News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
What's the difference between a Bachelor of Arts degree and a pizza? A pizza can feed an entire family.
Yes, we've all heard the joke and been subjected to the scorn of students who believe their degrees are more superior when compared to humanities degrees. It is no secret; universities are filled with some students who want to degrade certain degrees because they believe they are doing the degree that will guarantee them a job in their respective industry.
McGraw-Hill Education is an educational content publisher, considered as one of the big three educational content providers in the world. They have conducted a study titled the 2016 Workforce Readiness Survey that investigated which industry's graduates exuded the most confidence for postgraduate employment prospects. The study saw McGraw-Hill surveying 1,360 American college students between March 2016 and April 206. They interviewed both undergraduates and postgraduates.
 Group president of U.S. education for McGraw-Hill Education said: "Every college graduate deserves to enter the workforce with the confidence that their degree was worth the investment."
Group president of U.S. education for McGraw-Hill Education said: "Every college graduate deserves to enter the workforce with the confidence that their degree was worth the investment."
Their study revealed that 73 percent of students who study science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) degrees believe they are the most employable. The more worrying statistic, however, is that 40 percent of "college seniors" think their "college experience" is instrumental in landing them a job. It's 61 percent of liberal arts students that think their degrees are not worth much once they graduate from university.
When students were surveyed about how they think technology factors into their studies, 85 percent of students said using technology in a lecture and using it as a study tool would further equip them to be attractive to employers. It seems students are hungry for practical work in classes, and less theory.
Furthermore, when graduated alumni were quizzed about the use of technology, 96 percent of them conceded that practically working with tangible technology would definitely lead to better employment options in the current climate of employable graduates. The scary bit is, McGraw-Hill Education says that the number of students actively using "workplace-related" technology is sitting at 26 percent.
Now for the nitty gritty. 62 percent of students said that if they had the chance to choose different major without the heavy tuition fees, they would have chosen different majors.
So, whilst STEM graduates are confident that they are entering the workplace, we're not certain that these graduates have the technical know-how for the industries they're going into. However, engineering students - based on the study - are definitely still the most confident that they have a definite part to play as an employed member of society.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
As renewable technologies make their way into our lives, we wonder how we will integrate the newly available technologies with our older technology that we still use to power our homes, our electronics and much more. Ir's hard to imagine calling some sort of firm and asking them to strip your house of its electricity and replace everything with solar cells tomorrow. So what we are left with is buying home energy storage units and saving ourselves some money by using less energy from the old grid in peak times.
Enter, the passive solar building. A building designed with solar energy in mind. A guest blogger for Sturdy Structural defines the passive solar building as a building designed with energy saving elements. We're talking the entire building. From the roof to the walls, to the floors. Solar passive buildings take the climate into consideration, using energy-saving applications to collect any and all energy that the sun is giving to the units.
To see the engineering design principles behind passive solar buildings, check this video out. This uses a house as an example, however, more and more business complexes are building with passive solar technologies in mind:
 Cornell University has also gotten wind of further development in passive solar buildings. The university has seen designs that could make their next dormitories the most energy-efficient dorms in the world. The dorms will be a $115 million project and stand at 26-stories high. The passive solar design will ensure that the building uses 70 to 90 percent less energy than buildings of equal size. The engineers behind the building say it will be the largest passive-house building in the world once it is completed. The building will have 550 solar panels on the roof that will power the building. The dorms will be air-tight and will prevent any outside air of making its way in requiring more energy to be used. Special vents will be used to funnel and filter fresh into air into the dorms.
Cornell University has also gotten wind of further development in passive solar buildings. The university has seen designs that could make their next dormitories the most energy-efficient dorms in the world. The dorms will be a $115 million project and stand at 26-stories high. The passive solar design will ensure that the building uses 70 to 90 percent less energy than buildings of equal size. The engineers behind the building say it will be the largest passive-house building in the world once it is completed. The building will have 550 solar panels on the roof that will power the building. The dorms will be air-tight and will prevent any outside air of making its way in requiring more energy to be used. Special vents will be used to funnel and filter fresh into air into the dorms.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The time for getting your qualifications in engineering for oil and gas facilities has never been better. Kenya is ready to construct a 538-mile crude oil pipeline that will provide oil for a new port being built on the Indian Ocean coastline. This was confirmed by a government official on Thursday.
