Industry
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Syrian War has reached its fifth year with the death of an estimated 400,000 people. It is also responsible for the biggest refugee crisis in documented history. According to the UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR), 4.8 million Syrian refugees have fled to neighboring countries, with another 6.6 million displaced in Syria itself. They also report that “hundreds of thousands” have fled to Europe.
Photojournalists have shown that many Syrian cities are uninhabitable, with basic living and education no longer viable. However, a glimmer of hope does exist for a time when the rebuilding gets underway.

Image Credit: BBC
German military men, proficient in practical, structural engineering skills, have been training Syrian refugees. The hope is that they will return to Syria, once the war is over, to improve conditions and help rebuild their nation.

The program has been running for five months, with a pledge at this stage, to train 120 refugees. To the refugees’ benefit, the skills they are learning can also be used on German soil. Defence Minister Ursula von der Leyen launched the project saying:
“The goal is for these young people to get good, basic training. We don’t know how long it will take until they can return, so they have to be able to make a living while they are here.”
Engineering employment
A sad and bizarre correlation has emerged and begs the question: ‘Has a lack of Middle Eastern employment opportunities for engineering graduates led to a spike in terrorist group membership numbers?’
Researchers believe it has. A 2016 book published through the Princeton University Press, named Engineers of Jihad: The Curious Connection between Violent Extremism and Education, revealed that 800 known ISIS members were, in fact, engineering graduates.
The authors, Diego Gambetta & Stefan Hertog, also wrote: “In fact, of the twenty-five individuals directly involved in the 9/11 attacks, eight were engineers.”
The socioeconomic conditions in these Middle Eastern countries, some of which are war-ravaged, have made it incredibly difficult to find normalcy let alone skilled employment. The result has been a plethora of applications for resettlement in an assortment of countries, including those in Europe and in the United States. With their sought-after skills, refugees hope to forge new lives. Some destinations are more reticent and less welcoming than others and there are many and varied reasons for this.
The Travel Ban
President Donald Trump’s travel ban has thwarted the ambitions of many Middle Eastern engineering students and professionals hopeful of settling in the US. On the 27th January Trump signed an executive order to delay the entry of people from seven Muslim-majority countries: Iraq, Iran, Libya, Somalia, Sudan, Syria and Yemen.
Federal judges have since overturned the executive order, deeming it unconstitutional. Trump’s vow to appeal their decision is being watched closely by many.
The tug-of-war between the federal courts and the presidency has prospective MIT student, Mahmoud Hassan, concerned. Talking to CNN, Hassan, an 18 year old Syrian student from Damascus, says that even though he has a scholarship from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), his dream of obtaining an engineering degree from America’s top-tier university is “basically ruined.”
Works Cited
The Independent. Independent Digital News and Media. Web. 10 Feb. 2017.
"Gambetta, D. and Hertog, S.: Engineers of Jihad: The Curious Connection between Violent Extremism and Education. (eBook and Hardcover)." Princeton University. The Trustees of Princeton University. Web. 10 Feb. 2017.
"A Syrian Teen Was Headed to MIT and Then Came the Ban." CNN. Cable News Network. Web. 10 Feb. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Creating infrastructure on a large scale for a vast country with a growing population has, by necessity, been China’s focus. And they are very good at it. Many nations struggle to keep pace with the needs of their citizens and China is no different. It has, however, made some brave, but perhaps somewhat audacious investments in projects for the future.
One of the world’s biggest photovoltaic solar farms now exists in China. Construction began in 2013 and at completion the plant cost was estimated at US$721 million. It will produce 850MW, and power an estimated 200,000 households.
China also has the biggest wind farm in the world. The Jiuquan Wind Power Base is located in northwest China’s Gansu province. The farm has the ability to produce 10,572 kilowatts of power with a record number of wind turbines at 7000. The plant would be able to, according to the New York Times, “power a small country”.

Jiuquan Wind Power Base / Credit: Xinhua | English.news.cn.
The turbines are, however, standing idle. There is simply not enough demand to turn a profit. The demand from coal power plants remains strong and a cheaper source of energy.
There are additional project glitches, as with all engineering endeavours; the location of the turbines has made it difficult for engineers to erect transmission lines which reach populated cities.
China’s government is determined to have the country accept and use renewables – their emissions are very high and so they are actively addressing the issue. To this end China has begun a crackdown on coal power plants, ensuring that they operate under strict standards and future growth in the industry has been curtailed.
The country has pledged that they will spend $361 billion in renewable energies by 2020. Further large-scale solar plants are planned and investment into wind will also be sizable. According to Reuters, the cost of photovoltaic solar panels has dropped by 40% since 2010.
Over-engineering, over-investment
China has a long history of over-investment in engineering projects and real estate speculation. The country’s engineers overestimate the demand of several projects and then the investors over-invest in a project that has little public interest.
The New South China Mall - known as the biggest mall in the world, for example, was once branded a ‘dead mall’ due to the initial disinterest from the public. Twelve years after its construction it is now attracting customers.
Similarly and more concerning, in recent years there have been entire cities erected that have never seen inhabitants. The media refers to them as ‘ghost cities’.
Fortune published a story in 2014 that pointed out that 40% of Chinese investment projects were “either not finished on time or not completed at all.”

Credit: Wade Shepard / The New South China Mall
With this in mind the question is whether or not China’s renewable energy plans will achieve their objectives and reach their potential.
The Jiuquan Wind Power Base is only running at 40% capacity at the moment, but it is worth reflecting that China’s renewable energy plans will create thousands of new engineering jobs. China’s National Energy Administration said it would create 13 million jobs.
The New York Times reports that China is adding a new wind turbine to the country’s energy production every hour.
The Chinese government is certain that investment into renewables is going to be a success in the long-term. Lowering emissions from fossil fuel industries is in their best interest as they have been suffering from record levels of air pollution in their metropolitan areas; most notably in Beijing.
The rest of the world will be keenly watching how China’s investment in renewables plays out. Despite some nations achieving remarkable successes in these new technologies, most are more cautious about moving away from fossil fuels.
Works Cited
"China to Plow $361 Billion into Renewable Fuel by 2020." Reuters. Thomson Reuters, 05 Jan. 2017. Web. 02 Feb. 2017.
"China's Deserted 'ghost Cities' Appeal to New Residents." CBCnews. CBC/Radio Canada, 10 Nov. 2015. Web. 03 Feb. 2017.
"In Pics: Jiuquan Wind Power Base in China's Gansu." In Pics: Jiuquan Wind Power Base in China's Gansu - Xinhua | English.news.cn. Web. 02 Feb. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
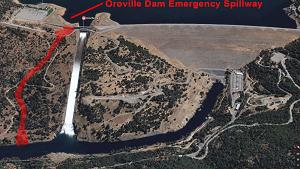
A primary and emergency spillway at Lake Oroville, California, have eroded to the point where repair is immediately required. Water levels have risen to historic levels resulting in worried authorities evacuating more than 190,000 people from the valleys below; they fear that the dam won’t hold.

The reservoir is California’s second-largest provider of water. The dam’s capacity is 4.363537 km3, which equates to 1.75 million Olympic swimming pools.
The dam recently reached capacity due to winter rains and snow melt. Worryingly, the main spillway has eroded - chunks of cement have recently given way. The deluge of new water is spilling into a 200-foot-long, 30-foot-deep hole, creating even more erosion.
Engineers now have to utilize the dam’s emergency spillway, unused since its construction in 1968. The concern is the erosion on this spillway too; it has not been adequately reinforced.
The dam safety engineers are anxious about keeping water away from the emergency spillway. Once water spills over into it the erosion there means that they have little control. This was what motivated them to hand down the evacuation order.

Auxiliary Spillway at Lake Oroville
Credit: Mike Anderson/ Twitter: @abros805
If the emergency spillway does indeed founder, the dam will begin draining. The officials are now concerned that the situation could lead to catastrophic failure.
To counteract further erosion on the main spillway, engineers are dropping bags of rocks into the hole. This will help mitigate the damage from the energy the dam is releasing and will slow the erosion.
The full repair of the damage to the spillways will cost, it is estimated by officials, between $100 and $200 million. The engineers believe they have the situation under control, but they describe it as a “dynamic”. Residents will not be allowed back into the county until they are sure it is safe.
The fact that more rain is forecast will be a setback, water levels will rise further and the emergency slipway could dump large amounts of water into the Feather River, which runs through downtown Oroville.
What went wrong?
The state of California has been sternly criticized for wilful ignorance. There is a claim that, at least a decade ago, documents were filed, warning the government that they could be facing the probable catastrophe they are facing today.
According to Mercury News, state officials had warned the federal government that the emergency slipway was eroding. The state officials, purportedly, continued to warn them for a decade. Head of the Californian Department of Water Resources, Mark Cowin, said he was unaware of any such documents.
Nonetheless, engineers have been clear in saying that they are not sure what caused the erosion on both the main and emergency spillways.
According to the LA Times, the spillway is checked annually and was repaired in 2013. Water Resources engineer, Kevin Dossey, told them: “We made repairs and everything checked out. Obviously, something has happened that we didn’t expect.”
Works Cited
Los Angeles Times. Los Angeles Times. Web. 13 Feb. 2017.
Rogers, Paul. "Oroville Dam: Feds and State Officials Ignored Warnings 12 Years Ago." The Mercury News. The Mercury News, 13 Feb. 2017. Web. 13 Feb. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Here’s a question you’ve (likely) never asked anyone before: Where does Bermuda get its drinking water from?
A rudimentary question, at best. However, a closer investigation into the topic, a legacy is revealed. A legacy of water engineering and management that the world could learn from.
Bermuda is essentially a series of small islands that are joined via bridges to make up a large land mass. The islands were built upon porous limestone mountain ranges produced by a now-extinct volcano.
Being so far out in the North Atlantic Ocean there is simply no fresh water in Bermuda. Even the lakes and water wells are brackish. Therein lies a clue: they are surrounded by the abundant ocean. Removing salt from salt water using desalination plants is perhaps the answer today, but how did the human beings who settled in Bermuda 400 years ago access drinking water? They needed a practical solution.
The short answer to the question is rainwater and roofing.
Bermuda’s roofs are engineered in such a way that they harvest rainwater. By law, every Bermudan house and building must employ the same style. Rain water was, and still is, the only source of truly fresh drinking water.
These roofs are civil engineering masterpieces, dating back to 1609.

How do they work?
The original settlers took the super absorbent, porous limestone Bermuda was built on, crafted it into roof tiles, and used these to construct stepped roofs. The roofs capture, and slow down, any rain droplets that hit them. This harvested rainwater is then collected into gutters which then transfer the water into storage tanks under the houses.
Traditionally the roofs were painted with what was known as a ‘lime-wash’, after construction was completed. The lime-wash had antibacterial properties. Currently, however, the roofs are still painted white because this reflects ultra-violet light from the sun, which also helps to purify the water.
Bermudans capture an average of 350,000 liters of water per house, per year. This is a startling achievement, but still Bermuda could not depend on this water catchment alone.
In response six desalination plants have been constructed; they produce 13,500 cubic meters of water per day so help address other water requirements that the island has.
Vital water infrastructure
Bermudan scientist, Tarik Smith, knows - all too well - how important water management is. He is now sharing this expertise with international research and development.
He delivered a speech at the Division of Arts and Science Corange’s public forum, named: “Water Engineering: Facing the Challenges of Water Management”.
In an interview with the Royal Gazette, he stressed the importance of research into water management and mentioned the benefits of recycling water – already used in may countries around the world. He also revealed a justified pride in the rainwater harvesting system in Bermuda. He said:
“Bermuda is very conscious in terms of water consumption. Rainwater harvesting systems are a model for many countries. I think we don’t realise how advanced we are with respect to that. Many places have a lot to learn from Bermuda,”
Are desalination plants the future?
In a book, published in 2015, named Concentrating Solar Power and Desalination Plants: Engineering and Economics of Coupling Multi-Effect Distillation and Solar Plants, it is revealed that water scarcity will only intensify. The authors detail that by 2030 47% of the world’s population “will be living in areas of high water stress.” The other 67% will not have adequate sanitation.

Desalination plants are becoming one of the only solutions to those grim statistics. Taking salt out of the seawater through reverse osmosis is the most used method around the world.
Countries in the Middle East are already utilizing desalination plants on a mass-scale due to their scarcity of water. In fact 70% of the world’s desalination plants are housed in the Middle East.
Credit: BetterWorldSolutions.eu / Desalination plant, Ras Alkhair, Saudi Arabia,
To see how a desalination plant works watch this video from Veolia Middle East. This company operates the Sur Desalination Plant in the Sharqiyah region:
There are unfortunately drawbacks with the use of desalination plants. Fossil fuels power their operations and this of course produces pollution. Moreover, the water from the plants has been called into question due to its lack of magnesium and other minerals normally found in fresh water.
Another concern is the waste. Concentrated salt is pumped back into the ocean, but is also mixed with the chemicals that facilitated the initial desalination process.
Despite the negatives and with engineers dedicated to the problem, these novel approaches to water management can only improve and they bode well for a future of depleting water resources.
Works Cited
Low, Harry. "Why Houses in Bermuda Have White Stepped Roofs." BBC News. BBC, 23 Dec. 2016. Web. 07 Feb. 2017.
PBSNewsHour. "Is Desalination the Future of Drought Relief in California?" YouTube. YouTube, 31 Oct. 2015. Web. 07 Feb. 2017.
"Water Management: A Worldwide Challenge | The Royal Gazette:Bermuda News." The Royal Gazette. 25 Jan. 2017. Web. 07 Feb. 2017.
Bermudabea. "Bermuda's Water Catchment." YouTube. YouTube, 06 July 2010. Web. 07 Feb. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A solar storm has been brewing in Australia. The country’s homeowners and business owners have lent themselves to renewable energy technologies. More specifically, they are investing in solar photovoltaic energy generation technologies.
Energy Minister, Josh Frydenberg, speaking on Q&A on March 22, 2106, stated that, “Nearly 15% of Australian households have solar panels on their roofs. That’s the highest number of solar panels on people’s roofs per capita anywhere in the world.”
By 2015, Australia became the world leader in household solar panel installations. They soon became a “testing field” for 27 different battery storage suppliers who were looking to store that generated energy. According to The Age, Australia began installing PV and wind energy sources at “20 times the annual worldwide rate” in 2016.
 Credit: TheRegister.co.uk
Credit: TheRegister.co.uk
As battery storage systems have been refined and engineered for efficiency, Australia has seen an upturn in residential battery systems powered via photovoltaic cells. Australia were so progressive in their adoption of home-based solar PV systems that Elon Musk’s Tesla set up shop and started running housing development pilot projects with Tesla’s own lithium-ion battery unit, The PowerWall.
The only issue with the quick uptake of solar PV solutions in Australia, was that energy storage batteries and their installation standards were being left behind. There was little to no regulation of the industry.
The upcoming standards
Standards Australia has laid the groundwork for the future standards of energy storage in their new report: Roadmap for Energy Storage Standards. Dr Bronwyn Evans, Chief Executor Officer of Standards Australia writes:
“In embarking on this uncharted journey of technology, it is critical that those inventors at the forefront of innovation can do so unhampered, and suppliers can get these products to market as quickly as possible. On the other hand, it is imperative that good technologies such as storage systems are safe, reliable and efficient.”
Standards Australia held industry forums and consultations with Standards’ stakeholders. The forums revealed that a technology that requires immediate standards amendments are lithium-ion battery storage applications. They were marked as ‘high priority’ by the forum.
The standard for the installation and safety requirements of battery storage systems (AS/NZS 5139) would need to be amended and aligned with international standards, and implemented for larger storage systems, not just home-based ones.
The big concern

Standards Australia is focusing on the home system for the immediate future. And it seems that they have ruffled some feathers with their report. The new proposed guidelines are taking into consideration the dangers surrounding lithium-ion batteries. The main concern is that lithium-ion energy storage systems are prone to catching fire.
As a result, Standards Australia’s new guidelines may lead to the restriction of home battery storage systems being physically installed inside homes. Standards Australia are suggesting PV battery storage systems be installed outside of the house in their own ‘kiosk’ or ‘bunker’.
The new guidelines would dictate that consumers of battery storage systems would have to have an external covering in which to house the system. Presumably it would have to be fireproof as well.
Prime Minister of Australia, Malcolm Turnbull, a proponent of having energy battery storage systems inside houses (since he has one himself), said:
“We have got so little energy storage in Australia. There are only three significant pumped hydro storage facilities in Australia and yet we are introducing all of this renewable energy. What do you need if you have a variable source of energy? You need storage.”
Are lithium-ion storage units really that dangerous?
In April 2016, an image of an exploded lithium-ion battery storage unit was circulated on Australian social media channels. The battery belonged to a company named Growatt, who were using Chinese battery technology in Australia. The consumer had the battery placed in his garage.
Following that, the Clean Energy Council of Australia began to put emphasis on ‘integrity and safety’ of battery storage units.

