uses sensors to maneuver around a tank whilst sending a high definition video stream to the screen the operator has in their possession. According to Scoop, the old way of doing this would be letting inspectors abseil down an industrial tank and survey any damage that might have occurred to the innards.
Now, what is being called a "multi-billion euro turnover company" is seeking the technology. The strange bit is that they are not being named as of yet.
Invert Robotics, James Robertson, told Scoop: "To be sought out by this European company, who could find no equivalent technology anywhere else in the world, is a massive vote of confidence for Invert Robotics and the team that has supported and guided us." The engineers are also focusing on the European dairy market next due to their successes of inspecting industrial dairy tanks in New Zealand. "We have been perfecting our inspection robots, working with trans-Tasman dairy companies, and over the past5 four years, we have carried out more than 250 inspections. We know we have a product that is truly market changing."
Elsewhere in the robotics world, SoftBank Robotics America is getting their Pepper robot ready for consumers to start tinkering with. Mastercard has jumped on the bandwagon and introduced an application that would assist with making digital payment to a merchant. Pepper will assist people when making purchases at a store and facilitate the digital payment.
"Consumers have come to expect personalized service, customized offers and simple and seamless processes both in-store and online. The app's goal is to provide consumers with more memorable and personalized shopping experience beyond today's self-serve machines and kiosks, by combining Pepper's intelligence with a secure digital payment experience via MasterPass," said Tobias Puehse, vice president, innovation management, Digital Payments & Labs at MasterCard.
The developers behind the Pepper are allowing other companies to see what they can improve the robot with, and MasterCard seems to be the first company that is keen.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A new report made available by MarketsandMarkets has estimated the amount of money the industrial robotics industry will make from now till 2022 is US$79.58 billion. That would mean a growth rate of 11.92 percent combined annual growth rate from this very second until we reach 2022. The report was titled Industrial Robotics Market by Time (Articulated, Cartesian, SCARA, Cylindrical, Parallel), Application (Automotive, Electric and Electronics, Metal and Machinery), Component (Controller, Sensors, Drive) and Geography- Analysis & Forecast 2022. So it is safe to say it covers the vast majority of industrial markets robots are currently applying to. No surprise then that the number of $79.58 billion is so high.
The report just cements the fact that industrial automation and the Industrial Internet of Things that will work in tandem with the industry is the next step forward. The report claims that the market is being dominated by the Asia-Pacific areas ; China, Japan, South Korea and India. The demand for robots is incredibly high. Also we have seen recently that Chinese companies are buying out European robotics companies to utilize the technology currently being developed. Kuka Robotics' purchase shows that the demand is high and billions will be forked out for the current technology.
The report actually names Kuka, amongst other companies that are currently performing well in the industrial automation industry:
- ABB Ltd. (Switzerland)
- FANUC Corp (Japan)
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd. (Japan)
- Yaskawa Electric Corp (Japan)
However, $79.58 billion is a very big number. It cannot seriously be true. But, then you remember, that there's even a robot that cuts marshmallows. Honestly, all we need is a taffy-pulling robot and then we've put Willy Wonka out of business. Check below for the kind of robotics that ABB supplies the food industry. If you notice how many different tasks robots can currently be doing in our world already, perhaps the estimates of how much money the industrial robotics industry might make by 2022, isn't that far off.
Source: Engineering.com
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Civil engineering at its finest. Mayerthorpe in Canda experienced a series of arson attacks that saw a railway trestle bridge engulfed in flames. A crew went straight to work on the bridge after the fire of April 26th and was completed by May 15th. It took a record 20 days to rebuild the bridge after a full redesign of the bridge, then using steel span and concrete tubs they began work. It took 190,000 metric tons of steel and concrete to rebuild the bridge. The bridge is now longer than before.The bridge is now longer than before and harder to destroy due to the bridge that burned down completely made of wood. The bridge was ready for the next train to pass over it under a month after it had burned down. These civil engineers deserve a beer.