Pipeline engineers are now in a unique position because they can now apply to be considered to design the front-end engineering design of the pipeline.
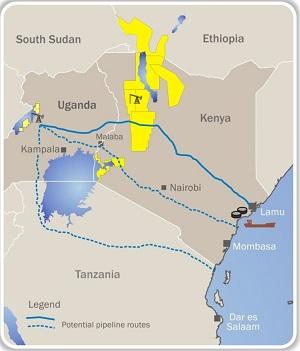 Ministry of Energy and Petroleum Principal Secretary Andrew Kamau, speaking to Bloomberg said: "Once we have the pipeline design, the engineering, procurement and construction contract would be awarded in first quarter 2018. It would take us that long as we need environmental impact assessment study conducted to international standards for the project to be able to attract international funding."
Ministry of Energy and Petroleum Principal Secretary Andrew Kamau, speaking to Bloomberg said: "Once we have the pipeline design, the engineering, procurement and construction contract would be awarded in first quarter 2018. It would take us that long as we need environmental impact assessment study conducted to international standards for the project to be able to attract international funding."
The east of Africa is seeing unprecedented successes in oil and gas. This week, a huge helium reserve was discovered in ancient rocks in Tanzania. Kenya is in the eight spot for the list of African countries with the biggest economy. They could jump up a few spots due to this refinery being its first refinery for the country. It will be delivering its first oil in June 2017. Africa Oil has said the South Lokichar basin will produce approximately 1.63 billion barrels of oil. The pipeline is estimated to cost $2.1 billion to build, which is a modest number based on other countries in Africa that have built bigger pipelines. Kenya seems to be playing catch up.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
If you're an engineering student currently studying towards your dream job, you've probably heard the question asked. When you make it into the industry, what is the dream company you'd want to work for? There's nothing wrong with setting your sights on some of the biggest engineering firms in the world because you never know when you might just get your big break. However, with thousands of fellow graduates getting their degrees and dreaming the same dreams, the industry is a tough one to compete in. Now, we have an idea of the most attractive engineering employers thanks to research group Universum. They have released their report titled The World's Most Attractive Employers 2016.
 The study was conducted on 267,084 engineering, business and IT students. The countries included in the report are: Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Russia, the UK and the USA. The Executive Director of CNN Money, Lex Haris, spoke about the legitimacy of the report, saying: "This is a critical time for the global economy and today's grads are the future leaders that will determine its fate. We wanted to hear directly from them. And Universum's survey gives us direct access to thousands of students in a dozen countries.
The study was conducted on 267,084 engineering, business and IT students. The countries included in the report are: Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Russia, the UK and the USA. The Executive Director of CNN Money, Lex Haris, spoke about the legitimacy of the report, saying: "This is a critical time for the global economy and today's grads are the future leaders that will determine its fate. We wanted to hear directly from them. And Universum's survey gives us direct access to thousands of students in a dozen countries.
So, we are looking at the millennials who are making their way into the respective engineering industries after graduating. Who do they want to work for? Here are the top 10 most attractive companies in engineering and information technology graduates' minds:
| Employer | 2015 | 2016 |
| 1 | 1 | |
| Microsoft | 2 | 2 |
| Apple | 3 | 3 |
| BMW Group | 4 | 4 |
| IBM | 6 | 5 |
| General Electric (GE) | 5 | 6 |
| Intel | 7 | 7 |
| Siemens | 9 | 8 |
| Samsung | 11 | 9 |
| Sony | 8 | 10 |
Analysts point out the interesting fact that energy companies are not attractive places for engineering students, as prospective places of employment. It's all about the tech companies in 2016, it seems. Analysts also say the results show that the millennials are aspiring to work for companies that seemingly have well-balanced work and lifestyle image. Interestingly, Google, Microsoft, Apple and BMW Group have retained their positions since last year, and IBM went up one position.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Rutgers University is New Jersey's own state university in the United States. The university's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering have shown off their new squishy robot. Yes, you read that right. To be more specific, the robot is considered to be a pneumatically driven elastomeric structure robot. The researchers have used the recent bendable robot technology to create a new robot that could have a host of applications in future industries where bendable, 'squishy' robots might be needed.