The CEO of the Australian Solar Council, John Grimes, was a strong supporter of tightening up the battery storage standards in 2016. He said:
“The fact that there is no standard means there is the opportunity for shysters and carpetbaggers to go out and put something in the marketplace.”
Grimes has yet to comment on Standards Australia’s draft report. He did, however, in an interview with RenewEconomy, say that evidence must be provided to prove that in-house installations are dangerous. Standards Australia will allow for nine weeks of public comment on the installation and safety issues before they move forward - they are expected to see a lot of protest.
However, lithium-ion battery storage units have been proven to be efficient and safe. Badly manufactured units, like those aforementioned ones, will not survive the safety installation benchmarks and will eventually be excluded from the market. This should strengthen the case for in-house storage unit installations.
Works Cited
Council, Climate. "The Critical Decade: Australia's Future - Solar Energy." Climate Council. Web. 17 Feb. 2017.
"Standards Australia." Standards Australia. Web. 17 Feb. 2017.
"Standards Australia Delays Storage Guidelines after Protests." Renew Economy. 15 Feb. 2017. Web. 17 Feb. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Altering leave days, with both men and women employees in mind, may help companies retain women in their jobs, particularly those with positions in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics).
PAE is an American engineering firm that designs “high-performing environments” that are designed with a focus on nature, but especially on water and energy conservation.

PAE’s Director of Employee Experience, Shiloh Butterworth, says that they are testing a method to keep their engineering women in the company: “We are proud to offer an equitable leave benefit to help sustain our employees at home and work.”
Presently, under law in the US, mothers-to-be get 12 weeks of unpaid leave (although there may be some variation between states). Whereas PAE’s new paid leave policy is believed to be one of the most unique in the engineering industry, in the United States. Their “Wellness Leave” system offers expectant mothers and fathers six weeks leave at full pay. This offer is on top of the leave benefits already available to staff.
But is this remarkable? According to research conducted by the Pew Research Center, the U.S. is the only one, out of 41 nationstudied that did not mandate paid paternal leave. Estonia offers a staggering 87 weeks of paid leave for new parents.
The thinking behind PAE’s Leave policy is interesting. Butterworth believes that if men took more paternal leave, it would “level the playing field” for the advancement of women’s engineering careers.
The program also allows leave for any PAE employee adopting a child or “dealing with a serious health condition of their own or a loved one.”
Retaining women in engineering roles has historically been difficult for companies due to several factors. PAE is hoping their equitable leave policies will lead to a “culture shift” in the industry, implementing an ideology that enforces equal rights between males and females in the industry.
Where are the women?

In 2016, Engineers Australia released a report that indicated that “half of female graduates in engineering do not enter the workforce”. The report revealed that only 13% of engineers in Australia were female.
The report also stated that only 1% of Australian women past the age of 50 are currently working in engineering industries.
Dorothy Thompson, the chief executive of Drax - a company that generates 7-8% of the UK’s electricity - admits that attracting women to the energy sector has been difficult. She told the Guardian that Drax set up an apprenticeship program and received two women applications compared to a staggering 76 from men.
Thompson said:
“We would like to have more female apprentices, more female engineers. We believe in diversity. But it is challenging,” she said. “Part of it is in education but part of it is perception. We as an industry need to be more proactive in explaining how interesting an opportunity we are.”
A concerted effort needs to be made to overcome the persistently low numbers of women in STEM industries. Roma Agrawal, a structural engineer, commented wisely in an interview with Making It Magazine, “Scientists and engineers work for people, if our teams do not reflect society, then how can we come up with the best solutions?”
Works Cited
Leadership, Center For Parental Leave. "A Bold Move to Retain Women in STEM: PAE Announces Gender-Neutral Paid Leave Policy." PRLog. Web. 31 Jan. 2017.
Livingston, Gretchen. "Among 41 Nations, U.S. Is the Outlier When It Comes to Paid Parental Leave." Pew Research Center. 26 Sept. 2016. Web. 31 Jan. 2017.
"Technical Societies." Home | Engineers Australia. Web. 31 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial engineering and IIoT expansion
Experts have been wondering if 2017 is indeed the year where the complete worldwide movement toward smart factories begins. The Internet of Things is slowly making its way into the factory, interconnecting everything inside of it, and producing large swathes of performance and operational data that needs to be analyzed by factory employees. The intertwining of internet and industry has produced a new name for IoT in industry: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).

It is predicted, quite bravely, that 50 billion devices will be connected by 2020. Some believe the figure is too overestimated. Many of these will involve automated machinery and sensors running in smart factories. We are heading for the fourth industrial revolution (Industrie 4.0), a transformation of manufacturing never seen before.
Even the interconnectedness of our cities and the utilities that power and provide for them is slowly changing to the IIoT-future, and engineers are the ones who have to make it happen.
The implementation of IIoT into industrial engineering means that the world will see more interconnected wearable technologies making their way into factories and mining operations. Data-providing sensors embedded into machinery and co-bots (robots designed to interface with humans) assisting and sometimes replacing workers will generally make an industrial complex work faster and more safely than ever before.
The industrial engineers that work in this field will see salaries of $83,470 this year, according to RevPart's predictions. RevPart, an engineering company which specializes in rapid prototyping and 3D printing for several engineering industries, has published their outlook on growing engineering industries with the most attractive salaries for the year 2017. (Engineering Employment Outlook from RevPart ).
And experts are starting to preach a message of: "Adapt or die."
"No industry produces more data than the manufacturing sector, and all of that information can be applied to making smarter business decisions. Companies need to participate in capturing that value. There is $65 billion worth of obsolete industrial automation in use right now. It's only going to get more expensive to repair and replace it. Companies have to commit to modernizing," said Brian Fourtney, a Global Business Manager at Rockwell Automation, speaking to Plastics Today.
(For more news on industrials wearable technology see our article: Industrial business and workforce benefit wearable technology
Space, the final frontier

What was once considered a pipe dream for many scientists and engineers in the field is becoming a reality, thanks to the vision of South African-born CEO Elon Musk. His aerospace engineering company SpaceX, with the help of NASA, have a 2018 deadline. That deadline involves transporting the company's aerospace equipment to Mars. Upon the success of that mission, Musk plans to send humans to Mars in just under ten years.
An engineer in the aerospace field can look forward to a cool median salary of $107,830 per year. But it is not all sunshine and roses when working for this industry. It was revealed back in 2015 that working as an intern in SpaceX required a 60 to 80 hour work week. The compensation may be good, but the stress that comes with working in the aerospace industry - which sometimes depends on precise results - might not be entirely worth it. However, if you can handle those hours, you'd be part of one of the most celebrated engineering industries in the world.
But before you decide whether or not you belong in the aerospace industry, one question needs to be answered: As a child, did you play with Lego? The interns from SpaceX seem to have this in common - as well as being engineers of course.
Works Cited
Nordrum, Amy. "Popular Internet of Things Forecast of 50 Billion Devices by 2020 Is Outdated." IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. 18 Aug. 2016. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"Plastic Injection Molding Prototyping Services." RevPart. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"PlasticsToday." PlasticsToday. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
Research, Persistence Market. "Smart Factory Market Estimated to Grow Strongly by 2021." SAT Press Releases. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"SpaceX Will Launch Private Mars Missions as Soon as 2018." Space.com. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Should we be afraid of the oncoming deluge of automation technologies that are being engineered in the world? These technologies are certainly having a massive impact already; what do they augur for the future of employment?
The White House released a report in December 2016 entitled: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Automation, and the Economy. An excerpt of the report reads:
“Today, it may be challenging to predict exactly which jobs will be most immediately affected by AI-driven automation. Because AI is not a single technology, but rather a collection of technologies that are applied to specific tasks, the effects of AI will be felt unevenly through the economy.”
The report specifically highlights the implications of self-driving technologies. The report states that 3.1 million drivers of trucks and taxis could lose their jobs in the US thanks to autonomous vehicles.
Although engineers initially involved in helping Google, Tesla, and Apple create their self-driving car technology, they have begun plans to automate trucks as well.
And according to AllTrucking.com, there are 8.7 million truck drivers (also known as ‘truckers’) in the US alone.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/bK76W1kH4jA" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
With the recent advent of Uber, the number of working drivers has increased as well. The White House report states that 1.7 million drivers could be out of a job due to automation.
Interestingly, Uber has made efforts to keep up with developments in the car industry, although it won’t save their drivers. They have announced that they are preparing their very own fleet of self-driving cars. The company recently moved their operations from California to Arizona; a state with a more lenient approach to testing self-driving vehicles.
Conservative news anchor Tucker Carlson (Fox News) has underlined the problems he sees with the self-driving technology that Uber intends to implement. He stated figures about driving employment, saying, in 29 out of 50 states, the single most common job is driving for a living. He added that it is also the single most common job for men with a high school diploma. He is deeply concerned that without the need for drivers many will be out of work.
Does Automation really kill jobs?
It depends who you ask. The big question on everyone’s minds is whether or not automation will create more jobs than it replaces.
Regarding vehicle autonomy, Governor of Arizona, Doug Ducey alluded to the process taking a bit longer and that people should relax...for now:
“This technology isn’t going to be ready this year, next year, and likely the year after, there are many people that will never get into an autonomous vehicle. We think this is good technology…..it will help the disabled, the blind, the elderly; people that can’t drive. There are conveniences that are possible here, but they haven’t come to fruition yet.”
In the manufacturing industry, the National Association of Manufacturers stated last year, that in the United States the manufacturing industry employed 12 million Americans, representing 9% of the country’s workforce. The Guardian reports that these numbers are lower than they were in 1940.
However, the Association also found that in 2001, when industrial operations started seeing automated industrial robotics placed among human workers, employment in the country as a whole rose. Similarly, in the years 2010 to 2014, the number of industrial robotics the U.S. bought skyrocketed, and once again employment numbers went up.
Is this evidence that when automation predominates in one industry, other industries are created, thus raising general employment rates? Outgoing U.S. President Barack Obama believes this. In June of last year a representative of a steel workers’ union alluded to jobs being replaced by automation. Obama responded:
“The good news is that there are entire new industries that are starting to pop up. What we have to do is to make sure that folks are trained for the jobs that are coming in now, because some of those jobs of the past are just not going to come back.”
It would seem that constantly equipping yourself with current and relevant training and education would set you apart in a world that is threatened by automation technologies. Even engineers themselves are in real danger of automation rendering their expertise useless.
Are you ahead of the pack?

Works Cited
The Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group. Web. 17 Jan. 2017.
"Driverless Cars Are Coming, but Will They Kill Jobs?" Fox News. FOX News Network. Web. 17 Jan. 2017.
"Truck Drivers in the USA." Truck Drivers in the USA | AllTrucking.com. Web. 17 Jan. 2017.
Vardi, Moshe Y. "Are Robots Going to Steal Your Job? Probably | Moshe Y Vardi." Opinion. Guardian News and Media, 07 Apr. 2016. Web. 17 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Cybersecurity has become one of the most important topics of conversation for business, governments and the general population, all those striving for the security and privacy of their data, some of which is stored in the cloud.
There are measures that can be taken to protect data, but the situation is worsening. Entire industries are being threatened with ransomware - one of the most malignant hacking enterprises - as criminal ‘businesses’ pop up around the world.
Experts warn that even connecting to a government-funded free Wi-Fi hotspot puts people at risk of being hacked. The danger for the individual, of course, is that personal data can result in the theft of identity which is potentially very costly and tricky to retrieve.
Warnings and cautions abound. One of these asserts, for example, that without a two-factor authentication on a Gmail email, incidents of account hacking are the fault of the owner.
However, for large-scale operations, that require interconnected servers like government and industry, securing data from prying hackers is not as simple.
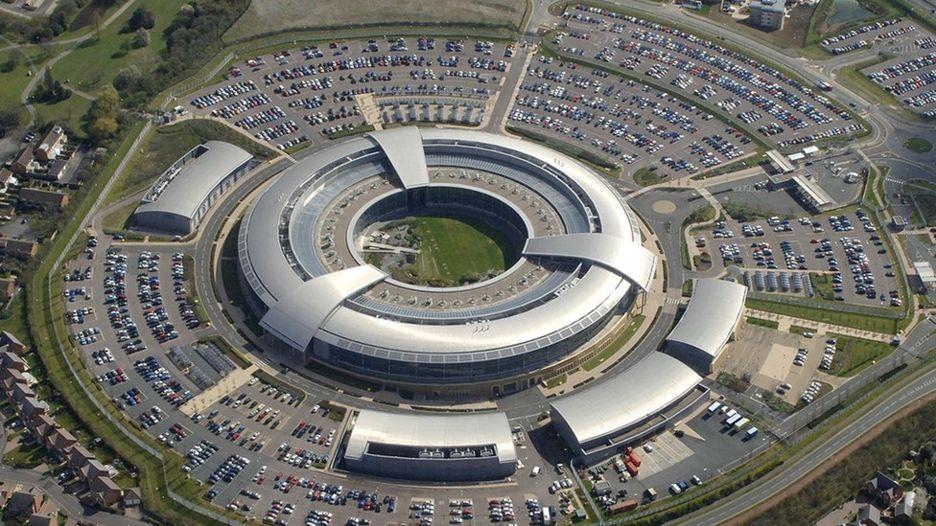

Image: The National Cyber Security Center in Gloucestershire. Credit: www.gchq.gov.uk
In the United Kingdom, seven start-up cybersecurity engineering firms have been handpicked by the national intelligence agency to assist in the operation of a countrywide firewall named the GCHQ Cyber Accelerator. It will be housed in the new National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) in Cheltenham in Gloucestershire, England.
The firewall is supposed to stop hackers from accessing government servers and those of key industries, including power generation, some engineering and education operations, charities and will also be used by small business.
At the Billington Summit in Washington D.C. on the 4th of October, 2016, the National Cyber Security Centre Chief Executive, Ciaran Martin, delivered a speech on cyber security. An excerpt from the transcript of his speech reads:
“Our critical systems are going increasingly digital. Systems like the power grid have long had significant computer networks and we’ve worked with those providers on security issues for a very long time. Manual systems, like the meters used for measuring gas and electric usage, are going digital too. This Smart Meter technology will keep costs down and improve the environment, but it will also mean a box connected to the Internet in every home and business in our country.”
The incoming 45th President of the United States, Donald Trump’s team took to his official Facebook page to announce that former New York City Mayor, Rudy Giuliani, will head up the department that deals with cyber security in the country:
“As the use of modern communications and technology has moved forward at unparalleled speed the necessary defences have lagged behind. The President-elect recognizes that this needs immediate attention and input from private sector leaders to help the government plan to make us more secure.”
Eugene Kaspersky, the CEO of Russian-based Kaspersky Lab, the specialists in computer firewall protection, dreams of a future where it would be too cumbersome a task to hack into any infrastructure worldwide. In 2016, Malwarebytes quoted him, saying:
“Securing infrastructure against hackers is a massive challenge, but I believe that one day we will achieve the state when you can have a wind turbine connected to the Internet, but still be absolutely secure.”
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, maintains that the introduction of ethernet and TCP/IP unfortunately raised the likelihood that engineering industries would be hacked.
“We need to design - into everything we do, both individually and holistically - some sort of cyber security. Furthermore, security must be multi-layered to foil hackers getting through initial firewalls. ” Mackay said.
The Engineering Institute of Technology offers a 6-week live, online course that covers the basics of cybersecurity for automation, control and SCADA systems, focussing on the current trends occurring in the industry today.
Increasingly the world will need engineering professionals able to implement security measures for industrial control systems in the cyber world.

Works Cited
"Donald J. Trump." Facebook - Log In or Sign Up. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
EngInstTech. "ENN36 Industrial Internet Security." YouTube. YouTube, 17 June 2016. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"GCHQ Backs Cybersecurity Start-ups in New Cheltenham Hub." BBC News. BBC, 11 Jan. 2017. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
Tsing, William. "Threat Modeling: What Are You so Afraid Of?" Malwarebytes Labs. Malwarebytes, 17 Oct. 2016. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter

An environmental engineer would surely agree that when it comes to public health, noise pollution is a dangerous threat to a person's wellbeing. It has been well researched and proven that citizens of a country who live near airports have higher blood pressures than those who live elsewhere. People's health is directly affected by noisy engineering design.
The Federal Aviation Authority says that an aircraft's noise output should, at maximum, be 65dBA, observed at ground-level. Gas-powered leaf blowers emit 90 to 102 dBA and generate their own carbon footprint - which has captured the attention of the environmentalists. A town in California named Sonoma, in the United States, has banned the use of gas-powered leaf blowers around the city. Citizens have expressed that they look forward to the "restoration of the quality of life" now that the blowers have been banned.
Thanks to engineering ingenuity a new battalion of leaf blowers are making their way to the markets - some have already arrived. The leaf blowers are battery operated and only emit 65dBA of noise. The newer blowers will also outclass plug-in blowers due to their wireless capabilities. However, with the cheaper gas alternatives, I’m sure some countries will still stick to these tried-and-tested blowers until proper bans are put in place.
More engineering ingenuity is, arguably, needed in all engineering industries, so that noise levels can be driven down.
Steve Mackay tends to agree: "In your next engineering design, think about noise. Think about how to reduce the effect on your wonderful clients. You will probably have a far happier client."
Works Cited
"Acute Effects of Night-time Noise Exposure on Blood Pressure in Populations Living near Airports." European Heart Journal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
EngInstTech. "ENN41 Noise and Audio." YouTube. YouTube, 30 June 2016. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"Gas Leaf Blowers Banned in Sonoma." Sonoma Index Tribune. 01 Dec. 2016. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Our buzzword for your engineering career this year is INVESTMENT. The modern world of business centers on the principles of investment. You put something in, and hopefully (with copious amounts of elbow grease) get something out.
When someone looks to invest their hard-earned money, the most important factor they consider is growth potential. The question they ask themselves is: Will my invested money grow?
Pursuing engineering as a career involves just such an investment, investment in your education for your future. Therefore, as a prospective engineer formulating career goals, it is well worth monitoring which engineering disciplines have the most growth potential for the future of your employment.
The Growers
RevPart, an engineering company which specializes in rapid prototyping and 3D printing for several engineering industries, has published their outlook on growing engineering industries with the most attractive starting salaries for the year 2017.
Engineering Employment Outlook from RevPart
RevPart indicates that the starting salary for Mechanical Engineers will be US$83,950 per annum as of this year. (They also say that mechanical engineers will be involved in the building of the next "wave of self-driving cars".)