 Charges were laid against a man named Lawson Michael Schalm, a 19-year-old Mayerthrope man. He was charged with 18 counts of arson. Funnily enough, Schalm was one of the firefighters who assisted with dousing the flames of the trestle bridge he had been suspected to have set alight.
Charges were laid against a man named Lawson Michael Schalm, a 19-year-old Mayerthrope man. He was charged with 18 counts of arson. Funnily enough, Schalm was one of the firefighters who assisted with dousing the flames of the trestle bridge he had been suspected to have set alight.
The swiftness of the engineers that rebuilt Mayerthorpe's trestle bridge were under pressure to do so due to the demand of the railway industry that runs on quick turnaround times and cannot afford to be delayed.
Watch the fly-by footage of the burning bridge from April 26 to the twenty days that followed wherein the bridge was rebuilt:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Electrical, mechanical and biomedical engineering come together once again. Researchers from MIT, the University of Sheffield and the Tokyo Institute of Technology have been working on a robot that you could soon be ingesting. You read that right. They're calling it an origami robot, in the sense that after swallowing it, it is supposed to unfold when it is inside the body. The robot will then be able to follow a specific order as programmed into it by an engineer.
 Daniela Rus, a director at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, said: "The robot can remove foreign objects, it can patch wounds, or it can deliver medicine at designated locations."
Daniela Rus, a director at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, said: "The robot can remove foreign objects, it can patch wounds, or it can deliver medicine at designated locations."
The researchers showed the robots off at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Stockholm this week. They worked with the case studies of children who had swallowed tiny button cells (used in watches, and electronic devices). These batteries that children ingest have harmful side effects and have to be removed through surgery, however, the researchers are confident that the origami robot could solve the need for surgery.
What about stomach acid? Rus explains: "The challenge with designing an ingestible robot is finding biocompatible materials that are easy to be controlled and amenable to the types of operations that are needed from the robot." The researchers used a pig-intestine casing for the robot so that a human body would not reject the robot upon ingesting it. The researchers built this second version that, according to Engadget, propels itself using the stomach's surface.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
MIT and the University of Edinburgh were recently awarded some of NASA's Mars-bound Valkyrie robots to test out and improve. The University of Edinburgh has given the world an idea of how challenging the robots are to work with in a new video they have released. The robot is 1.8-metres tall and weighs 275 lbs, equipped with 200 sensors. NASA wants to essentially deliver the bots to Mars in one of their upcoming missions in conjunction with SpaceX. The hope is that the robots will be more efficient and dexterous than the rovers that are currently circumnavigating Mars.
Robert Platt, as an assistant professor at Northeastern University who is working on the project, said: "The rovers get their instructions uploaded at the beginning of the day. Those instructions amount to, 'Go over there,' or, 'Check out that rock.' It's a completely different ballgame when the job for the day is to assemble a couple of habitats." Which is something the Valkyrie robots might have the task of doing.
The University of Edinburgh has shown the initial progress with Valkyrie and it seems the mechanical engineering behind the robot is increasingly complex and slow.
Another university that got one of the four robots to play around with was the University of Massachusetts-Lowell who are working in tandem with Northeastern University. Taskin Padir, a professor at Northeastern University expressed his dismay with the robot's awkward walking and mechanical issues, saying for a price tag of $2.6 million, there's still some progress to be made.
Holly Yanco, a computer science professor at UMass-Lowell's said: "It needs to be able to communicate back to Earth, very clearly and concisely what's going on." However, if it cannot climb over rocks or show dexterity by then, the robots would be mostly useless on Mars. What does look positive is its dense visual mapping, that sees the robot virtually mapping out the terrain that might be necessary for it to navigate around.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
It's an aerospace and aircraft maintenance engineer's worst nightmare. An Airbus 320 belonging to EgyptAir has gone down in the Mediterranean Sea. At around 2:30 a.m. Cairo time (UCT +2), the plane disappeared from radar tracking and by 4:26 a.m. the rescue operations received a distress signal from the plane's emergency devices. MS804 was being tracked by Greek air traffic controllers who said they had spoken to the pilot and ensured that everything was in order and then an hour later the plane made a sharp left turn and then a 360-degree spin to the right. The plane had taken off from France at around 11 p.m. and headed for Egypt.