Bendable elements on robots are not a new innovation. They have been used in deep-sea coral expeditions for the purpose of handling coral with care, due to conventional robotic arms being too forceful. However, now the Rutgers researchers want to grow the innovation of soft robotics. The uses could range from sending the robots into rocky mountains or even driving the robots on different planets. The bendable, flexible material could be invaluable due to its ability to get through terrain that conventional robotics would not be able to do. See the video below to see how the robot navigates rocky terrain.
"If you build a robot or vehicle with hard components, you have to have many sophisticated joins so the whole body can handle complex or rocky terrain. For us, the whole design is very simple, but it works very well because the whole body is soft and can negotiate complex terrain," said Xiangyu Gong, an alumnus of Rutgers University in the mechanical engineering department.
The researchers used silicone rubber to build a wheel and axle assembly and used motors that are engineered to be devoid of metal. On top of that, the researchers had to assemble the vehicle to ensure its safety should it survive some sort of impact.
The team used 3D printers to print the rotors they used. As a result, the researchers were able to create 'squishy' pneumatic internal and external rotors. The external rotors were able to be used as wheels that the researchers used to design a four-wheeled rover robot.
"With no metal components and moisture-sensitive electronics on the vehicle itself, the vehicle is equipped with the actuators. [The rotors] function not only in a dry environment but also underwater as an amphibious vehicle," the researchers said. The researchers also showed that the robot could be dropped from eight times its height and survive the fall.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
You've got your honours in chemical engineering, you're a junior engineer-in-training, you have less than 4 years of experience at a firm and suddenly you get fired. What do you do? Do you try and get your masters in chemical engineering? Do you try and find a job unrelated to engineering? What can be done? This was a question recently posed to anonymous engineers on a social media site and the reflection of the engineers currently working in the industry could inspire you to take control of your engineering prospects whether you're currently looking for a job or not.
 This year has not been kind to chemical engineers. We've seen chemical engineers with BTech degrees begging for jobs on street corners in South Africa, and now isolated incidents of firings of junior engineers in Canada. Employment in these fields is obviously few and far between in 2016. Nonetheless, employment issues are not limited to a certain type of engineering around the world, there are more industries that are struggling to accommodate engineers and the salaries that they demand. It's enough to stress out an educated, employable engineer.
This year has not been kind to chemical engineers. We've seen chemical engineers with BTech degrees begging for jobs on street corners in South Africa, and now isolated incidents of firings of junior engineers in Canada. Employment in these fields is obviously few and far between in 2016. Nonetheless, employment issues are not limited to a certain type of engineering around the world, there are more industries that are struggling to accommodate engineers and the salaries that they demand. It's enough to stress out an educated, employable engineer.
However, fellow engineers have offered their two cents on what to do to keep pushing for the engineering jobs, to ensure that you snag that job:
- Update your resume
- Update your LinkedIn Profile
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology (EIT), Steve Mackay, talks about constructing an engineering résumé in the fifteenth episode of the Engineering News Network. Here is a summary with some quotes from the Dean that might strengthen your curriculum vitae:
1. Focus on the job: "Most people think they can use a generic résumé because they are applying for lots of jobs but that is a sure fire path to destruction."
2. Make it simple: "Use simple English, lay it out simply, you don't have to address it to the village idiot but by the same token make it simple and easy and reasonable."
3. Grammar and spelling must be 100%: "Try and look at the English and the spelling to make sure it reads well."
4. Avoid excessive information: "The twenty page CV is long since gone. Employers don't have time to read."
5. Lots of white space and include an executive summary: Mackay says the executive summary should be included because it would state why you think you're the right pick for the job. "Try and be specific, give real employers names...who actually exist...plus your time with them and the job you had and the reason why you left," he said." He further says that you should try and avoid the 'job hopping' approach where your CV shows that you've only spent a few months at a place of employment because that doesn't look good at all.
6. Search for jobs you really want: "It's pointless going for a higher paying job if you hate it. Try and focus on the jobs you are looking for, make sure it's aligned with you."
7. Business strengths: Mackay says it should include 'business wins' from previous employment. Stating what kind of successes you achieved.
8. Experience: "No matter how many qualifications you've got, if you don't have the experience that matches up with the qualifications, you've got a pretty tough job selling yourself. Experience plus qualifications...great match."