Automotive engineering - an industry that utilizes the discipline of Mechanical Engineering - has become a serious bone of contention in the United States as the country approaches Inauguration Day (20 January 2017). President-Elect Donald Trump promised car manufacturers, Ford, Toyota, and General Motors, that if he were to become president, there would be a tariff imposed on any vehicles manufactured in Mexico and sold back into the United States
Ford has since announced that it would drop plans to open a factory in Mexico, and rather opted to expand the Ford plant in Michigan and create 700 American jobs.
Other automobile manufacturers are also doing an about-turn on any foreign plans: Fiat Chrysler has announced an investment of $1 billion into making three new Jeep models in the United States, and plans to revamp factories in Michigan and Ohio. The move is set to add 2,200 jobs, the company confirmed in a statement.
Daimler AG has pledged $1.3 billion to expand production of SUVs in Alabama. And Volkswagen Group has recently announced that a planned expansion in the US will top $7 billion.
Mechanical Engineers will be in the pound seats, but the automotive industry, which is going through profound change and modernization, demands expertise from a number engineering disciplines.
To see how automotive engineering could fit into your career goals, take a look at this video from Jaguar Land Rover:
Jaguar Land Rover sold a record 583,312 vehicles in 2016, according to Reuters.
The other industry showing growth this year is the biomedical industry. It's expected to grow by 23% over the next 10 years. And it's easy to see why with engineering endeavors such as this: A flexible, wearable, 'Star Trek tricorder' health monitor is here.
Monitoring and improving the health of humans through biomedical engineering technology is just another example of how engineers are continually changing and improving the world.
We focus on industrial, material and aerospace engineering in Part 2 of our series on: Choosing the right Engineering discipline for your future career. Look out for it.
Works Cited
"Ford Scraps Plan for $1.6 Billion Plant in Mexico after Trump Criticism." Reuters. Thomson Reuters, 03 Jan. 2017. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"Jaguar Land Rover Sells Record 583,313 Cars in 2016." Reuters. Thomson Reuters, 09 Jan. 2017. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"Plastic Injection Molding Prototyping Services." RevPart. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
"Your Future In Automotive - Rebecca Lees, Jaguar Land Rover." YouTube. 17 Mar. 2014. Web. 16 Jan. 2017.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter

Smart cities are much more than solar-powered street lights triggered when pedestrians walk beneath them.
Smart cities refer to cities that use the latest in technological innovation in infrastructure and IT systems, and the Internet of Things, interspersed with environmentally-friendly nature-inspired elements.
However, to design a smart city, a sizeable redesign to old infrastructure is usually required. Architecture needs rethinking and reforming, the traditional disciplines of engineering are stretched and smart technology is at the crux of it all. This is all in pursuit of a better quality of life for the humans who live in these bustling cities.
In the book ‘Human Smart Cities: Rethinking the Interplay between Design and Planning’, Louis Albrecht, a Professor in the Department of Architecture, Urbanism and Planning, at the Catholic University of Leuven writes:
“There is a growing awareness that a number of planning concepts (compact cities, livable cities, creative cities, multicultural cities, fair cities, just cities, smart cities) cannot be achievable solely through physical hard planning.”
Albrecht argues that the transformation of cities into smart cities has historically been overrun by the forces of free-market capitalism; by private companies seeing market opportunities that can be exploited. Instead governments, he suggests, should properly implement a move toward smart cities that benefit the humans that live and work in them. He writes:
“There is also awareness of the fact that (in addition to traditional land use regulation, urban maintenance, production and management of services) governments are being called upon to respond to new demands and to adopt a more entrepreneurial style of planning in order to enhance city and regional competitiveness.”
Governments are noticing that the technology-literate demand that everything, from electricity to water metering, become smart, efficient and data-analysis-friendly, so that they know where their money is going to when to pay their utilities.
Moreover, as smart cities pop-up, with more people gaining access to education and job opportunities (thanks to the smart-city benefit of a city-wide internet), new challenges arise. And most of these challenges are usually infrastructural.
More Cities, More Traffic
Engineers are called upon to rethink transportation because once a city becomes a hub of middle-income activity, it equates to an overcrowding of cars.
The congestion of city roads is unsustainable and is projected to worsen. The BBC reports that 70% of the world’s population “will live in urban areas by 2050”.
How do we cut congestion?