There is a list of things that could have gone wrong but what engineers are hoping is not true, is that the plane went down for mechanical reasons or for maintenance reasons.
Rescue operations started off the Greek island of Karpathos in Egyptian airspace.
Airbus confirmed the following facts on their Facebook page:
- The aircraft was delivered to Egyptair in November 2003
-Accumulated 48,000 flight hours
-Powered by IAE engines
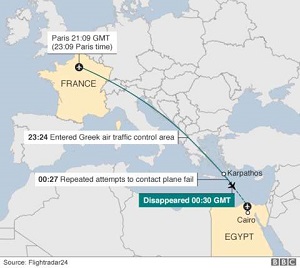 Egyptian prime minister, Sherif Ismail, a former engineer, said it was too early to say whether or not the crash was linked to terrorism or if it was a mechanical failure that took the plane down.
Egyptian prime minister, Sherif Ismail, a former engineer, said it was too early to say whether or not the crash was linked to terrorism or if it was a mechanical failure that took the plane down.
Associated Press reported that Russia's domestic security chief says structural failure was unlikely. Major General Robert Latiff, who is an expert on aerospace systems and emerging weapons technologies at the University of Notre Dame said the chance of structural failure was: "vanishingly improbable."
Later on in the day, Egypt's aviation minister spoke to media and said that the possibility of a terror attack as a cause for the Egyptair crash was "stronger" than technical failure.
Greek sources had confirmed that they saw "large floating objects" in the ocean and were going to investigate further.
Bloomberg reported at 6:22 p.m. UCT+2 that they had also joined the search for MS804, a report that was preceded by a Reuters report that airplane lifejackets had been found by search teams that were investigating in the area.
CNN was the first news agency to lead with headlines that mentioned any form of bombs possibly taking the plane down. The @cnnbrk (CNN Breaking News) Twitter page wrote: "2 U.S. officials: Initial government theory is that EgyptAir Flight 804 was taken down by a bomb"
The plane had 66 people on board who have been presumed dead, according to Egyptian aviation authorities.
More news on the engineering aspects of the crash will follow as that information becomes available.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Google's annual I/O conference kicked off yesterday. This conference is used as a platform for the engineers of the company to announce new products, show off the engineering behind these new products and give the industry a window into what is coming up in the company's future. The first day kicked off with a few updates to some of the preexisting technologies from the company but also brought a host of new consumer products that the world can be looking forward to. Some of what will be shown at the conference will display exactly how the Internet of Things will soon be integrated into our daily lives and shows just what engineering can achieve. Here are some of the highlights:

Google Home: A voice-activated home assistant device that will bring Google Assistant into your homes. Essentially, you would be able to surf the internet and get information by just talking to the device. A competitor to Amazon's Alexa, the device will also assist in playing music and automating some home tasks. They are being referred to as 'smart-speakers' for the home.
Allo & Duo: A Whatsapp competitor for mobile that has a host of new, innovative ways of text chatting, including a chat service with Google Assistant that seems to border on Siri-like behaviour. Duo is a Facetime/Skype competitor that will allow face to face video conversation over a network, that allegedly will even work when a network is slow.
Android N: The update to the operating system came with a host of new announcements that included the announcement of something called the JIT Compiler which would lead to app installations at a speed that is 75% faster than it currently is on Android.
To see further development in virtual reality and wearables, check out the full I/O keynote:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Suzuki Motor Corp and its engineers have decided to come out with the truth due to a scandal that has been spreading through the automotive engineering world. The car maker divulged details that led to certain discrepancies in fuel efficiency reporting, indicating that the company had not abided to Japanese guidelines, and rather worked around them.