- Send your CV everywhere: You never know where you might get a response from
- Find other employment in the interim: This is specifically for engineers who are between jobs or struggling to find the dream engineering job of their dreams. Sometimes, getting a job unrelated to your industry could give you more skills that will assist you once you get into your dream job
- Be prepared to relocate: Engineering experts say that limiting yourself to your city or town is a bad idea, especially if the industry is slowing down in a particular area.
The skills shortages in the STEM industries continue to plague the industry. However, engineers are being influenced to broaden their skill sets in entrepreneurship and other studies so that they are instantly more attractive to businesses who might be interested in hiring them. Keeping a job in the industry means continually learning and applied newly learned skills. It's never too late to learn some new tricks, according to the engineering aforementioned engineering experts.
How do you remain employable in the engineering industry? Let us know in our comments section.
Source: Reddit / The Engineering News Network
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
In March 2015 the Department of Trade and Industry in South Africa committed to funding a program that would see $67.6 million making its way into the industrial sector to create more black industrialists and engineers. The program was set up to further diversify the working force behind industrialists and engineers in the country.
Pricewaterhouse Coopers summarized the basic operations of the program. They wrote: "The concept of black industrialists refers to black people who are directly involved in the origination, creation, high-level ownership (>50%), management, control and operation of industrial enterprises that derive value from manufacturing goods and services on a large scale, thereby acting to unlock the productive potential of our country’s capital assets for massive local employment. Government is essentially looking for black industrialists who not only make long-term commitments to business but are also medium-to-long-term investors."
The sectors that will influence the employing of engineers in the country are as follows:
- Agro-processing
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Clean technology
- Energy
- Mining
- Automotive components
 "We believe there is room for participation of many black entrepreneurs in the manufacturing sector as industrialists," said President of South Africa, Jacob Zuma. "They will be able to benefit from amongst others the incentives provided for in the industrial policy action plan and the host of manufacturing incentives that government provides. We believe the black industrialist policy framework is the right formula to transform the industrial landscape."
"We believe there is room for participation of many black entrepreneurs in the manufacturing sector as industrialists," said President of South Africa, Jacob Zuma. "They will be able to benefit from amongst others the incentives provided for in the industrial policy action plan and the host of manufacturing incentives that government provides. We believe the black industrialist policy framework is the right formula to transform the industrial landscape."
The program is geared towards encouraging black entrepreneurs to broaden their skill sets and find a future in engineering industries. It could also influence black engineers to pursue their dreams and get their competency in industries that are now seeing more job creation due to the move.
The Trade and Industry Deputy Minister, Mzwandile Masina, said that the program would ensure that more black leadership roles would be opened up in industries where black people are normally laborers and factory workers.
The diversification of employees in the STEM industry is an issue that South Africa takes seriously due to its unbalanced past.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
The liquefied natural gas market will see demand double by 2030. The latest numbers have grabbed the attention of Chevron and other oil companies who hope to capitalize on LNG sales, due to decreased investment into fossil fuel energy technologies. Millions of dollars will be invested into LNG imports and exports in the upcoming years due to the fact that governments are encouraging cleaner energy. China's LNG demand is also skyrocketing at an annual rate of 15% over the next six years. They will be importing record amounts of LNG as natural gas power becomes more important across Asia. The demand is signaling a rise in prices for LNG that will continue until August.
 The growing demand for imports in Asia means that Australia is in the prime position for exporting liquefied natural gas to the region. Chevron's Gorgon LNG export plant in Western Australia was primed and ready to meet the demands from Asia, but then an unplanned shutdown in April caused several issues. Chevron now confirms that the plant is back in operation.
The growing demand for imports in Asia means that Australia is in the prime position for exporting liquefied natural gas to the region. Chevron's Gorgon LNG export plant in Western Australia was primed and ready to meet the demands from Asia, but then an unplanned shutdown in April caused several issues. Chevron now confirms that the plant is back in operation.
"We confirm start-up activities are underway on Gorgon train one with a plan to safely resume production in the coming weeks," a spokesman for Chevron said. The plant cost Chevron US$54 billion to set up.
The Gorgon plant is part and parcel of Australia's efforts in LNG production, making them one of the main exporters. The Sydney Morning Herald estimates that Australia has pumped $200 billion into LNG project investment. The United States has lagged behind in recent history but are dedicating themselves to becoming a big player in exports. With the renewed operations at the Gorgon plant, Australia could be surpassing Qatar as the biggest exporter of LNG. According to government data, Australia will be the biggest exporter by 2019.