Auto Manufacturers Ford has recommended that cities address mobility challenges with a “fully integrated transportation operating system”. Their goals for the future of smart cities - or as they call it ‘The City of Tomorrow - are: No accidents, no emissions, no congestion and universal access to mobility - a fully automated approach to a city and its mobility.
The BBC spoke to Peter Coker, vice-president of innovation at KuangChi Science; he is quite certain that jetpacking around town will become a social norm. He said: “Jetpacks will be part of future cities. I see it as being the Uber of the sky.” Pigs might fly too, but if this futuristic innovation does eventuate, fewer drivers will remain on the roads and ease congestion there!
What about the more realistic driverless car, will they ease congestion? Perhaps. They will have the capacity to work out optimal routes and departure times and fewer accidents will certainly prevent resultant traffic jams. The Department of Transport in the United Kingdom says that once the technology is fully adopted, it could reduce congestion by 40%. However, experts believe the driverless vehicles could increase congestion in the short-term as the technology is interwoven with cars with drivers.
While the concept of a smart city is not a new concept, finding a clear definition that can be applied cross-continentally is the bigger challenge, as is applicability. Futurologists might get carried away with their vision of a unified, smart city future, but the emergence of these cities is likely to be impeded by practicalities including decision-makers seeing eye-to-eye and budget constraint.
Works Cited
Concilio, Grazia, and Francesca Rizzo. Human Smart Cities: Rethinking the Interplay between
Design and Planning. Cham: Springer International, 2016. Print.
"Driverless Cars 'to Increase Congestion' Says Government." BBC News. BBC, 06 Jan. 2017. Web. 12 Jan. 2017.
"Media Log In." Ford Partnering with Global Cities on New Transportation; Chariot Shuttle to Be Acquired, Ford GoBike to Launch in San Francisco | Ford Media Center. Web. 13 Jan. 2017.
Wakefield, Jane. "Tomorrow's Cities: What It Feels like to Fly a Jetpack." BBC News. BBC, 11 Jan. 2017. Web. 12 Jan. 2017
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Steve Mackay, Dean of Engineering at EIT and sister company, IDC Technologies enjoys writing his weekly blog including useful tips and current industry matters for his fellow engineering colleagues. With a loyal and expanding following base reaching over 600,000 people around the world, click here to read all of Steve's blogs over at EIT's sister company, IDC Technologies.
Digitally Hunting for an Engineering or Technology Job
Have you experienced the frustration and futility of searching and applying online for hundreds of jobs – particularly in the engineering and technology space? Perhaps, you feel that you are casting your resume into the abyss whenever you apply online.
Unhappily today, you often have to get your resume past an army of robots looking for keywords before handing over a select few resumes to a human recruiter to look at. Some firms are even proactively scanning the web looking for personnel with the perfect characteristics matching a particular job profile. Other strategies are to require you to upload a video to the web with you answering specific questions.
This is all making it extraordinarily difficult for you to actually talk to a human. And it makes it critical for you to follow the right steps in dealing with this plethora of technology so that you can gain an interview.
Predictably the first step is simple
This is for you to review the job description and ensure your resume is aligned with what the recruiter requires in terms of experience and qualifications in a measurable way.
This is to make it easy even for an orang utan to see that you are the perfect match for the job. This doesn’t mean that you must lie but you must put effort in to visualise what the job requires and align your resume with the job. Ensure that you use the relevant key words so that they get picked up by the robots doing the initial scan of resumes. Perhaps put in the acronyms relating to the hardware or software requirements.
Stay up-to-date at all times
Keep everything relating to your online career up to date. This means not only your resume but LinkedIn profile and other social media sites.
Smile for the Camera
Many interviews are conducted online and through Skype. Ensure you are 100% presentable and prepared for any interview. Whether it is demonstration of your sales or technical skills or simply as an interview.
Assess your Performance and Consider Alternative Strategies
If despite all this work; you are still hitting the black hole in terms of results – sit down and consider what you are doing. Get a colleague to assess your resume or presentation and make suggestions. Consider that you may be applying for jobs in an overtraded area where demand is low and supply huge.
Perhaps you should be using other strategies to gain your dream job in engineering – such as gaining more credentials or experience or joining an online discussion group in the topic area. Actively networking with others in the industry is a strategy which engineers tend to be less enthused with but which can work wonders for a job search.
Above all – persist and don’t give up. Ultimately your grit and determination will prevail in your job search.
Yours in engineering learning
Steve
Mackay’s Musings – 16th August’16 #613
780, 293 readers – www.eit.edu.au/cms/news/blog-steve-mackay
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Could you visualise a world without technical drawing software? Showing the inner workings of something you engineered by hand sketching the details as accurately as possible. CAD software is the lifeblood of design engineers. Most modern engineers applying for patents for their tirelessly engineered innovations use CAD programs to create their technical drawings. Other design engineers will use the programs to show a mockup of what an eventual product design may look like, and can introduce hypothetical changes to the product and measure the effect it might have. The pen and ruler has been replaced by computer software. Eighty years ago, however, the inefficient pen and ruler is all engineers had.
A collector of technical drawings appeared on BBC’s Antiques road show in September, with a box full of technical drawings from a railway and civil engineer named Robert Stephenson, who drew technical drawings by hand in 1823. He was the son of who is considered to be the ‘Father of Railways’, George Stephenson. Jonathan Moller, who brought the box of drawings to the popular show bought the box on eBay for $115. The historian on the show valuated the drawings at more than $38,000.
There probably are still the purists who have not let go of the traditional pencil and eraser, however, there is no denying that technology has forever changed engineering. As a result, engineers have had to gain new skills related to information technology to keep as relevant to the industry. Their grasp on technical knowledge has undeniably grown over the years.
LinkedIn have published their list of skills that are most in demand and will most likely get a candidate hired in the modern workplace. The conundrum that engineers face is how to implement non-engineering skills into their daily work life without losing focus on their main skills. The most ‘in-demand’ skills, according to LinkedIn are:
1. Cloud and distributed computing
2. Statistical analysis and data mining
3. Web architecture and development framework
4. Middleware and integration software
5. User interface design
6. Network and information security
7. Mobile development
8. Data presentation
9. Search engine optimization marketing
10. Storage systems and management
Those look more like individual jobs than skills, to be frank. What is apparent is that information technology skills have become very crucial to landing a job in the global village. Having ten of these skills on top of an engineering degree is probably being optimistic. Having some of these skills, however, could put you ahead of the pack. Gone are the days where just being a people person, with the ability of being a team player, gets you the job.
In some cases, engineers abandon their initial engineering studies and move to a DevOps engineering role or software engineering role, away from traditional engineering endeavour. And perhaps some are not wrong. CareerCast.com published a report that showed that software engineers, computer system analysts and web developers are the most in demand jobs of 2016, with petroleum engineering only coming in at fourth place. The starting salaries for engineers may be higher but there seems to be more job opportunities for people going into information technology roles, where only some rely on engineering.
Moreover, there is a push for engineers to become proficient in marketing and entrepreneurial skills as well. Engineers with the market-know-how of Steve Jobs and the technical skill of Steve Wozniak. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology launched a minor degree in Entrepreneurship & Innovation earlier this year, encouraging engineers to enroll due to the lecturers being part of the MIT Schools of Engineering and Management.
Some critics, however, are giving a different perspective on the way engineering is being advertised to future students. Critics say it should not be advertised as a field of study that leans heavily on entrepreneurship and makes it look all shiny. The reality of it is a bit different. Although, working for Tesla or SpaceX would be cool.
“The value of engineering is much, much more than just innovation and new things. Focusing on taking care of the world rather just creating the new nifty thing that’s going to solve all of our problems,” said Lee Vinsel, an Assistant Professor of Science and Technology Studies at the Stevens Institute of Technology. He spoke to journalist Stephen Dubner on a recent podcast episode of Freakonomics, named ‘In Praise of Maintenance’.
“If you look at what engineers do, out in the world, like 70-80 percent of them spend most of their time just keeping things going. And so, this comes down to engineering education too, when we’re forcing entrepreneurship and innovation as the message, we’re just kind of skewing reality for young people and we’re not giving them the real picture and we’re also not valuing the work that they’re probably going to do in their life. That just seems to me to be a kind of a bad idea” Vinsel said.
This is where LinkedIn’s ‘in demand’ skills come in. A good number of industrial facilities now run on completely automated systems that rely on SCADA systems, PLCs and more. Technical know-how is a must when it comes to these systems, because the Internet of Things lies on the horizon. This means that learning how to secure network information and operations is critical to keeping key engineering industries (like power plants) functioning. It would be advantageous to become well equipped with the skills that could save a company a lot of money, and could get you a pay raise.
Here at the Engineering Insittute of Technology we offer Professional Certificate of Competency in 3D Engineering Design and Printing for Rapid Prototyping 3 month course, as well as various SCADA 3 month courses: The Professional Certificate of Competency in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) & SCADA Systems and Professional Certificate of Competency in Modern SCADA Communication Systems including DNP3 & IEC60870.
Please contact us for more information.
- Details
- Written by: Evangeline Newby
W. Richard Bowen, author of Engineering Ethics: Challenges and Opportunities, says that engineers are in charge of several industrial operations that have the power to change the society they live in. He lists some of the ingenuities that engineers have designed: “Clean water production and sanitation, energy generation, large-scale pharmaceutical manufacture, hygienic food processing, functional buildings transport infrastructure, mechanical devices, medical diagnostic equipment, instrumentation and computing and telecommunications.”
Bowen says, in the past, “high priority” has been given to the designing of impressive engineering technologies without much attention given to “ethical responsibility”. However, as the title of his book stipulates, these are challenges and opportunities for the engineering man/woman. Engineering companies have historically abided to a code of ethics, a practice that almost all companies in every single industry in the world stick to. But how much do we trust these so-called engineers?
Gallup, a world renowned American research company with a focus on global performance management recently conducted an over-the-phone survey with the help of 1,028 Americans. The poll was conducted to measure the American public’s perception of honesty and ethics in selected professions. The Society of Fire Protection Engineers of the United States, in one of their recent publications, drew a graph according to Gallup’s figures from 2011-2014, which indicated engineers were second in terms of professional and ethical standing, with nurses gaining the top position. Nursing professionals have been lauded in the survey for the last 14 years, getting the top spot every year since 1999.
| Profession | Percentage of respondents |
| Nurses | 85% |
| Engineers | 70% |
| Military Officers | 69% |
| Medical doctors | 65% |
| Pharmacists | 64% |
| Dentists | 61% |
| College teachers | 54% |
| Police officers | Less than 50% |
| Judges | Less than 50% |
Gallup’s American’ Ratings of Honesty and Ethics in Selected Professions 2011-2014 ; as reported by the Society of Fire Protection Engineers of the United States
Moreover, The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, in a YouTube series titled The Engineering News Network has spoken about ethical engineering. He said: “Ethics for engineers means engineers in the fulfillment of their professional duties should uphold, as paramount, the safety, health and welfare of their fellow citizens.”
With reference to the American Society of Civil Engineers, Mackay outlines what he believes are the fundamentals of ethical engineering. When approaching any engineering project, there are a few “rules of thumb” he believes one can apply:
● Hold safety, health and welfare of your fellow citizen in high regard
● Only work in areas where you are competent
- “Don’t build bridges if you’re an electronics design engineer. Focus on your areas of competence,” Mackay said.
● Be truthful and objective in everything you do
- “Be honest, tell the truth and be objective when communicating with others”
● Try and hold the highest professional standards in whatever you do
- “Don’t take shortcuts; don’t go for the cheap and nasty approach”
● Avoid conflicts of interest
● Ensure that your professional reputation is built on real, objective successes
● Have zero tolerance for fraud, corruption and bribery. Say no
● Always focus on enhancing your skills
Works Cited
Bowen, W. Richard. Engineering Ethics: Challenges and Opportunities. Print.
EngInstTech. "ENN39 Engineering Ethics." YouTube. YouTube, 23 June 2016. Web. 24 Aug. 2016.
"Honesty/Ethics in Professions." Gallup.com. Web. 24 Aug. 2016.
- Details
- Written by: Evangeline Newby
When the United Kingdom famously opted to exit from the European Union this year, what was the dominant feeling among them? The question sounds like the unanswerable million dollar question at the end of a trivia show. The answer is: uncertainty. They felt that the country had isolated itself from the rest of the world and that engineering endeavor and business was going to be wrapped up in...uncertainty. Engineers are in an era of uncertainty. The world wants new, shiny, efficient things from engineers. And it breeds uncertainty. What are those things, you ask? Society demands more efficient transport, more power production, safer energy exploration, less waste, smarter products, self-driving cars, more impressive entertainment technology, and on top of this, they want it all to be safe and reliable.
This is where engineering in safety, predictability, and risk comes in. Safety engineers are one of the most sought after kinds of engineers because they attempt to shield the general public from the risk attached to engineering endeavor and innovation. Engineers ensure that the systems they build are the safest and most reliable systems they can possibly design. In key engineering industries, risk-related procedures must be followed to ensure that the highest level of performance is possible. And when failures occur, it is the safety engineer's responsibility to figure out the ‘why’ and ‘how’ the failures happen, and adjust their systems’ safety accordingly. In their book, ‘Reliability and Safety Engineering’, Ak. Srividya and Durga Rao, say: “Reliability deals with the failure concept, whereas safety deals with the consequences of failure.”
What are the consequences of failure? Well, sometimes it is the worst possible result; death. The Dreamworld theme park in Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia, has seen the result of an engineering failure. The Thunder River Rapids ride saw a malfunction that caused the colliding of two of the ride’s rafts, positioned on the conveyor belt. Four people lost their lives after being ‘ejected’ from the ride after the raft was flipped over due to the collision. The Australian Workers Union had reportedly approached the theme park’s operators, Ardent Leisure, and the Queensland safety regulators to bring the park’s safety and operation of equipment into question back in April 2015.
Safety, predictability, and reliability of theme park rides are something automation and control engineers will be making a lot of money out of in the entertainment industry in years to come. A report by Global Industry Analysts predict that theme park revenue, in the United States alone, will reach $44 billion by 2020. Safety PLCs are usually used to automate theme park rides, and will continue to be engineered within the parameters of reliability and will ensure engineers can respond to failure quickly with a fail-safe mechanism. Continuous operation of theme parks means more maintenance being necessary - this is where safety engineers are needed.
Safety, reliability, and predictability of engineering systems have never been more important in a world that will be seeing driverless cars in the future. The question is - can we engineer something that controls a car in a safer way than humans do? Globally 1.2 million people die in car accidents every year. As a result, we have seen companies like Google, Tesla Motors and others; begin to engineer hardware that drives the car for you. But is it safe? Missy Cummings, the director of a robotics focused lab named the Human and Autonomy Lab at Duke University predicted a year of challenges for self-driving in March 2016. She said: “There is no question someone is going to die in this technology. The question is when, and what we can do to minimize that.” The self-driving car has changed the world of traditional safety engineering and presented it with new and unique challenges.
Chris Urmson who was attached to Google’s self-driving car project in March said that self-driving technology is safe. He said that Google’s driverless cars had done 1.4 million miles of driverless driving; the equivalent of 108 years on the road. Urmson has since departed from Google but professed that Google’s fleet was safe and ready for public deployment.
Elon Musk’s Tesla Motors will be equipping every car that comes off of their assembly line with new hardware that allows the car to operate itself. In the near future, you could have a fully autonomous car sitting in your garage. It has been, very much, trial and error with Tesla and self-driving hardware. In June, Tesla’s software was criticized when their Autopilot Technology Package failed to spot a trailer sprawled across a freeway in a customer’s Tesla Model S. The software reportedly was not able to discern that the trailer was in front of it because of its white color. The car slammed into the trailer and the driver unfortunately died. The National Highway Transportation Safety Administration opened an investigation. The safety engineers, presumably, had to go back to the drawing board.
However, they are back and Tesla now has full autonomy hardware named the ‘Drive Me’ program, using the Nvidia Drive PX 2 computing platform. The company has now set a safety goal, to not have any serious injury or death in their new fully autonomous cars by 2020.
The Engineering Institute of Technology is hosting the Master of Engineering in Safety, Risk, and Reliability. Through online interactive training, the next generation of safety engineers will bring their knowledge to industries that require system safety in the early stages of projects to the operation of those projects. The course covers key safety modules including:
● Safety Systems and Risk Management
● Incident and Accident Investigation
● Health, Safety and Environment Management
● Human Factors Engineering
● Reliability Engineering
● And more
The Master's program will equip you with the necessary knowledge for reducing risk in key engineering industries. Through live webinars and interactive sessions, industry experts will train the new realm of safety engineers. The next automation, process and design engineers will be developing new engineering innovations that will need safety, risk and reliability engineering. Any uncertainty of new engineering innovation can be diminished.
Below are a list of engineering programs that we at the Engineering Institute of Technology offer:
- Master of Engineering (Safety, Risk & Reliability)
- Professional Certificate of Competency in Safety Instrumentation Systems for Process Industries
- Professional Certificate of Competency in Hazardous Areas and Instrinsic Safety for Engineers and Technicians
Please contact us for more information.
- Details
- Written by: Evangeline Newby
Globally, there will be two billion people aged over 60 years old and older, by 2050. That figure is given to us by the United States government, who use the estimations to build policy around the elderly in their country. How many of these two billion will still be employed in 2050? It is perhaps impossible to say. How many will be let go because of their age? That is also an impossible question to answer. It was George Orwell who famously said: “Each generation perceives itself to be more intelligent than the one that went before it, and wiser than the one that comes after it.” Whether current engineering leadership believes that or not, there seems to be a hiring culture that favors younger postgraduates above older engineers. Or at least that is potentially true for Silicon Valley.
Google has been accused of ageism hiring practices in new claims that could see the search engine giant going to court. A judge has called for engineers - of forty years old or older - who unsuccessfully interviewed at Google for employment to testify in a “collective action” case. The judge said that “software engineers, site reliability engineers or systems engineers” who applied for employment in August, and were turned away, should speak up so that an ageism case can be built.
A spokesperson at Google told media: “We believe the allegations here are without merit and we will continue to defend our position vigorously. We have strong policies against discrimination on any unlawful basis, including age.” On Google’s campus, there is allegedly a diversity group - or club - that sees 40 years old and older engineers engaging in social activities. They’re known as the GREYGLERS or ‘Grey Googlers’. When Yahoo Finance requested a report on the median age and gender ratio of Google, the company were reluctant to provide any information.
However, Google is not the only tech company that has seen an ageism suit being filed. At Elon Musk’s Tesla, a 69-year-old engineer is alleging that he was fired because of his age. He is certain that his age played a factor in his dismissal. The 69-year-old Mr. Thomas Flessner said that when he worked at Tesla, he would have to work harder than everyone else because he had to prove that an engineer of his age could compete with the younger engineers. A spokesperson for Tesla told media: “While we aren’t commenting on the specifics of this litigation, we are committed to upholding a discrimination-free workplace.” Other tech companies also embroiled in ageism claims include Microsoft, Twitter, and IBM.
Patricia J. Bronwell and James J. Kelly authored a book named Ageism and Mistreatment of Older Workers: Current Reality, Future Solutions. Their book positions ageism right alongside racial and gender discriminatory practices. They also write about how ageism is a human rights issue. The book references the stance the United Kingdom Department for Work and Pensions took in 2011. They wrote, that in workplaces, equal training needs to be given to all employees “regardless of their age,” and that, training options need to be communicated to every employee. It is perhaps the contravention of this stance that sees older engineers falling behind with the times and getting fired because of their inability to keep up with the technological changes within a company.
This is most apparent in South African telecoms company, Telkom. There seems to be a divide in the education and training of newer technicians versus the older, more experienced technicians. The divide that exists is one that sees the younger employees grappling with and understanding new technologies pertaining to LTE and fiber infrastructure, but, leaving the older technicians oblivious to the newer technologies. For example, once an aged technician is called out to a customer’s house, they could be seeing technology - belonging to the company they work for - that they have never seen in thirty years of working at the company. A lack of adequate training for older technicians means they get left behind.
Although, there are some skills that engineers and technicians could acquire that would keep them afloat in a world where the younger, budding engineer is taking over. The Dean of Engineering here at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, says that staying employed as an elderly engineer is all about networking. He said: “I often have people - especially in their forties and fifties- saying they’ve applied for jobs, can’t get them, and that they think there is discrimination against us older guys. It’s possibly true, but, one of the amazing things you can do is build up a network of colleagues, friends, whatever. You start doing that when you’re in college or at university and you keep building it up. The network will actually help you get employment or point you towards opportunities.”
References
Brownell, Patricia J., and James J. Kelly. Ageism and Mistreatment of Older Workers: Current Reality, Future Solutions. Print.
Numbers, By The. "More Software Engineers over Age 40 May Join a Lawsuit against Google." More Software Engineers over Age 40 May Join a Lawsuit against Google. Web. 10 Oct. 2016.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
President of the United States, Barack Obama decided to veto the application and in turn canceled the project. Some experts believed it was politically motivated, however, activists had expressed their concerns pertaining to the pipeline. Activists said that “tar sand transport” would have released toxic chemicals into the air, having an adverse effect on the health of the people of Oklahoma. Additionally, the 850,000 barrels of oil that the pipeline would have transported, per day, would have also gone on to be environmentally harmful. Obama’s office cited the debate on climate change as a reason for the rejection of the plan.
Nonetheless, the engineers behind the Keystone project, when it was still being greenlit, tried to reassure the public that it would not be as harmful as some people thought. They said, “The Keystone XL Pipeline will be the safest and most advanced pipeline operation in North America. It will not only bring essential infrastructure to North American oil producers, but it will also provide jobs, long-term energy independence and an economic boost to Americans.” Some engineers believe that whilst other engineers work to build a future where renewable energy is the norm, the current energy-producing methods must still go forward.
Therefore, engineers who are proficient in onshore and offshore pipeline systems are still needed in the world. Offshore-Mag.com estimates that almost 4,000 miles of oil and gas export and transmission pipelines will be built from now, through to 2020, in offshore operations alone. Offshore pipeline installation requires engineers to know quite a bit about hydraulics; fluid dynamics, flow, and conveyance of fluids (oil, gas and water).
Amidst the outcries of protestors claiming the environment is damaged by pipelines and the subsequent emissions they produce, engineering experts have assured the public that the transportation of oil through pipelines is five times safer than transporting oil via railway. Spectra Energy says that long haul pipelines have a clean safety record and are reliable for onshore natural gas transmission. The pipelines are continually monitored to ensure they are working as efficiently and safely as possible, twenty-four hours a day. Should something go wrong with the pipeline, engineers are prepared to deal with the fallout as it happens.
The importance of safety in pipeline design cannot be understated. Billions of dollars have been spent on enhancing pipelines and securing their safety in the United States alone. The process of securing a pipeline’s safety occurs long before construction even begins. Qiang Bai and Yong Bai’s book Subsea Pipeline Design, Analysis and Installation outlines the design procedure for a possible pipeline system. The design guidelines are very similar for both onshore and offshore applications:
1. Design requirements
2. Pipeline wall thickness
3. Grade of pipeline material
4. Type of coating-corrosion and weight
5. Coating wall thickness
Corrosion, erosion or third-party damage to pipelines could result in environmentally damaging accidents, which is what the environmentally-conscious public is aware and scared of. When engineers design pipelines, however, the stress loads are calculated and a probability of failure figure is produced. Additionally, environmental safety impact assessments are also done, to measure the impact the construction and the operation a pipeline design might have.
Are you interested in diving into the very profitable world of oil, gas and water transportation and transmission engineering? A three-month course from the Engineering Institute of Technology will get you started on the basics of pipeline design and much more. Once the three months are over, you will be awarded a Professional Certificate of Competency in Onshore and Offshore Pipeline Systems. Best of all, you can do it in the luxury of your own home as all of the engineering training is done through interactive online sessions. You will learn about the key principles of pipeline design, construction, installation, operation and maintenance. You will be taught several pipeline specifications and standards to ensure that the pipelines you eventually work on will be built in a correct manner and are free from any sort of damage.
The EIT offers a three-month course related to the above, called the Professional Certificate of Competency in Onshore and Offshore Pipeline Systems. Please ask us for more information.
References
Bai, Qiang, and Yong Bai. Subsea Pipeline Design, Analysis, and Installation. Print.
- Details
- Written by: Evangeline Newby
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States (NASA) has said that after 136 years of global temperature record keeping, 2016 is irrefutably the hottest year on record. The revelations come after September’s data showed that the month was the warmest month in history, according to NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS). They reported that September was 0.91 degrees celsius warmer than the mean September temperatures from 1951 to 1980. The warmer global temperatures have already caused long-lasting droughts in the United States, South Africa, India, and Australia.
It all started in 2015 with the El Niño climate cycle. Coupled with the global climate change phenomenon, air temperatures were altered and a drought ensued, which led to less rain and thus less water. It has caused one of the worst droughts South Africa has seen in 30 years. In India, 134 farmers have committed suicide in just two months due to a two-year drought that has led to crop loss. In South Africa, several provinces have had water shortages. The provincial governments have ordered water restrictions be put in place at the utilities and cautioned citizens to use water sparingly or face the consequences. The consequences being...complete water cut-offs.
Even with the El Niño’s natural regression, the realities of climate change have been apparent. The immediate issue is the lack of water. Engineers are hard at work to figure out how to bring technology to the drought-fight at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). At a third-party moderated discussion, Madelyn Glickfeld, a member of the UCLA Water Group and Institute of the Environment of Sustainability said: “The technologies that are most promising are smart technologies - technologies that use smart sensors to help people know how much water they’re using. This helps change behavior.” A recent poll by a Californian company named Xylem revealed that 76 percent of people believe that recycled water is the step forward for the region’s water infrastructure.
In response, Eric Hoek, a civil engineering professor at UCLA said: “I can take any quantity of water and turn into any other quality of water. The technology is there. It has been there for 20 years. The question is how much you’re willing to pay. Reusing water should be completely uncontroversial. The reality is it’s much safer to intelligently implement technology than to put water back out into the environment and pray that nature magically cleans it up.”
Hoek is talking about toilet to tap technology and reservoirs that capture rainfall runoff which, in turn, runs the water through a water purification process and eventually produces drinkable and reusable water. These are inventions that engineers have been successfully implementing in several countries for many years. However, Californians are unfamiliar with Direct Potable Reuse (DPR)/the toilet to tap wastewater reuse method. This system could lead to more water being accessible in the drought-stricken state.
However, drinking water aside, the other issue countries will have with further drought climate conditions is in the hydroelectric power plants. In Daniel L. Calzi’s book Dams, Drought and Energy-water Interdependencies, he details how droughts have the potential to affect “the operation of dams in ways that can be detrimental to hydropower production.” Less hydroelectric electricity being produced means higher electricity costs for utilities and customers. This is specifically bad for the United States.
The country’s hydroelectric facilities generated 51% of the renewable energy in the U.S. in 2013, and continue to play a large role to this day. Calzi points out that hydroelectric plants are the least expensive source of electricity and produce no fossil fuels. The only issue is that the facilities rely on precipitation to continue running, which feeds the local water sources. Engineers also have to consider humidity, wind patterns and reservoir dynamics, which in a drought, is nothing less than difficult. Annoyingly, if there is too much water - in the event of a flood, or a related event - hydroelectric plants also stop working.
In an attempt to remedy the water scarcity crisis that is becoming prevalent in the world, Sir James Dyson the industrial designer, is encouraging engineers to lend their expertise to saving water. Speaking of the situation in his own country, Dyson said: “Parts of the country are waterlogged, while in others it’s illegal to use a hosepipe.” He says that the United Kingdom still relies on “antique infrastructure” handed down to them from the Victorian era. He says it is time for the latest generation of engineers to redesign the water system and improve it.
“It is politicians who should be leading this charge. They must think big, think long-term and they must reinforce the value and importance of great engineering,” Dyson said. Engineers in the UK have ensured that leaking pipes are replaced, Dyson adds, however, he says new technologies could be introduced that improve these water infrastructure processes.
Engineers have a plethora of options when entering water industries. A Professional Certificate of Competency in Programmable Logic Controllers & SCADA Systems could see you tackling the digital side of controlling a water utility that relies on automated processes to keep it functioning. You could get your certificate in Structural Design for Non-Structural Engineers and see how water and wastewater infrastructure is built. You could also pursue a certificate in Onshore and Offshore Pipeline Systems - the water has to be transported somewhere. And much more.
Contact us at the Engineering Institute of Technology today to enquire about which course would be right for you: http://www.eit.edu.au/course-enquiry
References:
Calzi, Daniel L. Dams, Drought and Energy-water Interdependencies. Print.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Under the headline "Labor Shortage Persists In Some Fields," the Wall Street Journal (2/7, Light; subscription required) reports the number of people looking for jobs may number almost 14 million, but so far there are still four open computer engineering jobs at startup firm Gowalla Inc. of Austin. The company wants more programmers to add to a 27-member staff, but finding those people is difficult. CEO Josh Williams said, "Most people we want are employed somewhere already." The scenario is repeated nationally by companies that want technical talent, and some end up hiring people with fewer qualifications than the company needs, or reworking their overall strategy. Gowalla, for instance, solved its problem by outsourcing development of an Android application. The Journal says other fields where companies find it difficult to hire the right talent include engineering, accounting, some types of consulting and marketing, sales, and some types of construction-related jobs. Finding engineers for IT-related companies is especially difficult, the Journal says.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
German nuclear engineering firms are within their rights to claim damages and receive compensation for the country's plans to shut their nuclear facilities, a senior judge has ruled. The Constitutional Court found that government's impending interference with nuclear plants violated property rights. The country's government has set the date for complete nuclear decommissioning; 2022./
The German utilities and their engineers will be seeking compensation that will amount to billions of euros. E.ON, a nuclear utility, is suing for 8 billion euros. RWE is hoping for 6 billion and Vattenfall wants 4.7 billion.