- All 16 vehicles currently available used data that did not accurately report emissions through the correct processes leading to improper testing. The improper testing affects 2.1 million cars. Instead of using the proper coasting test of the entire car, individual parts of the car were tested and factored into the final reports.
- They used the air-tunnel on single parts of the car and reported it as if it was the full car that had gone through the air tunnel tests
- The issues they are admitting to are subject ONLY to cars manufactured in Japan
 "The company apologizes for the fact that we did not follow the rules set by the country.," said Chief Executive of Suzuki, Osamu Suzuki.
"The company apologizes for the fact that we did not follow the rules set by the country.," said Chief Executive of Suzuki, Osamu Suzuki.
At Mitsubishi, the President of the company, Tetsuro Aikawa, has taken responsibility for their scandal and stepped down from his position.
However, now that Suzuki is testing the vehicles in accordance with Japanese guidelines, the company says all of their efficiency is in order.
"Any wrongdoing, such as manipulation of fuel efficiency data, were not found," Suzuki said to the media. During the briefing, Suzuki's shares fell by 9%.
It seems that Suzuki will emerge better off on the back of this scandal than companies such as Volkswagen and Mitsubishi. However, there is still time for more carmakers to come out of the woodwork and admit to fuel efficiency data manipulation.
Source: Reuters
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Think about where you store your information and the processes behind the storing of that information. We have DRAM to hard disk drives and flash memory as well. IBM has made a breakthrough in phase-change memory (PCM) that might replace flash storage and RAM. IBM Research engineers have released their findings in a journal video named Reliable Triple-Level-Cell-Phase-Change Memory Demonstrated for the First Time.
Dr. Haris Pozidis, a non-volatile memory scientist for IBM Research explains how the technology works:
The storing of a '0' or a '1', as known as 'bits', on PCM storage the following methods are followed:
- Apply a heated current to glass materials at 600 degrees centigrade, the material melts and then when it is cooled rapidly, then the material becomes solid, but is in an amorphous state.
- Then the amorphous state material is heated at 200 degrees centigrade and leads to crystallisation, which leads to a polycrystalline phase.
- Blu-ray DVDs are created this way
Recently, only 1 bit was stored, per cell, but the scientists at IBM have made a breakthrough whilst testing the technology out and are successfully storing 3-bits per cell.
"Reaching 3 bits per cell is a significant milestone because at this density the cost of PCM will be significantly less than DRAM and closer to flash," said Pozidis.
Pozidis points out that this process has been used in optical disk technology before and has been practised for 15 years but now they are able to superimpose the technology into PCM data storage.
The hope is that the creation of this PCM data storage could be created at low cost that works with the characteristics of DRAM but at higher densities. Therefore, as PHYS points out, a mobile phone's operating system could be stored on PCM storage, leading to a phone booting in a few seconds.
Use of PCM storage:
- Storing databases in memory
- Memory processing: Online banking, analytics processing
- Add-on to storage systems: Metadata can be absorbed in PCM
- Won't lose data when powered off
- It can survive 10 million write cycles - compared to flash which can only do 3,000
The engineers are looking at the possibilities of making a PCM and flash storage hybrid as well as letting PCM speak for itself as a memory storage standalone.
For more information and how it all works, watch the video below:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Are civil engineers in the United States ignoring the opinions of seismologists and other engineers when it pertains to building in earthquake-prone areas? The Seattle Times definitely thinks so. They have been running a feature of articles called Seismic Neglect, that references decades of engineering research that has indicated building practices in unreinforced masonry construction (URM) occurring in areas that could be hit by earthquakes. Meaning, construction in unreinforced buildings is going ahead despite seismology data that directly indicates the area could see earthquakes topple those constructions.

The opinion makers say it is a bit disconcerting that there are still unreinforced masonry constructions in an area that lies directly in the Cascadia Subduction Zone area that could experience a megaquake of 9.0 quite soon. Some structures are able to withstand earthquakes - and they have - but a 9.0 magnitude could send these buildings toppling.