Alexandra Heath from the Reserve Bank of Australia said:
The decline in (LNG) prices is unlikely to lead to a significant reduction in production from existing producers because the high fixed costs of building the infrastructure have been paid and marginal production costs are relatively low. Our ability to benefit from rising demand for cleaner fuels will depend on our willingness to invest and innovate. It is important that Australian companies remain at the forefront of developing expertise in these fields, not just for the environmental benefits that they will bring, but to be able to export these technologies to other countries."
The International Energy Agency also recently affirmed the fact that LNG investment will be growing by leaps and bounds. The investment will increase by 45% between 2016 and 2021.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
A survey conducted by the Boston Consulting Group has revealed that Germany has shown more interest than the United States in industrial automation technologies. After receiving the opinions of 300 German and US manufacturing executives, the study showed that German executives were more ready for digital solutions in factories. However, only 17 percent of American and German manufacturers have adopted industrial automation. Business Insider confirms that 40 percent of German companies plan to update their factories with current automation technologies however only 25% of US factories feel the same way.
 The competition continues. 8% of U.S. manufacturers have autonomous robots and collaborative robots whereas Germans almost double that demand by having 14% of factories equipped with them. The US will want 20% more of those robots working in their factories in the next two years whereas Germans will want 39% more, of what they already have.
The competition continues. 8% of U.S. manufacturers have autonomous robots and collaborative robots whereas Germans almost double that demand by having 14% of factories equipped with them. The US will want 20% more of those robots working in their factories in the next two years whereas Germans will want 39% more, of what they already have.
The report also stated that worldwide spending on IoT connected factory automation technology reached $29 billion by the end of 2015 and will top $70 billion in 2020.
Germany's unique position on Industrie 4.0 has related to 47% of the companies surveyed saying that they have developed IoT strategies for the future of their companies. American companies say only 29% of them have strategies prepared.
"German companies' strong ambitions for Industry 4.0 reflect their need to overcome the challenges of significant factor costs that arise from high wages and a less flexible labor market. These factor costs encourage companies to strive for greater productivity and, thus, promote faster adoption of new technologies. The fast pace of adoption in Germany is also fueled by companies' advanced industrial-manufacturing capabilities. Companies can apply these capabilities to accelerate the introduction of new digital technologies, thereby reducing costs, increasing flexibility, and accelerating the speed of manufacturing," the researchers wrote.

"The early adopters have set a fast pace for implementation and are building capabilities that will enable them to increase their lead. To maintain their competitiveness, all companies will need to accelerate their efforts along the Industry 4.0 journey," the report concluded.
Source: Yibada
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The world needs helium. We use it for many things, and then usually waste it by sucking it out of a balloon and putting on a cartoonish voice. Recent reports have indicated that the world is running low on helium due to the lack of new reserves. Thankfully, researchers in Tanzania have discovered a new reserve. Good news for balloon animals but also good news for MRI scanners and nuclear power plants. However, nuclear power plants need a special kind of helium, but the good news continues because the researchers in Tanzania say the new reserve is filled to the brim with "world-class" helium. The researchers have been working with a Norwegian company specializing in helium named Helium One. The researchers are from the University of Oxford and Durham University.
 "This researcher shows that volcanic activity provides the intense heat necessary to release the gas from ancient, helium-bearing rocks. Within the Tanzanian East African Rift Valley, volcanoes have released helium from ancient deep rocks and have trapped this helium in shallower gas fields," said the University of Oxford in a statement.
"This researcher shows that volcanic activity provides the intense heat necessary to release the gas from ancient, helium-bearing rocks. Within the Tanzanian East African Rift Valley, volcanoes have released helium from ancient deep rocks and have trapped this helium in shallower gas fields," said the University of Oxford in a statement.
The researchers use similar drilling techniques used in oil and gas discovery. Chris Ballentine, chief of geochemistry at Oxford who worked on the team that discovered the new helium, spoke to the Washington Post. He said: "We look for source rock, we look for a mechanism to release the gas from the source, and we look to understand how gases migrate and looking for trapping structures."