The nuclear utilities initially lodged complaints that the decommissioning of plants was expropriation, but the courts were not convinced by that case. As a result, the utilities changed their case to one centered around the rights to private property.
The senior judge, Judge Ferdinand Kirchhoff, presiding over the case said: "It was permissible for lawmakers to take the accident in Fukushima as a prompt to speed up exiting nuclear energy to protect the health of people and the environment."
The decommissioning of nuclear plants in Germany has been a long, hard road for the utilities - they were ordered to power down their plants in 2000. Once Angela Merkel became chancellor of te country, she relaxed the country's plan to decommission the plants. However, Japan's tsunami and earthquake in March 2011 convinced the government to step up decommissioning progress. Moreover, the country has invested much into their renewable energy technologies and are now seemingly ready to part ways with nuclear energy.
The nuclear decommissioning process
 The nuclear meltdown that captured the attention of governments around the world and is a contributing factor to Germany's nuclear shutdown, is the renowned Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant meltdown. The Tokyo Electric Power Company (Tepco), the company who built the nuclear reactors is now in charge of decommissioning the plant.
The nuclear meltdown that captured the attention of governments around the world and is a contributing factor to Germany's nuclear shutdown, is the renowned Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant meltdown. The Tokyo Electric Power Company (Tepco), the company who built the nuclear reactors is now in charge of decommissioning the plant.
Three reactors affected by the earthquake of 2011 are to be decommissioned. The process will take 30 to 40 years. However, the engineers don't seem to know where the spent fuel of Reactor 1 is, causing widespread fear that they will not be able to complete a decommission in the allotted time.
Engineers from Tepco spoke to the Guardian, saying: "No one has ever done what we're doing but 30 to 40 years is a target that we can work towards. There are so many people involved that it would be wrong to alter that deadline on a whim. We've established a goal and need to show ingenuity to reach it, not take the easy way out."
The decommissioning process will reportedly cost $19 billion. The cleanup costs will amount to $180 billion. IEEE has named it one of the "biggest engineering challenges of our time." What makes the situation more difficult is the threat of further earthquakes ; which puts other nuclear reactors in Fukushima at risk as well.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Network Rail Causes Christmas Chaos in London
Have you submitted your annual leave form for the festive season yet? Some engineers in London aren't going to be that lucky this year. Five major London railway stations will be undergoing 42 engineering improvement projects (27 daytime and 15 nighttime) from the 19th of December, stretching through to the 2nd of January, 2017.
The number of passenger journeys that utilize the railway between 19 December and 2 January? 20 million.

It is estimated that the engineering maintenance works are the "biggest ever" Christmas engineering projects ever observed in the UK. The projects will force delays on passengers. According to the Mirror, a London to Cardiff trip, that usually takes 2 hours and 1 minute, will take "up to 3hr 17min" as a result of the engineering projects. Paddington Station is to go completely train-less from December 24th to 29th - surely disrupting some travelers plans.
The engineers will really only get a break on the 25th and 26th of December, but then it is back to work to ensure that the railways are fully functioning by the time New Years Eve celebrations begin.
Network Rail, the owner and infrastructure manager of a large portion of the railway in England, Scotland, and Wales, has decided that while the majority of workers are not going into their offices, the upgrades should take place. Network Rail estimates that the railways experience 50 percent less traffic during the festive season.
A travel expert, speaking to The Sun newspaper, said: "Network Rail has been over-ambitious and ramped up the quantity of works as commuters are off work -- but Christmas leisure travelers will take the hit instead."
However, Network Rail still maintain that the Christmas season is the best time to do it. They said: "Large-scale work is done around public holidays because the railway is relatively quiet and disruption affects fewer people. Improvements we are making allow trains to run, at higher speeds, and also improves the reliability of the rail network, reducing delays in the future."
The maintenance works are going to cost £150 million ($189 million) to complete. According to the Sunday Times, the improvements will bring new tracks, elongate platforms, add cabins to some trains and general maintenance as well.
Engineer Approved Lego-Tree
On a lighter note, a lego enthusiast named Ryan McNaught has completed New Zealand's biggest lego build. A 10-meter lego Christmas tree is now towering over Auckland's Aotea square. The build took six weeks. McNaught had to recruit some engineers to ensure it's stability.
"Because it's so big we actually have to get real engineers to sign it off, not us Lego engineers. It has to be wind-rated, safe," McNaught said to TVNZ.
Around half a million lego blocks were used. The tree weighs in at 3.5 tons.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Queen of England has already spent £600,000 ($748,932) of taxpayer money with trusted engineers and architectural designers that have compiled blueprints for what is being called a 'reservicing' of Buckingham Palace. The taxpayers have been informed that they will be expected to foot the bill of £369 million ($459 million) for a full update of the Palace. All the bells and whistles!
The main engineering company attached to the project is WSP Parsons Brinckerhoff. There are six

other organizations that will also lend their expertise to the reservicing. The refurbishment of the Palace would be the biggest update since World War II. There are aged boilers to repair, 20 miles of pipework and 100 miles of electrical cable that will need replacing.
Official pictures from the report showed the aged cabling and made a point that all of the electrical cabling needed to be redone. Furthermore, the heating of the Palace was installed 60 years ago.
The official report read:
A series of detailed technical assessments have examined the material state of the Palace, including the electrical cabling, power generation, hot and cold water pipework and data systems (fire alarms, telephones and IT). These established that elements of the Palace's essential services are significantly beyond their maxium useful life and require urgent replacements to avoid the risk of devastating failure.
The Palace employs 300 staff that utilize offices and reportedly hosts 90,000 people per year due to events and functions.
 The Monarchy seems adamant that if the infrastructure of the Palace is not updated, the "catastrophic" failure of infrastructural mechanisms could result in a fire or a flood. The report says that the drainage system consists of a mixture of "lead and cast iron pipework" that needs to be overhauled.
The Monarchy seems adamant that if the infrastructure of the Palace is not updated, the "catastrophic" failure of infrastructural mechanisms could result in a fire or a flood. The report says that the drainage system consists of a mixture of "lead and cast iron pipework" that needs to be overhauled.
The reservicing would ensure that the Palace would not have to be updated in the next fifty years. The reservicing will start in April 2017 and continue for a decade, reservicing the Palace wing-by-wing.
The report states that the reservicing presents a unique opportunity for the "a new generation of construction professionals" who will work on the historic building through "apprenticeships and graduate programmes."
It is also rumored that Buckingham Palace might be going solar. A mock-up of what the Palace might look like with solar panels on the roofs give hope that the electricity bill might - at least - be significantly less in the next ten to fifteen years.
For the official report: CLICK HERE
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A referendum on the subject of scrapping forty-five-year-old nuclear plants in Switzerland has resulted in a categorical NO. Put forward by the country's Green Party, the motion was denied by 54.2% of voters. Green Party president, Regula Rytz, said: "The high number of yes (to dismantle nuclear plants) votes confirmed that citizens wanted to opt out of nuclear power in the long run."
 The country's energy minister Doris Leuthard was also quoted saying that the vote showed that some citizens were optimistic that Switzerland would one day not have to rely on nuclear power but understand that it is probably still a necessary mechanism of creating energy for the country.
The country's energy minister Doris Leuthard was also quoted saying that the vote showed that some citizens were optimistic that Switzerland would one day not have to rely on nuclear power but understand that it is probably still a necessary mechanism of creating energy for the country.
"Voters do not want a hasty shutdown of nuclear power plants. A policy change is not feasible from one day to the next," Leuthard said.
The concern from the other 45.8% of voters - who voted for the dismantling of nuclear power plants - is that the nuclear reactors have been operating since the '70s, hence their safety and maintenance were brought into question. The country has five nuclear reactors that contribute 34.5% of the energy output.
Renewable energy strategies have been established and passed through parliament, but until then, the majority of voters are comfortable with keeping the nuclear plants operating.