You can also read the Federal Emergy Management Agency's (FEMA) report on Unreinforced Masonry Buildings and Earthquakes. The three biggest concerns for FEMA in unreinforced masonry construction are: Injury, Property Damage, and Loss of use [of the building]. The agency suggests a strategy that can be implemented so that risk can be minimized with the unreinforced buildings.
The principal means of reducing the seismic risks of unreinforced masonry buildings is retrofitting, although changing a building's use in order to reduce its occupant load (number of occupants) also reduces risk.
What remains clear is that unreinforced masonry constructions need to be listed and worked on by engineers so that buildings all around the world can be retrofitted for earthquake safety, especially in areas which fall under fault lines and known seismic areas.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Internet of Things industry will be connecting over 34 billion devices by 2020, and a lot of that will be industrial factories. We reported at the beginning of May, that manufacturing, households, transportation and almost everything engineering is going to be connected to the Internet of Things in 2020. We also reported that currently only 8 percent of the manufacturing world is utilizing IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) but will grow by 18 percent over the next five years.
 "No industry produces more data than the manufacturing sector, and all of that information can be applied to making smarter business decisions. Companies need to participate in capturing that value. There is $65 billion worth of obsolete industrial automation in use right now. It's only going to get more expensive to repair and replace it. Companies have to commit to modernizing," said Brian Fourtney, a Global Business Manager at Rockwell Automation, speaking to Plastics Today.
"No industry produces more data than the manufacturing sector, and all of that information can be applied to making smarter business decisions. Companies need to participate in capturing that value. There is $65 billion worth of obsolete industrial automation in use right now. It's only going to get more expensive to repair and replace it. Companies have to commit to modernizing," said Brian Fourtney, a Global Business Manager at Rockwell Automation, speaking to Plastics Today.
Fourtney is adamant to underline the fact that some factories are not modernizing as fast as they should be. The lack of modernizing a factory floor is like cutting off the nose to spite the face at the end of the day when 2020 could be approaching quite quickly. A country that has no delaying tactics when it comes to embracing technology that utilizes IIoT is, unsurprisingly, China.
"With the development of robotics, unlit and unmanned factories will be the next industrial trend," said Deputy Dean of the Overseas Education College at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Gu Liafeng. He calls it 'smart manufacturing', where industry will be connected through IIoT and what is being called "Chinese-style Industry 4.0". Chinese companies are on the forefront of ensuring that factories utilize sensors and data-generating components along with A.I. machines that can perform tasks more efficiently and safely than humans can, whilst generating analytics.
However, replacing workforce is not an easy task when thinking about the societal damage a company can do by replacing all of its workforces with robots who can do their jobs.
"We always talk about migrating systems -- software and hardware -- but what we're really doing is migrating people. Just ask any engineer -- migrations rarely go smoothly -- and migrating people is no different. We have to create a pathway for folks in operations to control their own destiny and achieve success," says Fourtney.
According to South China Morning Post, Europe bought 50,000 industrial robots in 2015, whereas sales in the U.S., Canada and Mexico only reached 34,000 sales combined. Grey Orange, an Indian company who specializes in assisting factories with robotic inventions (see video below), has seen the benefit of working alongside the Chinese and have moved into the market to hopefully get a slice of the automation market that is booming there. A market that trumped the rest and purchased 66,000 industrial automation robots in 2015.
The butler systems are given commands by a human, and according to the video, teaching a human how to direct these robots to do the hard work is not difficult. The Industrial Internet of Things will be bringing the robot revolution, but perhaps it won't take as many jobs as we once thought.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Tony Seba is a lecturer at Stanford University who was given the opportunity to address the Thailand energy sector. He spoke about four key areas that would see rapid change and bring the most market disruption: energy storage, self-driving cars, electric vehicles and solar. He referenced a report that said that the U.S. and Canada would be running off 80 percent renewable power by 2030, saying the report lacked any truth.
Seba thinks that consumers would be fully utilizing electric vehicles by 2020 and by that time hopefully fossil fuels would become obsolete. He fully believes that by 2025, gasoline and diesel cars will no longer be sold but also concedes that the sales of EVs will not be enough to fully diffuse fossil fuels in our world today.
Disrupting the car industry is something we have already seen taking place, however, what about solar energy and moving away from utility grids all around the world?
"You have to ask yourself if solar keeps doubling every two years, how much more doublings before solar is 100 percent of the world's energy-- and not just electricity," said Seba. He says that subsidizing solar is the most disruptive things governments can do to businesses that are currently making money on fossil fuels. "All of this leads me to believe that solar will be by far the number one form of energy, and by 2020, it will basically wipe out every other form of energy."
Therefore, Seba thinks the 2030 projection by some scholars is wrong and rather the aim should be that by 2020 the world will be fully on solar and renewable energy.
For more from Seba, check out this video below on what will be disrupting the fossil fuels market and causing them to fully collapse by 2030:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
As reported on yesterday, Hyperloop One, the company behind taking Elon Musk's desire to redesign the world of public train transport, was to conduct its first open air test. You can see the results of the test below...and spoiler alert...it's quick and disappointing to watch. However, to the engineers working on the project, it is what they need to gather the data and prepare for the next test.
The sled - seen in the video above - reached 2.5 Gs and got to 167 MPH before ending its run in a sandpit. The next step in the testing phase is putting together tubes that are currently at the test facility in Nevada and building a 1.5 kilometer (0.93 mile) test tube. The engineers are hoping they will be able to test out the levitation system and reach speeds of 400 MPH and more.
The video below is from Hyperloop One itself and drums up a bit more excitement for the future of the project. Engineers around the world are still criticizing the project and questioning its feasibility, however, time will tell whether or not this is a pipe dream or not.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Caterpillar is in the news again, soon after they announced their energy storage offerings to the world. Now, in their Global Research & Development Center in the U.S., they have officially opened a 3D Printing & Innovation Accelerator center. Caterpillar produces most of the construction equipment you would see on sites today and will now be 3D printing some of its parts. The new center will also allow engineers to test out creative ideas

Jim LaHood, who works for Caterpillar's additive manufacturing team said: "The possibilities are endless in the factories. Things that are previously done out of metal that doesn't need to be -- like little tools and gauges -- can be made from plastic now."
Moreover, Caterpillar says they are not strangers to 3D printing. They say that they have printed 50,000 models over the last 25 years when 3D printing looked a little different than it does today. The company says it is glad there is now a cost-effective way to print that uses less energy and money.
Caterpillar is not allowing themselves to be left behind in the modernisation of civil engineering and how it is changing. They call this changing nature of the industry the 'Age of Smart Iron' and say they are prepared to take on the task. Thus, their energy storage solutions and 3D printing facilities show that they are ready for the immediate future.
But wait...there's more. Caterpillar Inc is not done yet. Chief Executive of Caterpillar, Doug Oberhelman met with ministers in Cuba in hopes that they can start moving some of their tools into the country and improve trade ties once the U.S. trade embargo is fully lifted.
He spoke to reporters, saying: "We have talked about a number of projects. I think the most interested one in the near term would be the Mariel harbor...making an efficient modern harbor that competes with others around the world." Caterpillar will be working with a Puerto Rican company in Cuba, named Rimco, who will act as their dealer over there, Reuters confirmed. "The idea is for our dealer to set up a facility here in Cuba. We would supply most of our products from Brazil."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Are you keen on marine engineering by any chance? Submarine drones are the new buzzword when talking about the South China Sea this year. China has been slowly reclaiming islands in the South China Sea, so, to keep an eye and allegedly "retain its edge" the United States is sending submarine drones to patrol the areas around these islands.
Ashton Carter, the US defense secretary, said that the drones are able to navigate in shallow waters, something that submarines cannot do. He also said: "Countries across the Asia-Pacific are voicing concern with China's land reclamation, which stands out in size and scope, as well as its militarization in the South China Sea."