Japan's Scare
The Swiss vote comes after an earthquake and subsequent tsunami scare in Fukushima, Japan. After the tsunami of March 11, 2011, the geographical positioning of Japan's nuclear reactors became an issue of contention. The Fukushima Daiichi plant released radioactive materials into the Pacific Ocean after the earthquake and tsunami, an event comparable to the Chernobyl fallout.
A costly decommissioning of the plant is ongoing. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has said that the decommissioning process would take 30 years and cost up to $19 billion.
The earthquake on the 21st of November, 2016, brought fresh threats to the other nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Diani plant. The water cooling systems of the third nuclear power plant had stopped working causing temperatures in the nuclear reactor to rise.
The plant's limit is 65 centigrade, and a few hours after the earthquake, it had risen to 28.7 centigrade. It was a dangerous situation.
Engineers eventually brought the reactor under control, but it was a scary reminder that nuclear energy is perhaps too unpredictable to keep secure amid a natural disaster.
The March 2011 disaster in Fukushima signaled a downturn in nuclear power plants being erected. Countries like Germany have completely moved away from nuclear power to avoid any future, potential incidents. Vietnam has also decided to cancel any nuclear power plans.
It seems that the gradual adoption of renewable energy technologies is slowly phasing out any future nuclear power plant deals that are being made around the world. Whether renewables are the more cost-effective approach compared to nuclear energy...time will tell.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Flash floods have been plaguing the planet in 2016. In June, flash floods forced the government of France to close the Louvre in Paris and 25,000 people were left without power. 500 miles away, Germany also experienced flash flooding that caused 5 deaths and left several people missing. Lest we forget the 2015/16 floods of Ireland and Great Britain. Storm weather also battered South Australia at the end of September, this year. Engineering industries were shut down due to the weather. Power stations went down and 80,000 people were without power in Adelaide. The storm was thought to be a "one-in-fifty-year" weather event.
 The fact that weather is delaying the work of engineering industries and leading to loss of life - in some countries - is not an understatement.
The fact that weather is delaying the work of engineering industries and leading to loss of life - in some countries - is not an understatement.
Now, South Africa has received a fresh bout of flash flooding due to stronger storms that are exacting cloudbursts over Johannesburg. The explanation behind why the sudden flooding events are happening relates to the weather cycle of El Niño's departure, and the onset of La Niña . Some are also pointing the finger at climate change to try and explain why the storms are so severe. South Africa has gone from unprecedented drought, and now is facing the same problem India is: replenishing water - but too much of it.
On Wednesday afternoon, severe storms caused flash floods in the South of Johannesburg. The South African Weather Service has said that extreme weather conditions will continue up until Friday. The N3 highway in Johannesburg saw flooding in both directions. Cars were swept away due to the high volume of water due to the rainwaters. A Twitter user @mandlamZA, wrote: "So clearly, our roads and highways were not built for the rain."
Flooding also cut off access to the country's main airport and forced airplanes to circle the airport before they could make a landing. As a result, flights were also delayed.
The City of Tshwane's Facebook account wrote: " Of late, four people died after a cloud burst at Midrand and OR Tambo, flooding the freeway at the Linksfield off-ramp. Massive water accumulated at low-lying areas of the freeway and many cars were caught up unexpectedly and covered with water up to their roofs."
 Municipal governments and civil engineers are now debating how to avoid deaths in flash flooding events. Low-lying areas are unfortunately in the crosshair of a storm and are more prone to flooding than built up areas at the top of hills. Citizens in shanty towns built along the Jukskei River were displaced due to the rising floodwaters there. The area was the worst hit, 200 families lost their homes.
Municipal governments and civil engineers are now debating how to avoid deaths in flash flooding events. Low-lying areas are unfortunately in the crosshair of a storm and are more prone to flooding than built up areas at the top of hills. Citizens in shanty towns built along the Jukskei River were displaced due to the rising floodwaters there. The area was the worst hit, 200 families lost their homes.
A disaster management center has started investigations into the drainage systems and general destruction of the floods.
Johannesburg Roads Agency director Sean Phillips said: "When you get very unusual rainfall like we had last night then it overloads the drainage system. It would be possible to design the drains to be able to cope with these extreme rains, which occur occasionally." The water exceeded the stormwater systems' capability.
The question that remains, globally, is, should governments be looking at storm drain redesigns in preparation for climate-change-level volumes of rainwater?
The Department of Civil Engineering at McMaster University in Canada has researched the topic in their study entitled Climate Change Impact on Design Storm and Performance of Urban Storm-Water Management System. They write:
A number of future climate projections indicate a likelihood of increased magnitude and frequency of hydrological extremes for many regions around the world. The urban storm-water management infrastructures are designed to mitigate the effect of extreme hydrological events. Changes in extreme rainfall events will have a significant implication on the design of strom-water management infrastructures.
The study they conducted found that even Canada's infrastructure would suffer under "future climate condition."
Over-capacity drainage systems can also lead to sewage making its way into the waterways. Including the aforementioned: transport systems and residential flood damage are the main areas of focus for drainage systems that are being pushed past their capacity with the increase in water volume that the world is experiencing.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Sinkholes. They swallow houses, they devour cars. They eat up road, and they're happening around the world. A section of a five-lane street in Japanese business district Fukuoka was swallowed on Wednesday in what is being called a sinkhole. Subways were delayed and 800 houses were left without power. The sinkhole happened uncomfortably close to other buildings, so officials evacuated the people in the surrounding area to minimize the chance of any injury due to exploding gas lines or any further sinkholes. There were no injuries reported.
The Mayor of Fukuoka said that the sinkhole occurred due to construction on a subway line extension nearby the collapsed road. Exposed, severed sewage pipes leaked water into the sinkhole due to the collapsing of the street.
The United States has also had its fair share of sinkholes. The worry with sinkholes happening on roads, especially in America, is that gas transmission lines and subways could be affected by collapsing sections of road - very much like Japan. Donald Trump has promised that under his presidency, roads would be repaired.
Construction works play a part in making surrounding areas' ground unstable. A 2005 book named Sinkholes and Subsidence: Karst and Cavernous Rocks in Engineering and Construction details how sinkholes induced by ground disturbance occur.
Vibrations from construction traffic could conceivably induce sinkholes in unstable soil cover, but their effects appear to be masked by the greater influence imposed by drainage modifications.
Vibration caused by cars driving over unstable roads are also a contributing mechanism that can cause the roads to collapse. This happens if the road is already weakened by something like other construction work or more pressing issues like burst pipelines.
Water erosion is usually also factored in when explaining why a sinkhole happened, however, vibration seems to be what the municipal government of Fukuoka is going with.
Construction crews are working around the clock to have the street repaired by next week. Workers will also presumably get back to work once the street is repaired. Fukuoka's Municipal Government is patching the road up with cement. Government officials say that 7,000 cubic meters of soil are required to repair the street.
The certain kind of sinkhole observed in Japan is called a cover-collapse subsidence hole. It suddenly appears and continues to collapse. Engineers that are experienced in sinkhole remediation are now tending to the sinkhole in Japan. The support beams of buildings were exposed during the collapse, and as a result, engineers now need to ensure the foundations of buildings are still reinforced and not affected by the sinkhole.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The U.S. Presidential Election has finally arrived after one of the longest campaign cycles in recent history. The winner of this presidential election will become the leader of the free world and have a monumental task ahead of them. There are only a few hours to go before the leader in the polls is announced, and as a result becomes the president. The stock market nervously waits in the wings to either congratulate or deflate depending on who wins. The reality is, some engineering industries, depending on who wins, could be seeing tough times ahead. The Economist magazine called a Trump presidency the third biggest “source of global risk”.
 Engineers and business leaders should not make the mistake of thinking that politics doesn’t influence the outcome of their jobs in the future. In the final rally Donald Trump gave on his campaign trail, he promised that today’s election day would be called BREXIT PLUS after he won the presidency. The engineering implication of calling it BREXIT PLUS means that engineering industries are about to be clouded in uncertainty due to the conflicting opinions of both Hillary Clinton and Donald Trump.
Engineers and business leaders should not make the mistake of thinking that politics doesn’t influence the outcome of their jobs in the future. In the final rally Donald Trump gave on his campaign trail, he promised that today’s election day would be called BREXIT PLUS after he won the presidency. The engineering implication of calling it BREXIT PLUS means that engineering industries are about to be clouded in uncertainty due to the conflicting opinions of both Hillary Clinton and Donald Trump.
A post-Brexit engineering study conducted with the help of 424 engineering respondents, revealed some illuminating facts. The respondents were from “energy, transport, defence, oil and gas, agriculture and marine” industries. 64% of the respondents said that the EU was instrumental to their businesses. 62% said they were employing EU citizens. And once Britain opted to exit the European Union those relationships were in trouble. Worries about foreign investment into engineering industries also became very real.
Thus, the same industries in America could experience a slip-and-slide of emotions especially in energy, oil and gas, and defence. In truth, many industries are sitting on the edge of their seat to see if things stay the same with a Hillary Clinton presidency or drastically change with a Donald Trump presidency. Some engineers celebrated Brexit, others didn’t. Therefore, a study of how engineering industries will react to a Clinton presidency versus a Trump presidency is needed.
IF DONALD TRUMP WINS THE PRESIDENCY
Based on Trump’s campaign rhetoric, industry could be expecting major change and - in his opinion - a return to form. The industries that would see a massive, instantaneous bump in the stock market would be:
Military Defence industry: Lockheed Martin manufacture military defence equipment. Trump has famously said he will amp-up the military expenditure once he gets into office to ensure that America has the strongest military in the world. Aeronautical engineers would greatly benefit under this plan.
u>Infrastructure: Construction industries will see money coming in as The Don would say, “big league.” Trump has criticized the lack of road maintenance and the third-world state of America’s airports. Caterpillar is expected to benefit from a Trump presidency. Trump has said he wants to bring industry and jobs back to America, and in turn, make America great again.
Manufacturing: Trump also deeply criticized companies like Ford who had migrated some of their operations to countries like Mexico, and called for manufacturing to be brought back to America. Trade and immigration are very big question marks in Donald Trump’s America. To what extent, we don’t know. Many a time, engineering professionals immigrate to other countries to use their very specific set of skills on international projects. Would they be welcomed in Trump’s America?
 Construction: Not to mention that wall that Trump supposedly wanted to build. He eventually said that Mexico would be paying for it - to which the Mexican president said a resounding “no”. The 50-foot, 2,000-mile wall would require construction if they go through with it. CNBC estimated back in March that the wall would potentially cost $25 billion to construct. A Mexican architecture firm named Estudio 3.14 also produced this render of what the wall might look like./b>
Construction: Not to mention that wall that Trump supposedly wanted to build. He eventually said that Mexico would be paying for it - to which the Mexican president said a resounding “no”. The 50-foot, 2,000-mile wall would require construction if they go through with it. CNBC estimated back in March that the wall would potentially cost $25 billion to construct. A Mexican architecture firm named Estudio 3.14 also produced this render of what the wall might look like./b>
Moreover, The energy production industry will experience a shake-up due to Trump’s position on global warming. What will receive the bump it has been lacking will be the oil industry. Trump has also said that the Keystone XL Pipeline, that Barack Obama vetoed, will go ahead.
The concept of global warming was created by and for the Chinese in order to make U.S. manufacturing non-competitive.
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) November 6, 2012
In the last presidential debate in September of this year, Trump said: “Hillary Clinton wants to put all miners out of business.” Trump also swears by clean coal. He said: “There is a thing called clean coal. Coal will last for 1,000 years in this country. Now we have natural gas and so many other things because of technology. We have unbelievable -- we have found over the last seven years, we have found tremendous wealth right under our feet.”
F HILLARY WINS THE PRESIDENCY
 Something that Hillary has, that Donald doesn’t, is a renewable energy plan. And this has an effect on what kind of engineers America will be employing. Clinton wants to cut U.S. oil dependency by one-third by 2027. She also wants the U.S. to generate 33 percent of its energy capacity from renewable sources by that date. $60 billion will be given to that initiative and will see engineers seeing the benefit of being involved in those industries. But what about the other energy engineering industries? Obama has been delaying the advancement of oil pipelines, most notably, the Keystone XL Pipeline.
Something that Hillary has, that Donald doesn’t, is a renewable energy plan. And this has an effect on what kind of engineers America will be employing. Clinton wants to cut U.S. oil dependency by one-third by 2027. She also wants the U.S. to generate 33 percent of its energy capacity from renewable sources by that date. $60 billion will be given to that initiative and will see engineers seeing the benefit of being involved in those industries. But what about the other energy engineering industries? Obama has been delaying the advancement of oil pipelines, most notably, the Keystone XL Pipeline.
In September 2015 Hillary Clinton said: “I don’t think we need to have a pipeline bringing very dirty oil, exploiting the tar sands in western Canada, across our border.” She said pipelines “distract [America] from the real challenges facing the the energy sector.”
Hillary also stated: “On my first day as President, I'll set two big goals. I want the U.S. to have half a billion solar panels by 2020. And I want us to generate enough renewable electricity to power every home in America in the next 10 years. With the right investments, we’ll create good-paying jobs and make America the world’s clean energy superpower.”
Furthermore, one of the industries Hillary would’ve single-handedly boosted during this election is the state-owned and private cybersecurity companies - some have already been established and are generating huge profits. Hillary famously said that Wikileaks had acquired the Democratic National Committee, her, and her campaign manager’s private emails from a Russian source. She said that the Russians were trying to interfere with the presidential election. Whether or not the emails were from the Russians, Clinton might have just handed a battalion of site reliability, network, and cybersecurity engineers new jobs due to her cybersecurity paranoia.
Ted Koppel, American journalist, who wrote the book Lights Out, focusing on cyber attacks on America’s electric grid, spoke to CNN, saying: “We live in an age where walls physically don't mean anything. Cyber attacks go right past walls. They can be enabled no matter where in the world you are.” Therefore, cybersecurity companies will be seeing an unprecedented level of investment.
Should engineers pursue politics?
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, has spoken about where politics and engineers intersect. He said:
You have to get involved because [in politics] because you as engineering professionals have something more than most of these people in these parliaments have and that is that you are considerably more objective in what you do. A lot of the parliaments are riddled with lawyers, accountants and people that perhaps don't have the necessary technical knowledge to make considered technical decisions. Obviously, engineers have got potential problems ; building nuclear power plants, contaminating water and things like that - that we need to avoid. But really, you do have a major contribution.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A pipeline explosion in the United States on Monday has forced the Governer of Alabama, Robert Bentley, to declare a state of emergency. The pipeline explosion killed one and injured six workers. The subsequent fire as a result of the explosion has caused damage to what is known as the Colonial Pipeline which delivers gasoline to millions of customers. The South and Eastern United States regions will face gas price hikes and some will face shortages due to the pipeline's damage. The shutdown will affect 13 states.
 The accident happened on October 31st, 2016, when a contractor struck a 36" below ground transmission gasoline pipeline. Repairs were being done on the pipeline after a previous pipeline rupture on September 9th, 2016. The previous rupture caused a big gas leak that was considered to be the pipelines biggest leak in 20 years.
The accident happened on October 31st, 2016, when a contractor struck a 36" below ground transmission gasoline pipeline. Repairs were being done on the pipeline after a previous pipeline rupture on September 9th, 2016. The previous rupture caused a big gas leak that was considered to be the pipelines biggest leak in 20 years.
"My thoughts and prayers are with the six injured workers and with the family of the fatally injured worker. An accident of this magnitude is tough for any community to deal with, and I want to personally thank the local first responders for their immediate assistance to this accident, as well as the first responders from surrounding counties," said Governer Bentley.
The Alabama Department of Environmental Management is now monitoring the air where the explosion occurred to ensure that the area is safe and not contaminated. It is the gasoline line that was ruptured, however, the other transmission lines are still operational, which deliver diesel, jet fuel, and other petroleum products. The Colonial Pipeline carries 2.5 million barrels of fuel a day - that fuel delivery is what has been delayed due to the explosion.
The State of Emergency will last until December 1st, 2016.
The pipeline explosion is not good news for the Energy Transfer Partners.The company is trying to emphasize the safety of oil pipelines to persuade the public that the Dakota Access Pipeline should be built. They have been assembling the pipeline that is to span four states wide. It will reportedly cost $3.8 billion and will transport 470,000 barrels of "light sweet crude oil" from North Dakota, all the way to Patoka, Illinois, twenty-four hours a day. The pipeline has been protested against for months. Business Insider confirms that since 1995, there have been 2,000 "significant" oil and gas pipeline accidents. They also reported that from 2013 to 2015, more than one hundred accidents happened every year. The Colonial Pipeline accidents have shown that human error very much an area of concern for the pipelines.
Here is footage of the Colonial Pipeline's damage and the subsequent fire that ensued:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The first worker to die of a "work-related" incident at one of Qatar's World Cup 2022 stadiums, has been mourned by the organizers of the tournament. The worker was reportedly hit by a water truck at the Al Wakrah stadium and has become the first person to die whilst physically working at a Qatari stadium. "It is with deep regret we announce a work-related fatality on one of our projects. A full investigation is underway to determine the factors which contributed to the death of one of our workers," The Supreme Committee for Delivery and Legacy said on their website. Three workers had previously died at World Cup construction sites in what organizers claimed were non-work-related circumstances.
 One of the non-work-related incidents involved a 52-year-old painter who died working on the main stadium, the Khalifa International Stadium. The organizers say he died of cardiac arrest in one of the site's dining halls a year ago.
One of the non-work-related incidents involved a 52-year-old painter who died working on the main stadium, the Khalifa International Stadium. The organizers say he died of cardiac arrest in one of the site's dining halls a year ago.
Qatar has been under constant scrutiny for the labor conditions the workers have had put up with since construction on the 2022 venues began. Ninety-four percent of the workforce involved in the construction of World Cup venues are of South Asian background ; Pakistanis, Bangladeshis. Indians and Nepalese people. There are 1.4 million migrant workers in the country. The country was criticized by the International Trade Union Confederation in 2013 who reported that 1,239 deaths had occurred from 2011 to 2013 in Qatar. They also said that 4,000 migrant workers would die before a ball is kicked off in 2022, irrespective of whether they work on World Cup venues or not. It is in their, and other groups like Amnesty International's opinion that a World Cup should not take place in a country where worker deaths happen at an unprecedented level.
 "FIFA has not done enough to address the situation from the very beginning. It should have known even before it awarded the World Cup to Qatar, that this is an environment where labor abuse is endemic. In its bidding process, it made no mention of human rights, let alone labor rights," said Mustafa Qadri, a researcher for Amnesty International.
"FIFA has not done enough to address the situation from the very beginning. It should have known even before it awarded the World Cup to Qatar, that this is an environment where labor abuse is endemic. In its bidding process, it made no mention of human rights, let alone labor rights," said Mustafa Qadri, a researcher for Amnesty International.
Qatar's World Cup will bring engineering jobs to the country in industries including transport - a new railway system is planned - new hotels and of course, the new stadiums. They are also planning to install state-of-the-art air conditioning in the stadiums.
However, Amnesty International say the workers' situation has not improved since it was exposed in 2013/14. One of the workers, speaking anonymously to the NGO said: "I am an electrician, and I agreed to electrician's work. But when I came to Qatar, they only gave me electrician work for the first two months. After that, they said I had to do iron fitting work."
Engineering Innovation
 Engineers at Qatar University have been utilizing rapid prototyping technology to 3D print models of the stadiums. They will use these models in weather simulation tests in their labs to test their resilience to sand storms that might flare up during the World Cup. Regardless of their hosting in winter, the stadiums will be used in summer as well, and that is when most sand storms occur.
Engineers at Qatar University have been utilizing rapid prototyping technology to 3D print models of the stadiums. They will use these models in weather simulation tests in their labs to test their resilience to sand storms that might flare up during the World Cup. Regardless of their hosting in winter, the stadiums will be used in summer as well, and that is when most sand storms occur.
They will test the model by putting it in a wind tunnel and letting the wind run over it, testing both for weather and inside-stadium temperature. Qatar University Professor Dr. Saud Abdul Aziz Abdu Ghani, talking to Doha News, said: "We can see the temperature per tier, add in variants as sweat produced and amount of spectators, and then run simulation and see the effect on the temperature inside the stadium. For the cooling, we want a minimal amount of air to go in, and we want the air inside to stay there. We can change the direction and stimulate different directions at this facility."
According to the engineers, the aerodynamic testing and modifications have led to good results. One of the stadiums, after aerodynamic model testing, revealed that it didn't need as much steel as the designers initially thought.
The engineers lauded aerodynamics testing and said it is the future of building design.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Follow our live blog below:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
An engineer from the automaker Volkswagen has spilled the beans. James Robert Liang (62) has pleaded guilty to the very first criminal charges in the '#Dieselgate' scandal. Liang reportedly agreed to a plea deal for charges handed down by U.S. prosecutors. The prosecutors said Liang admitted to being a part of a "nearly decade-long conspiracy to defraud US regulators and VW customers." He also pleaded guilty to the violation of the Clean Air Act.
 Where did it all start?
Where did it all start?
According to the Telegraph, Liang, an American himself, worked at VW's Wolfsburg branch from 1983 to May 2008. Then he moved back to America to a U.S. branch to work on "environmentally-friendly clean" diesel vehicles in 2006. Liang admitted that it all started in 2006 when the team of engineers was unable to get their diesel engines to emissions standards. As a result, they decided to develop "engine management software" that would underreport the vehicles' emissions.
"I knew that Volkswagen did not disclose the defeat device to U.S. regulators," Liang said. He is allegedly assisting the government in their investigation and will be instrumental in the prosecution of other engineers involved with the emissions scandal.
The investigations by the U.S. Justice Department uncovered that the Jetta and the Golf models between 2009 and 2015 were the cars that sprung the 2006 plan to underreport emissions, into action.
Earlier in June, it was confirmed that Volkswagen AG was looking at a hefty penalty for its emissions untruths to the tune of $14.7 billion. Liang's confession also happened in June but was only mentioned in media publications this month.
When the emissions-control module was discovered, Yotam Lurie, a business lecturer of business ethics at Ben-Gurion University in Israel, spoke to Spectrum, saying: "This is shocking. It's shocking that the software engineerings of Volkswagen overlooked and neglected their fiduciary responsibility as professionals. Professionals who have a semi-regulatory responsibility within the organization to ensure safety, in this case, environmental safety, even when this is less efficient or economical." (via Spectrum)
The Dean of the Engineering Institute of Technology Steve Mackay, says it best when talking about engineers and the ethics they should consider. Earlier this year in a series of engineering news updates, the Dean said: "Ethics for engineers, means engineers in the fulfillment of their professional duties shall uphold paramount the safety, health, and welfare of their fellow citizens. That should be the highest possible consideration. It's a very expensive process if you want to rip the system but ethics is something we as engineers and technical professionals have to do all the time."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Lithium-ion batteries are back in the spotlight this week. Samsung's brand new flagship smartphone, the Galaxy Note 7, is undergoing a global recall that is estimated to cost the company $1 billion. The President of Samsung's mobile business department Dongjin Koh told reporters that there was a "tiny problem in the manufacturing process" that caused the phones' batteries to catch fire. In a YouTube video posted by a man named Ariel Gonzalez, the damage the battery fire causes to the phone can be seen:
The video shows only one of the 35 known cases of ill-manufactured batteries in the Note 7 series. No injuries as a result of the Galaxy Note 7 battery fires have been reported.
However, according to ClassAction.com, three months before the Galaxy Note 7 recall, a Galaxy S7 Edge caught fire in the pocket of a construction worker in Ohio. The man in question has now filed a product liability lawsuit against Samsung for the third-degree burns he suffered due to the phone catching fire.
Samsung is now asking the media to be patient as they fully investigate the battery flaws. The official answer given to media and the public right now is the aforementioned "battery manufacturing flaw".

Nonetheless, media speculations have already pointed the finger at "thermal runaway". Previously, a rare condition for lithium-ion batteries, thermal runaway has been reported in several industries that utilize lithium batteries. What happens is, a battery gets overheated to the point where the heat reaches temperatures it can no longer contain. Once the battery gets hotter at a faster rate than it, itself, can produce and absorb heat, a fire or explosion is sometimes likely. Lithium-ion batteries are used in smartphones, laptops, pacemakers, watches, e-cigarettes, and cars. The most alarming case of thermal runaway was reported in September of 2013 when the lithium batteries inside a Boeing 747 caught fire. Qantas, Jetstar, and Virgin Australia (along with a cautionary word from the Federal Aviation Authority) have ordered Galaxy Note 7 owners to switch their phones off inside their aircraft. Not only are aircraft at risk, so are cars. A family's Jeep was destroyed after the phone exploded inside the vehicle, leading to a much larger fire. The family confirmed that the phone was charging in the center console of the Jeep when the  fire occurred.
fire occurred.
Donald Finegan, a chemical engineer at the University of College London explains what happens to phones that suffer from thermal runaway when charging. He said: "The battery can continue to charge and can become even more unstable and eventually just burst into flames itself, without any kind of external heating. The snowball effect happens so fast that, within a second, the entire cell goes from being intact to being completely destroyed."
The new Note 7's with the battery flaw being fixed will start shipping on September 19th. How will you know you're getting one with the new battery? Samsung says that they will be putting a sticker with a blue 'S' on the box, which will clearly identify the fixed range of smartphones. They will also launch an online service where customers can insert their IMEI numbers and check whether or not their phone is pre-recall or post-recall. The service will cross-check a database of IMEI numbers and inform a user whether or not they are using a phone that needs to be replaced due to the battery flaw. Samsung said they would start replacing the faulty phones by the 19th of September, 2016.
Samsung confirmed that for pre-recall Galaxy Note 7's they would be rolling out an update that prevented the phone from charging beyond 60% in hopes that they become less fire-prone.
Lithium-ion batteries are growing in importance in the world we live in today. It is paramount for engineers to figure out how to design them in safer ways. Watch this video below to see how this might be possible:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Follow our live blog on the situation:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
This news event is no longer live. Read our comprehensive recap of the events below:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A skyscraper under construction in Dubai caught fire on Tuesday afternoon, leading to evacuations of not only the structure but also the Beach Rotana Abu Dhabi hotel nearby. This is reportedly the fifth blaze the United Arab Emirates has seen in 18 months. If you recall, on New Year's Eve, the Address Hotel, a 63-storey five-star hotel, caught fire due to what engineers said was an "electrical short circuit". The blazes will no doubt be a topic of conversation between the civil defense engineers from the Civil Defence Fire Code Council, and the fire safety professionals who banded together to write the UAE Fire and Life Safety Code of Practice.
 According to Business Insider, experts say that "exterior cladding used for decoration or insulation" could have could be causing small fires to spread considerably in buildings in the UAE. The Director of Dubai Civil Defence Maj Gen Rashid Al Matroushi had rubbished these claims back in April. He said: "We are addressing bad construction practices, but civil defense officers cannot monitor every step of the process...There are some who may be cheating when it comes to the materials used in buildings."
According to Business Insider, experts say that "exterior cladding used for decoration or insulation" could have could be causing small fires to spread considerably in buildings in the UAE. The Director of Dubai Civil Defence Maj Gen Rashid Al Matroushi had rubbished these claims back in April. He said: "We are addressing bad construction practices, but civil defense officers cannot monitor every step of the process...There are some who may be cheating when it comes to the materials used in buildings."
The rumor is that flammable cladding materials made from plastic fillings are positioned in between aluminum panels and bad construction practices could be responsible for the spreading fires.
For safety sake, in June 2015, the Dubai Civil Defence connected 40,000 buildings to a system named the Dubai Life Safety Dashboard. The system checks if fire sprinkler systems are in working order and ensures that fire safety is where it needs to be. All of this checking up involves fire protection engineering.
Jane Lataille, a fire protection engineer who published her book Fire Protection Engineering in Building Design, says that fire protection engineers, from a structural standpoint, are in charge of the "strength, thickness and fire resistance rating of building construction materials."
Therefore, the fire protection engineers need to be questioned about the fires that are breaking out in business areas where new high-rise buildings are being constructed in Dubai.
Fire protection engineers concern themselves with the following elements when contributing to the construction of a building:
- Locations of buildings
- Exposures to buildings
- Sizes of buildings
- Size of fire areas
- Building layout
- Combustibility of building finishing materials
- Security issues
- Jane Lataille, Fire Protection Engineering in Building Design
The combustibility of building finishing materials is something that has been focused on since New Year's Eve in Dubai. A crackdown on combustible materials must occur if there is still contravention of the rules as stipulated by the Civil Defence.
The National Fire Protection Association in the United States, as a result of bad construction practices, has published multiple codes and standards guidelines. For the finishing materials - like the cladding that has been criticized in the UAE - there are codes and standards that inform the fire protection engineers what needs to be checked. According to Lataille, the engineers should do tests for "radiant flux of floor covering systems", tests for any burning characteristics of the actual building materials, the heat release statistics of any materials used in the construction process, the evaluation of the textile wall coverings and ceiling coverings.
After that, fire protection engineers have to worry about interior building layout which involves portable fire extinguishers, hoses, and indoor sprinkler systems. To see how crucial engineers are to the fire protection industry, check out this video from the Department of Fire Protection Engineering from the University of Maryland:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Science fiction is a genre completely defined by the theoretical applications of engineering and science in a fictional context, showing what the future of our world (or the worlds after ours) might look like. Fictional stories with fictional engineers have inspired the real-world engineers from all over the world, all wanting to emulate their favorite characters. Moreover, engineers sometimes even look to science fiction to study the effects of what a writer has warned the world of creating, or encouraged the world to create. For example, the Orwellian video surveillance, GPS tracking and more that Goerge Orwell warned of in his book 1984, was an eerily accurate prediction of how the world would progress up to present day. Isaac Asimov's books are still instrumental to this day. They help in hardwiring the three laws of robotics into the future of collaborative robots that will coexist with humanity.
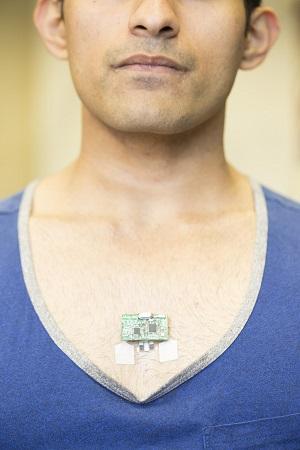 Some engineers talk of how watching Star Trek inspired them to further investigate how things work and developed their knack for being an engineer. MIT Media Lab Researchers Dan Novy and Sophia Brueckner, in 2013, hosted a class named Science Fiction to Science Fabrication to show how science fiction writers' theoretical principles have made their way into the real world. The class would show how augmented reality, virtual reality, ideas of utopia and dystopia, nanotechnology and even wearable technologies have been inspired by fictional texts. Similarly, The Center for Science and the Imagination at Arizona State University also started a project in 2014 named Project Hieroglyph. The project would see students in both engineering and science reading a science fiction anthology of stories named Hieroglyph. In their own words, Project Hieroglyph say the anthology is "set in the future, from some of today's leading writers, thinkers, and visionaries" to try and encourage a new wave of innovators who could improve our world.
Some engineers talk of how watching Star Trek inspired them to further investigate how things work and developed their knack for being an engineer. MIT Media Lab Researchers Dan Novy and Sophia Brueckner, in 2013, hosted a class named Science Fiction to Science Fabrication to show how science fiction writers' theoretical principles have made their way into the real world. The class would show how augmented reality, virtual reality, ideas of utopia and dystopia, nanotechnology and even wearable technologies have been inspired by fictional texts. Similarly, The Center for Science and the Imagination at Arizona State University also started a project in 2014 named Project Hieroglyph. The project would see students in both engineering and science reading a science fiction anthology of stories named Hieroglyph. In their own words, Project Hieroglyph say the anthology is "set in the future, from some of today's leading writers, thinkers, and visionaries" to try and encourage a new wave of innovators who could improve our world.
In May of this year,a group of engineers at the University of California San Diego announced that they had developed the world's first, flexible, wearable device that could monitor "both biochemical and electrical signals". The engineers called it a tricorder and were hoping to take it the Qualcomm Tricorder X competition that promises prize money of up to $10 million. A tricorder is a fictional hand-held device used in Star Trek that would scan a person's body and do a data analysis, eventually supplying medical data so that a patient could be diagnosed.
"Reading science fiction is like an ethics class for inventors, and engineers and designers should be trying to think like science fiction authors when they approach their own work," Brueckner said. Science fiction allows engineers to see what the possible impact an invention might have on the future of the world and could ensure stricter design principles when designing an item that could lead to societal change.
The world has seen a plethora of science fiction due to innovations that present the world with new obstacles and new opportunities. We went scouring the web for answers on who the best fictional engineer of all time was. What we found was that there are a whole bunch of engineers new and old in the world of fiction that could be inspiring the next generation of young people to further pursue STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) careers. These were the results:
 #1: Tony Stark
#1: Tony Stark
Some say Elon Musk is the living, breathing Tony Stark of our real world, however, no one can match up to the fictional owner of Stark Industries. Named the "quintessential capitalist" in the Marvel comics, the fictional engineer has been inspiring mechanical engineers for decades. The innovative suit is an impressive feat of mechanical engineering and has been used as an example of what future U.S. Military Tactical Assault Light Operator Suits could look like in the future of warfare. If you watch Marvel movies, you would see all sorts of influences from the writers behind Stark Industries that envision a future policed by Iron Man suits and flying cars. These flashy, capitalist ideas of engineering marvels have cemented Tony in the number one spot.
#2: Doc Brown
In science fiction, time travel is an idea that could not be perfected without engineers or scientists. In the Back to the Future trilogy, the world renowned Delorean Time Machine gets itself in and out of timelines by using the flux capacitor. Doc Brown got the idea when he slipped and bumped his head whilst trying to hang a clock up in his bathroom. So, engineers, next time you bang your head and have an idea, follow your gut and just invent it. Throughout the trilogy we see the zany engineer utilizing all sorts of futuristic technologies and warning about how it could all impact civilization.
#3: Mark Watney
Matt Damon plays Mark Watney in the film, based on a book named The Martian. It sees aerospace engineer, Watney, left on Mars after a manned mission goes wrong. Watney then has to utilize his engineering skills to both grow food on Mars and figure out how to make contact with NASA to try and get himself rescued. SpaceX and NASA are in talks about a possible Mars mission in 2018, and potentially manned missions soon after that. It would be a good idea to pick up a copy of the blu-ray before they decide to send anyone up there.
#4: The pig who built the brick house
We all know the story. The three little pigs who were tormented by the big bad wolf who blew their houses down. Except, one engineering-savvy pig who built a brick house the wolf couldn't blow down. Now that's the sort of civil engineering ingenuity we can all be proud of.
#5: MacGyver
A new series of MacGyver has been announced for 2016, however, we're talking about old school MacGyver that lit up the screens from the year 1985. He is considered to be an engineer due to his complex understanding of how things work and can repurpose everyday items into tools that help him escape from danger. His resourcefulness sees him turning items into different end products. Additionally, MacGyver always carries a Swiss Army Knife and duct tape with him.
#6: Wayne Szalinski
Ah, yes. The dad-engineer from Honey, I Shrunk the Kids . If he didn't inspire a host of fumbling engineer-wannabes we don't know who did. An inventor by nature, Wayne had a solar-powered car, predicting a future of solar-powered vehicles which are becoming a big reality. He just seemed to be an engineer that suffered a bad case of Murphy's Law. But his forward-thinking inventions cements him as one of the internet's favorite fictional engineers.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Royal Academy of Engineering, the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, the Institution of Civil Engineers and a list of 33 other engineering organisations have banded together after the results of the Brexit Referendum. The super-group of engineering industries want to collectively pressure the British government into making a good deal with the EU, for the engineering sector. As Britain leaves the European Union, all of the warnings that were issued before June 23rd need to be double checked to measure what kind of damage engineering sectors will experience as a result of the exit.
 Nigel Fine, Chief Executive of the Institution of Engineering and Technology said: "This is a period of huge change and uncertainty so it’s imperative that we work together to ensure the best outcomes for UK engineering, which is so important to a vibrant and successful economy. We will do everything we can to ensure the interests of engineers and UK engineering are represented as strongly as possible."
Nigel Fine, Chief Executive of the Institution of Engineering and Technology said: "This is a period of huge change and uncertainty so it’s imperative that we work together to ensure the best outcomes for UK engineering, which is so important to a vibrant and successful economy. We will do everything we can to ensure the interests of engineers and UK engineering are represented as strongly as possible."
Negotiations need to be held to ensure that engineering industries are protected under the 'severance package' Britain might get once they fully leave the EU. According to Engineering & Technology, the group represents 450,000 engineers and will continue to collaborate to ensure that British engineering remains an influential force in the world.
Together, the industries represented make up 27% of the United Kingdom's GDP. The group has noticed that the uncertainty caused by the 'leave' vote has already swayed investors opinions. Notably, Siemens immediately suspended UK wind power plans once the results of the referendum were unveiled.
Head of External Communications at Siemens, Anne Keogh, said: "Siemens has always made it clear that this was a decision for the British people and their view must be respected. As a global business with significant, long-term investments in the UK and high local value creation, Siemens is not so much exposed to negative effects that we might see. Nevertheless, the government must now move swiftly to unify and agree the nature of the UK’s relationship with the EU and other trading partners, creating clear roadmaps to encourage future investment."
Engineers are saying they have never been in a situation that requires so much "strategic collaboration" between engineering industries. Unfortunately, uncertainty was unavoidable with a 'leave' vote. The super-group will now measure how powerful the vote is, in terms of how damaging it might be to the engineering sector.
“We are rising to this challenge and pooling our resources to provide government with the best advice and access to our networks to inform its planning and leadership role. We are building a new, proactive framework for making engineering advice available to government on these critical matters for now and for the duration of the change process," said Phillip Greenish, Chief Executive of the Royal Academy of Engineering.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
It's hard to ignore the effects the Brexit is having on engineering. The first physical marks the Brexit referendum has made on engineering has been shown by Markit, a company that covers global market trends. As the referendum's results were unveiled at the end of June, the construction Purchasing Managers' Index fell to 46.0. To indicate how significant this is, one needs to consider that Britain's index sat at 51.2 in May. The numbers are now the lowest they have been since 2009, which were as low as they were due to the recession.
 "This is an absolutely dire survey that fuels serious concern over the construction sector...and can only intensify concern as to just how much the construction sector will be hampered by the Brexit vote," said chief UK economist at IHS Global Insight, Howard Archer.
"This is an absolutely dire survey that fuels serious concern over the construction sector...and can only intensify concern as to just how much the construction sector will be hampered by the Brexit vote," said chief UK economist at IHS Global Insight, Howard Archer.
Tim Moore, economist at Markit, speaking to Bloomberg, said: "Construction firms are at the sharp end of domestic economic uncertainty and jolts to investor sentiment, so trading conditions were always going to be challenging in the run-up to the EU referendum, However, the extent and speed of the downturn in the face of political and economic uncertainty is a clear warning flag for the wider post-Brexit economic outlook.”
Commercial building and home building was the hardest hit, however, civil engineering seemed to be stable. Markit said it was the first instance since April 2013 that the index had fallen below a 50 level. Companies want to stay above 50, due to 50 being the level that divides "contraction from expansion."
We've also recently reported that Britain's energy policy might also be damaged by the Brexit, however, no solid facts will be available until a new Prime Minister is appointed.
Markit points out that construction makes up 6 percent of Britain's economy. However, manufacturing in the country is said to be undamaged by the Brexit vote, as far as the preliminary investigations can see.
"The vast majority of June's survey responses were received ahead of the EU referendum, so the worry is that the ensuing political turmoil will hit construction spending decisions for some time to come," Moore concluded.
So, more woes for Britain as leadership falls away and uncertainty spreads. The question is, is engineering completely doomed in the country? We'll keep our eye on the situation and provide the cold, hard evidence as it is presented to the people of Britain in one of the most controversial political moves of all time.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Is it back to the drawing board for the engineers of Tesla? The company's self-driving technology has claimed its first victim. Tesla driver Joshua Brown, 40, has died in an accident caused by the self-driving technology inside the Model S. The car's self-driving technology was reportedly unable to recognise a white tractor trailer against "the brightly lit sky".
The technology that drives Model S cars is Tesla's own 'Autopilot' software.
"What we know is that the vehicle was on a divided highway with Autopilot engaged when a  tractor trailer drove across the highway perpendicular to the Model S," Tesla said in a statement. "It is important to note that Tesla disables Autopilot by default and requires explicit acknowledgement that the system is new technology and still in a public beta phase before it can be enabled."
tractor trailer drove across the highway perpendicular to the Model S," Tesla said in a statement. "It is important to note that Tesla disables Autopilot by default and requires explicit acknowledgement that the system is new technology and still in a public beta phase before it can be enabled."
Therefore, Brown knowingly put his life in danger once he had agreed to be part of the beta testing for the car. He also uploaded a video on YouTube showing the capabilities of the Autopilot feature. The video is unrelated to the crash. In the video, you can see the Autopilot feature physically dodging an oncoming truck that is merging into its lane:
"The customer who died in this crash had a loving family and we are beyond saddened by their loss. he was a friend to Tesla and the broader EV community, a person who spent his life focused on innovation the promise of technology and who believed strongly in Tesla's mission," Tesla added.
The crash comes at a time when automakers are reaching out to governments to show them that self-driving technology is the future. The crash will most likely be a reference point for critics who think self-driving technology is not ready for consumers. Now, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration are investigating the Tesla crash. The group has said that in their initial reports, the car failed to apply the break due to the failure of the software to identify the white side of the tractor trailer.
The New York Times spoke to Karl Brauer, an analyst at Kelley Blue Book auto research. He said: "This is a bit of a wake-up call. People who were maybe too aggressive in taking the position that we're almost there, this technology is going to be in the market very soon, maybe need to reassess that."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Getting started with PLC programming could make you instantly more valuable as an engineer. Without PLCs, we would not be able to run our industrial factories that contribute to every economy all over the world. We need PLCs to use real-time software to monitor what happens inside an industrial system and control what the results will be. The running joke is that a person could come into contact with a PLC without even realizing it due to PLC uses in elevators, amusement parks, etc.
The PLC does a program scan that uses the entire system to scan for any incoming inputs and then does what it has been programmed to do. The scan takes one to two milliseconds. The scan happens as follow:
- The state of inputs (sensors, switches, pushed buttons) are scanned ; what the PLC needs to continue its scan
- The program is executed the pre-programmed logic of what the engineer wants the PLC to do with the input values
- Housekeeping of any devices connected or related to the PLC currently scanning
- 'Scan' the user's ladder logic left to right, sequencing through the 'rungs'
- Compute the results and write updates to the outputs
- Do diagnostics and if all is well, repeat the scan
Sometimes things can go wrong. Once a PLC malfunctions, the reasons might not be glaringly obvious. The PLC might need troubleshooting. Whether you are an engineer-in-training or a veteran, learning how to troubleshoot a PLC could save an industrial complex some money.
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay, has spoken about troubleshooting PLCs in the fortieth episode of his online series named the Engineering News Network. He says there are two areas that experience two types of faults in PLCs; internal and external. He says that eighty percent of the faults are usually the external components being faulty.
Internal