The U.S. want to, as Carter put it, ensure their navy efforts are the "most lethal and most advanced undersea and anti-submarine force in the world."
The Financial Times reported that the U.S. allegedly also want to build a submarine that would have smaller drones within it that could be deployed.
Then the recent announcement of the automated boat the United States Navy had built was announced.
Meanwhile, engineering students from all over the world are hard at work every year to try and improve ROV technology and win big at the Marine Advanced Technology Education (MATE) ROV Competition hosted by NASA. Norwegian engineering students took to social platform, Reddit, to show off their latest ROV iteration that navigates in 6 degrees of freedom with an autopilot feature. This sort of fluidity in ROVs could prove helpful to future underwater vehicles that could utilize the technology produced at NASA's events to work alongside the Navy in future endeavors where marine engineering is required.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Last month, social networking giant, Facebook, announced a new terrestrial connectivity system named Terragraph and Project ARIES. The company believes that no matter where people are in the world, they deserve a premium internet experience, and this new project will assist communities that experience slow internet speeds and perhaps even some places that are devoid of the internet altogether.
Facebook also didn't mince their words when throwing the laying of fiber, and technologies like LTE infrastructure under the bus. The company said in a statement: "...the high costs associated with laying the fiber makes the goal of ubiquitous gigabit citywide coverage unachievable and unaffordable for almost all countries."
Therefore, Facebook put their Connectivity Lab to work. The result was Terragraph, a 60 GHZ multi-node, wireless system for supplying the internet to urban areas.
Although 60GHZ has traditionally been avoided due to its high absorption of oxygen and water, countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, China, South Korea, Japan and others saw the benefit of making this part of the spectrum.
- Facebook Terragraph statement
To see how the technology works, look at the video of the physical components that Facebook would be using to connect urban areas to the internet below:
A month later, the software engineers working with the hardware that will be capable of giving full urban areas internet coverage, have released software to modulate a distributed network application platform for the Terragraph project. The software's name is Open/R, and you can read the intricate details of how the software engineers developed the software: HERE.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Now that the United States is a liquefied natural gas exporter, they no longer need to import as much gas. The U.S. joins immediate neighbor, Canada, in exporting a good amount of gas, so much so, that the two countries could be influencing the price of gas very soon.
The Canadian National Energy Board have estimated that natural gas exports will shrink in numbers over the next 30 years due to the exports that the U.S. is now making.
Net imports of natural gas from Canada have been falling for years. Rising shale gas production in the United States, especially in the Northeast, is key among several factors affecting this trend.
- EIA Independent Statistics & Analysis for U.S. Energy Information Administration

The United States has indicated that they would be building 15 LNG plants across the country that would be solidifying them as a huge player in the game for LNG exports and presiding over what the price should be.
Elsewhere, Chile will be sending liquefied natural gas Argentina's way this week. Trade relations between the two countries have recently "warmed", according to Reuters. Argentina and Chile haven't exchanged gas in 16 years since exports were cut off in 2000. An industry insider said that Chile could be exporting up to 1.5 billion cubic meters of gas at $6.90 per million British thermal units.
Further afield, the liquefied natural gas industry is ignoring the traditional Asian markets that have supplied LNG to them before and are now looking for new, more expanding LNG markets, according to The Wall Street Journal. An employee involved with the International Group of Liquefied Natural Gas Importers, Vincent Demoury spoke to WSJ. He says that LNG exports have jumped up by 2.5% in 2015. Due to Asia's declining interest in LNG, Demoury says Egypt, Jordan and Pakistan have grabbed hold of 72% of the market share that Asia is leaving behind.
Source: BOEREPORT
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Hannover Messe 2016 is the biggest conference where industry heads come together to chat about where the world is going in the context of the world renowned fourth revolution, known as Industrie 4.0. Now that the conference is over, the immediate outlines of what the world should be expecting can now be summarized and contemplated. This year both Barack Obama and Angela Merkel attended the conference.
Obama spoke about the fully 3D printed electric car that the United States was showing off at the conference, joking that he would give it a test drive. He also pitched the United States as a world-class country where the companies attending should consider "setting up shop" in. "It's even easier for companies like yours to come and build in America," the President said. He underlined the fact that the United States and the European Union already have the largest trade and investment relationship in the world. Obama pointed out the numbers that this partnership has led to:
- 3 billion dollars of goods and services every single day
- Investment of $4 trillion in each other's economies
- 13 million jobs
Obama also ended his speech off by saying the TTIP (Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership) policies that they are infusing into global law would assist a free and open internet. This would help the world of the Internet of Things, industrial automation and more.
Professor Thomas Bauernhansl, the Head of Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation told SAP TV: "What we see at the moment is that we try to connect all resources in production and that will offer us a completely new world for optimisation of the whole manufacturing processes."
Siemens was particularly instrumental in the topic of Industrie 4.0, who had one of the biggest stands at the conference this year.
Current CEO of Microsoft, Satya Nadella, also had a keynote at the show and gave his impressions on what the future of Industrie 4.0 will be. He said: "The very thing that you produce, the very thing that you manufacture, for the first time, is connected with all of the web of activity around it. It's not just the connection with everything, it is the ability to reason about that activity, that data that's being generated continuously."
A plethora of other companies showed off their robotics solutions for the impending revolution of automated factories that are connected to the internet. The fact that Merkel and Obama both attended the conference shows that Hannover Messe is now the most important showcase of industrial automation in the world today and will continue to grow into the conference that leads the conversation in what is next in that industry.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Electric vehicles. A word that is forever in our collective vocabulary in the world because of the need to cut down fossil fuels in the world today. We've reported on Tesla's recent intentions to produce half a million of their Model 3s by the end of 2018, Toyota investigating what could be powering vehicles in the future and almost every automaker out there trying to move their operations to cleaner processes after being named and shamed in emission scandals.
Cars are being powered by the kind of lithium-ion technology you'd find in energy storage units that are now making their way into houses. However, carmakers are reaching the conclusion that EV (Electric vehicle) batteries can be reused AFTER they've been utilized inside a car. There is a point that EVs come to when the battery no longer functions as it should, under guidelines that would render an EV operational. However, it is said that even after it is has served its purpose, it still has 70% of its energy storage that can still be utilized. This is allegedly surprising the industry due to recently thinking that the batteries wouldn't have much use after used in vehicles.
Navigant Research recently observed that a 2012 Chevrolet Volt had driven up to 300,000 miles without any "battery degradation" issues.
 The idea is that once the battery has been used in the EV and decommissioned for use in a car, it can be added to a solar PV system and power a house. Essentially, making second-hand car batteries reusable and expanding a growing trend of grid peak time shaving.
The idea is that once the battery has been used in the EV and decommissioned for use in a car, it can be added to a solar PV system and power a house. Essentially, making second-hand car batteries reusable and expanding a growing trend of grid peak time shaving.
The batteries inside electric vehicles have also been suggested as a possible energy source for the grid whilst they are parked in an area, which would assist utilities at alleviating some of the strain on the grid. Now with the reusability factor of these batteries, the possibilities of how many hours kilowatt-hours could be generated is staggering.
Pablo Valencia, GM's senior manager for Battery Life Cycle Management said: "Even after the battery has reached the end of its useful life in a Chevrolet Volt, up to 80 percent of its storage capacity remains.
The technology will no doubt grow and grow as more electric vehicles are sold and the battery technology is further developed to see how EVs batteries could be repurposed after the use in cars. This is not new information, the feasibility of reuse has been spoken about since 2014. In ScienceDirect in a journal entitled Environmental feasibility of re-use of electric vehicle batteries the researchers wrote: "The magnitude of CO2 mitigation associated with battery re-use is similar to that of switching from using a conventional vehicle to an electric vehicle, meaning the greenhouse gas benefits of vehicle electrification could be doubled by extending the life of EV batteries, and better using off-peak low-cost clean electricity."