The internal issues within the PLC could relate to the decision-making CPU. The CPU is the main decision-making module within the PLC so it is a good idea to keep that as safe as possible. The communication ports are also important to keep safe consider that they can be connected to other PLCs and so they can both share data. Mackay says the earthing and grounding of the chassis that houses the PLC's elements could not have been done properly. He says: "That has to be done firmly and effectively. I've had many problems with that occasionally. Obviously, the power supplies to your PLC and the racks need to be continuously operative." The internal workings of the PLC could also be experiencing electromagnetic interference problems. "Those [electromagnetic interference problems] are intermittent, very difficult to trace but can be the cause for a lot of angst. Corrupted programs need to be looked for," Mackay added.
The batteries also need to be monitored to ensure that they are working all of the time so the PLC can function.
External:
"Check power supplies, the power, the fuses - you've got voltage continuously to your inputs," Mackay warned. Checking the wiring is also a good idea, noticing any corrosion could lead to thwarting a problem before it gets worse. He points out that there could be problems with a leakage current: "You think the input is off when its actually on. There is enough leakage current coming in that makes it appear off when its actually off."
This would be done by checking the digital outputs which would tell an engineer whether or not there are irregularities in the PLC's operations. This is done by using a meter to ensure that the proper voltage is coming out of a PLC.
Outside noise could also be a cause of a PLC malfunctioning. Ensuring that external sources are not producing noise is sometimes inevitable and so a filtering process then needs to be followed, by installing a noise filter.
Due to eighty percent of PLC faults being external, the PLCs are equipped with diagnostic LED indicators that will show whether or not a module is performing as normal or malfunctioning. Tracing the source of a fault is, therefore, easy to locate.
Finding the faults in PLC controllers are paramount to the continual operation of industrial automation to ensure that manufacturing plants work around the clock and work efficiently. Learning how to program is all good and well, however, learning how to troubleshoot is as important so that you can keep an industrial factory working optimally.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The liquefied natural gas market will see demand double by 2030. The latest numbers have grabbed the attention of Chevron and other oil companies who hope to capitalize on LNG sales, due to decreased investment into fossil fuel energy technologies. Millions of dollars will be invested into LNG imports and exports in the upcoming years due to the fact that governments are encouraging cleaner energy. China's LNG demand is also skyrocketing at an annual rate of 15% over the next six years. They will be importing record amounts of LNG as natural gas power becomes more important across Asia. The demand is signaling a rise in prices for LNG that will continue until August.
 The growing demand for imports in Asia means that Australia is in the prime position for exporting liquefied natural gas to the region. Chevron's Gorgon LNG export plant in Western Australia was primed and ready to meet the demands from Asia, but then an unplanned shutdown in April caused several issues. Chevron now confirms that the plant is back in operation.
The growing demand for imports in Asia means that Australia is in the prime position for exporting liquefied natural gas to the region. Chevron's Gorgon LNG export plant in Western Australia was primed and ready to meet the demands from Asia, but then an unplanned shutdown in April caused several issues. Chevron now confirms that the plant is back in operation.
"We confirm start-up activities are underway on Gorgon train one with a plan to safely resume production in the coming weeks," a spokesman for Chevron said. The plant cost Chevron US$54 billion to set up.
The Gorgon plant is part and parcel of Australia's efforts in LNG production, making them one of the main exporters. The Sydney Morning Herald estimates that Australia has pumped $200 billion into LNG project investment. The United States has lagged behind in recent history but are dedicating themselves to becoming a big player in exports. With the renewed operations at the Gorgon plant, Australia could be surpassing Qatar as the biggest exporter of LNG. According to government data, Australia will be the biggest exporter by 2019.
Alexandra Heath from the Reserve Bank of Australia said:
The decline in (LNG) prices is unlikely to lead to a significant reduction in production from existing producers because the high fixed costs of building the infrastructure have been paid and marginal production costs are relatively low. Our ability to benefit from rising demand for cleaner fuels will depend on our willingness to invest and innovate. It is important that Australian companies remain at the forefront of developing expertise in these fields, not just for the environmental benefits that they will bring, but to be able to export these technologies to other countries."
The International Energy Agency also recently affirmed the fact that LNG investment will be growing by leaps and bounds. The investment will increase by 45% between 2016 and 2021.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Australia, The United States, and Britain. Who is winning the renewable energy race? Who is doing more to secure green energy in their country? The answer is Germany. They have installed and are achieving 38301 MWp (Mega Watt peak) with photovoltaic devices. They have strategies in place to ensure that their country could run fully renewable energy by 2030. However, how close are the other superpowers and forward thinking countries? Those aforementioned countries that are considered to be big players in the renewable energy game. Let's take a look.
 Australia's Labor Government has established a Strategic Industries Taskforce to further the renewable energy conversation in the country. The taskforce wants to set up a Strategic Industries Reserve Fund that would see AUD $300 million to encourage renewable energy in "emissions intensive industries". This would include modernizing companies that are still operating with a big carbon footprint. The money will also be funneled into research in STEM fields to further investigate ways of making Australia's energy reach its renewable energy goals.
Australia's Labor Government has established a Strategic Industries Taskforce to further the renewable energy conversation in the country. The taskforce wants to set up a Strategic Industries Reserve Fund that would see AUD $300 million to encourage renewable energy in "emissions intensive industries". This would include modernizing companies that are still operating with a big carbon footprint. The money will also be funneled into research in STEM fields to further investigate ways of making Australia's energy reach its renewable energy goals.
Bill Shorten, the Opposition Leader for the Labor Party, spoke to media recently, saying: "Renewable energy is not just a fringe industry anymore. It is a key strategy in delivering jobs in Australia delivering investment into Australian industry. That is why we are prioritising our goal of 50 percent of our energy mix by 2030 will be derived from renewable energy sources such as these remarkable solar farms [referring to the Royalla Solar Farms]."
The United States are set to commit to a new clean power goal at a summit being held in Ottawa this week. Countries set to co-sign the bill are Canada and Mexico as well. They're calling it...and wait for it, it's worth it...The Three Amigos Summit. The summit will see the three countries agreeing to power their country through renewable means by up to 50% by the year 2025. A senior advisor in Barack Obama's camp said that the goals are aggressive but they are certain the three countries will be able to do it, making it a continent-wide agreement. According to The Guardian, a third of America's power is already being produced from renewable energy sources. Interestingly, Canada already produces 81% of its energy through renewable means.
And now for the inevitable news. Britain has been told that the exit from the European Union will amount to less renewable energy technology making its way into the country. The offshore wind industry is rumored to be impacted by the Brexit as well. After the Brexit results were unveiled, Siemens halted wind power investment in the UK due to uncertainty in the market. Dong Energy is also one of the bigger investors in UK offshore wind. Their spokesperson told the Guardian: "We will await clarity over the implications of the vote to leave the European Union. However, we don't believe that UK energy policy is dependent on EU membership." Therefore, the UK should say a collective, "Whew!" What is apparent, however, is that time will tell what the Brexit's impact on British energy policies is. Hopefully, for the engineers who work in the industry's sake, everything will be fine. It depends on the change in leadership and what those leaders have in mind for renewable energy in the UK, a country who was tipped to be the dark horse in the renewable energy game before the Brexit.
Source: Renew Economy / The Guardian
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A cyber-takedown of the Ukranian electricity grid in December of 2015 has sent the cybersecurity industry spiralling. Since then, governments across the globe have been equipping themselves with cybersecurity firms that will try to ensure a takedown of a similar nature doesn't occur. What is apparent is that governments need some pretty efficient firewalls to ensure that criminals can't take down their country's power grids with complex lines of code. Industrial control systems being interceptable by outside forces poses a big risk for the future of ensuring the safety of grids. It's all about the smart-grid now, but is it smart enough to ensure that hackers don't take them down?
The United States' Office of Electricity Delivery & Energy Reliability said: "Addressing cybersecurity is critical to enhancing the security and reliability of the nation's electric grid. Ensuring a resilient electric grid is particularly important since it is arguably the most complex and critical infrastructure that other sectors depend upon to deliver essential services."
 So what have the US government done to secure that a virtual takedown doesn't happen? They put the U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team (ICS-CERT) to work and learned from the loopholes that allowed hackers to take down the Ukranian power grid.
So what have the US government done to secure that a virtual takedown doesn't happen? They put the U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team (ICS-CERT) to work and learned from the loopholes that allowed hackers to take down the Ukranian power grid.
Robert Lee, a former cyber warfare operations office for the U.S. Air Force spoke to Spectrum, saying: "Everything about this attack was repeatable in the United States. While their security wasn't awesome, it definitely wasn't below the industry standards."
America has a Critical Infrastructure Protection standard that protects the country's important SCADA systems. But professionals are saying more powerful firewalls are needed to make sure the SCADA systems never get touched. Experts warn that the more "smart meters, electric car chargers, rooftop solar installation, and other intelligent devices" open the grid up for attack.
DNP3 protocols allowing communications across substations and field devices are the entry points that need to be continually monitored for potential hacking. Using open source extensions like DNP3 SCADA, the utility can set up alarms. Alarms enable utilities to monitor intrusion on a network that is in the process of being hacked. However, experts say the willingness of utilites to embrace DNP3-compatible extensions that monitor intrusion have only been adopted by four or five utilities in the US. Experts also warn that not enough utilities are taking cybersecurity seriously.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Heartbreak, dismay, disappointment. Just some of the words that academics are using to express themselves with after the British public decided that the United Kingdom would not remain in the Europe Union. Universities are now saying they anticipate considerable changes in the future of studies in engineering and science.
When the referendum's results were announced the Institution of Engineering and Technology immediately demanded discussions be held to measure what kind of damage a Brexit will have on the engineering industries. The group says the vote comes at an inconvenient time due to the shortage of engineers the country has. They say the vote will impair the economy
 According to a poll, the publication The Independent ran, 56 percent of students believed that leaving the EU would lead to "detrimental effects" on career prospects in the country. What academics are worried about is the loss of the European Union research funding. £687 million ($907 million) is made available for research and a lot of that is used for engineering and science research and innovation.
According to a poll, the publication The Independent ran, 56 percent of students believed that leaving the EU would lead to "detrimental effects" on career prospects in the country. What academics are worried about is the loss of the European Union research funding. £687 million ($907 million) is made available for research and a lot of that is used for engineering and science research and innovation.
President of Universities UK, Julia Goodfellow said: "'Leaving the EU will create significant challenges for universities. Although this is not an outcome that we wished or campaigned for, we respect the decision of the UK electorate. We should remember that leaving the EU will not happen overnight – there will be a gradual exit process with significant opportunities to seek assurances and influence future policy.
However, Patrick Flaherty, Chief Executive of AECOM UK said that due to the fact that no nation has ever left the EU before, the long-term impact couldn't be measured as of yet.
However, students are anxious about what the Brexit means for the high-ranking British universities. Five percent of students in the UK are from EU territories, and the exit could have implications for them, depending on what politicians decide about immigrating students. Universities UK wants to ensure that EU student exchange stays in place.
"Our first priority will be to convince the UK Government to take steps to ensure that staff and students from EU countries can continue to work and study at British universities in the long term, and to promote the UK as a welcoming destination for the brightest and best minds. They make a powerful contribution to university research and teaching and have a positive impact on the British economy and society. We will also prioritise securing opportunities for our researchers and students to access vital pan-European programmes and build new global networks," Goodfellow concluded, in her statement after the Brexit results were published.
Source: Universities UK
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The results are in. The British public has decided that they want to leave the European Union. The vote to leave the EU won by 51.9%, compared to the 48.1% who voted to 'remain'. The result will now ensure that the opinions of those who warned that engineering and science industries were in trouble if a 'leave' vote went through, will be given another read through.
In Support of 'REMAIN'
Roland Berger says that UK exports rake in GBP390 billion annually and that engineering industries are in charge of 44% of those exports. Their data tells them that a 'leave' vote would damage foreign investment into the country which could hurt their export numbers. The group says that foreign direct investment has produced up to 84,000 jobs in 2015 alone and that the exit of the EU will ensure that the UK doesn't produce these kinds of numbers again.
 Roland Berger said: "Leaving the EU would on balance be expected to have a damaging effect on both international trade terms and FDI attractiveness, particularly in the near term. Politicians, academics, and economists can merrily debate the long term, and the consensus is that the long term will be damaged also, sadly the near term is the one we are living in. The Engineering sector requires continuous investment decisions if it is to retain its international position, and so will shrink throughout this near term; indeed we are already seeing these effects.”
Roland Berger said: "Leaving the EU would on balance be expected to have a damaging effect on both international trade terms and FDI attractiveness, particularly in the near term. Politicians, academics, and economists can merrily debate the long term, and the consensus is that the long term will be damaged also, sadly the near term is the one we are living in. The Engineering sector requires continuous investment decisions if it is to retain its international position, and so will shrink throughout this near term; indeed we are already seeing these effects.”
We also recently reported that Rolls-Royce was against a Brexit. The company - who are very respected in the automotive engineering industry - said that investment decisions would be put on hold if the vote went through.
In support of 'LEAVE'
Sir James Dyson was one of the engineering experts that showed his support for a 'leave' vote and is probably quite pleased with today's historic results. This year, Dyson opened the Dyson Center for Engineering Design at Cambridge University. The center cost $11.6 million to build and will ensure that students have A-grade facilities to design and engineer new products in.
 Dyson thinks leaving the EU would lead to "more wealth and more jobs" despite what the 'remain' camp says. He said: "When the Remain campaign tells us no one will trade with us if we leave the EU, sorry, it's absolute cobblers." He spoke of the trade imbalances with the EU that are already bad but further pokes at the EU's free movement of people beliefs. He says that Britain isn't getting the kind of engineering professionals they need.
Dyson thinks leaving the EU would lead to "more wealth and more jobs" despite what the 'remain' camp says. He said: "When the Remain campaign tells us no one will trade with us if we leave the EU, sorry, it's absolute cobblers." He spoke of the trade imbalances with the EU that are already bad but further pokes at the EU's free movement of people beliefs. He says that Britain isn't getting the kind of engineering professionals they need.
"We're not allowed to employ them unless they're from the EU. At the moment, if we want to hire a foreign engineer, it takes four and a half months to go through the Home Office procedure. It's crazy," Dyson told the Telegraph. "It's just that on this issue I think they're fundamentally wrong. I don't just mean from the business point of view, I mean from the point of view of sovereignty and our whole ability to govern ourselves. We will create more wealth and more jobs by being outside the EU than we will within it and we will be in control of our destiny. And control, I think, is the most important thing in life and business."
Dealing with Brexit
After the Brexit result was unveiled, it was the automotive engineering industry that was quickest to reply.
Aston Martin is not defeatist about the referendum. They believe their exports may be boosted by the move. Chief Executive Andy Palmer said:
"We acknowledge the decision and the rule of democracy. Aston Martin will now orientate its business to deliver our mid-term plan in the context of the exit and the market volatility that may exist during the period of transition. As the UK could now be subeject to new trade tarriff barriers, we also ancitipate the need for additional productivity and efficiency in the medium term."
Ford also broached the subject, saying:
We will continue working toward this goal with key stakeholders in the UK and across the other Member States and EU institutions to ensure they understand our concerns which mirror those of the majority of the UK and European auto industry.
While Ford will take whatever action is needed to ensure that our European business remains competitive and keeps to the path toward sustainable profitability, we have made no changes to our current investment plans and will not do so unless there is clear evidence that action is not needed.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial control systems need to be protected in a world where automation opens avenues for criminals to exploit them. Air gapped SCADA systems will become more and more difficult to stick to in the era where the Internet of Things is striving to connect and automate industrial control systems. There is just no escaping the fact that networks will have to be connected to a cloud-based solution that could enable cyber criminals.
Last year, only 24 percent of engineers who took part in a survey by SANS Information Security believed that there were moderate to severe attacks on industrial control systems. This year, 67 percent of the engineers agree that the situation is becoming dire.
 Derek Harp, the director of industrial control systems global programs at Bethesda said: "It's a trend driven by a problem that's been getting worse. There are more incidents being reported, and more awareness at the senior levels of the companies about what their exposures are."
Derek Harp, the director of industrial control systems global programs at Bethesda said: "It's a trend driven by a problem that's been getting worse. There are more incidents being reported, and more awareness at the senior levels of the companies about what their exposures are."
Bengt Gregory-Brown, a SANS Information Security analyst said: "Control systems are increasingly integrated with IT networks and assets, offering more breach opportunities and attack surfaces in the ICS environment. Unfortunately, we are not seeing a commensurate improvement in the efforts or outcomes of ICS and SCADA security."
Now, industrial security professionals are saying that there is no information sharing across the industry concerning the safeguarding of industrial control systems. Respondents to a study pertaining to information-sharing partnerships have revealed that
"Knowledge is a big problem here. There are a lot of undetected problems. It's widely held that most systems have had some sort of probing, but it's really hard to know if someone was there," Harp said.
These sorts of probings are now the interest of private cybersecurity firms that will attempt to prevent attacks by cyber-criminals who are trying to brute force access to control industrial control systems.
Harp says that their study data indicates that there is a lot of misunderstanding in the industry in terms of ignorance of underlying software being targeted by cybercriminals. He said: "We find the lack of concern with this ubiquitous communication mechanism connecting IT and ICS assets troubling, as it is often targeted by bad actors. Attackers use it to pivot from the business network into the ICS."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial robot sales have skyrocketed in the last two years. In 2015, 248,00 robots were sold globally. That number was 12 percent up from the previous year and made it a record year for industrial robotic purchases. By 2018, 2.3 million industrial robots will be employed in the world. These figures are according to The International Federation of Robotics in a study named 2016 World Robotic Statistics.
Based on geographical positioning, the IFR conducted a study on which continents and countries spent the most money on industrial robotics in 2015. The results were as follows:
- Europe in 2015: 50,000 units ; 10% up from the previous year
- America in 2015: 37,000 units ; 15% up from the previous year
- Mexico in 2015: 5,500 units ; Sales more than doubled in one year
- Asia in 2015: 156,000 units ; 16% from the previous year
China's industrial robotics sales grew by 17% compared to the previous year and are actively trying to secure the sales of industrial robotics companies. Recently, Chinese companies tried to buy German-run Kuka Robotics to further cement China as the leader in industrial robotics.
The industries that reported the most sales in industrial robotics were:
- The automotive industry: 95,000 units purchased in 2015
- Metal industry: 63% more purchases than 2014
- Plastics and rubber industry: 40% more robots purchased in 2015
- Electronics industry: 16% rise in industrial robot purchasing
The President of the International Federation of Robotics said: "The wave of digital transformation and automation will continue to drive the robotics boom forward until 2018. Revolutionary developments in IT connected with all aspects of the Internet of Things and new networked services are changing the producing industries fundamentally. Machines, logistics, and production plants are merging into integrated cyber-physical systems. The aim is to use smart factories to work more flexibly, more cost-efficiently and more productively."
Why is there a big jump in the sale of industrial robots? The Head of Robotics for ABB, Per Vegard Nerseth: "People today don't want to do dull, dirty, dangerous and delicate jobs anymore, so many companies see when the older generation of factory workers retire they really struggle to get hold of people who wants to take up on those jobs."
The elimination of repetitive tasks at industrial level was recently highlighted when Foxconn retrenched 65,000 human workers and replaced them with industrial robots. Companies want humans to work on higher-value elements in their jobs and minimize the amount of work that could easily be done by a robot. Therefore, the industrial robotics sales numbers for 2016 could be astronomical.