We also use helium in semiconductor manufacturing. Rodney Morgan, the vice president of procurement at the Semiconductor Industry Association said: "Although the semiconductor industry consumes only a small amount of the overall quantity of helium used today, it remains a critical, irreplaceable input into our manufacturing process."
Helium is also used to clean NASA's space shuttle engines. So, we imagine Elon Musk is probably doing the same. This means, we need a lot of helium in the world, without even considering what uses the most helium, which is, of course, helium balloons.
So, good thing we've found more, then. Diveena Danabalan of Durhan University's Department of Earth Sciences spoke to CNN, saying: "We are now working to identify the 'goldilocks-zone' between the ancient crust and the modern volcanoes where the balance between helium release and volcanic dilution is 'just right."
The researchers say that the new discovery could see more than a million MRI scanners being filled. Professors at Oxford say the discovery is a "game-changer" and will lead to more discoveries through the same methods soon, ensuring that society never runs out of helium. The researchers say the discovery comes at the right time, due to a helium price escalation of 500% in the last 15 years.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Emissions testing company Emissions Analytics have written a report indicating that Diesel cars produce more emissions during winter. The group says that once the outside temperature reached below 18 degrees centigrade (65,4 Fahrenheit) cars began to release more emissions. The company reportedly tested 213 different models from 31 different auto engineering companies. The group found that cars built in the 2009-2011 bracket have produced the most emissions.
The tweaking of the engine in colder conditions has been proven to underreport the number of emissions the cars produce. Chief Executive of Emissions Analytics, Nick Molden, said: "If we were talking about higher emissions below zero, that would be more understandable and there are  reasons why the engine needs to be protected. But what we've got is this odd situation where the temperature threshold has been set far too high, and that is a surprise." The group found that the Euro 5 vehicles (manufactured between 2009-2011) produce 4.6 times the legal parameters for Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) when the outside temperature dropped.
reasons why the engine needs to be protected. But what we've got is this odd situation where the temperature threshold has been set far too high, and that is a surprise." The group found that the Euro 5 vehicles (manufactured between 2009-2011) produce 4.6 times the legal parameters for Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) when the outside temperature dropped.
The group did, however, say that the Euro 6 cars manufactured from September 2015 onwards reported better numbers, only reaching 2.9 times above the legal NOx limits.
Engineers say without the pollution controls partly switching off under colder temperatures, engines would undergo amounts of damage. The carmakers say it is a necessary method to ensuring that vehicles don't break down.
These revelations come at a time of an ongoing emissions scandal that has rocked the automotive engineering industry. Volkswagen has confirmed that they will use $15.3 billion to buy back vehicles from consumers. The carmaker admitted to developing software that underreported the amount of emissions their cars did.
VW will also be focusing on cleaner, more efficient technologies. According to Reuters, VW will be paying $2 billion over 10 years to a Californian company who specialize in electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
However, what are the automakers doing to shake off the pointing fingers, forcing their engineers to admit their years of underreporting? According to BBC:
- Vauxhall says that it is using diesel cleaning systems to prevent emissions
- Suzuki says it will be altering 3,200 cars' software to report more accurate emissions performance
- Renault has committed to buying back cars sold from September 2015 to July 2016. They will also change software to report accurate emissions
- Mercedes will tweak 26,000 A class and B class models in the UK to lower emission levels.
The Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders spoke to the BBC, saying: The temporary reduction or switching off of some emissions control systems under certain temperatures is allowed by law and necessary to avoid damage to vehicles’ engines.Without it, there could be a significant cost to the consumer for major repair work. In its recent report, government recognised the need for such technology and was satisfied with how vehicle manufacturers were using it. Manufacturers are investing billions of pounds in developing ever-more-advanced technology, and this along with new Real Driving Emissions regulation from next year will see significant lowering of emissions across a full range of driving conditions and temperatures."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
Chinese engineers have unveiled the world's longest and highest glass-bottom bridge in the Zhangjiajie Grand Canyon. The bridge serves as a skywalk from one side of the canyon to the other. And it's very strong. So strong that they decided to hold an event to show off its strength that included a journalist taking a sledgehammer to the glass walkway. To add to the anxiety of standing on a glass bridge, the engineers allowed a car to be driven on the glass surface.
The glass bridge is suspended 300 metres (984 feet) in the air and 430 metres (1,411 feet) long and 20 feet wide, suspended in Zhangjiajie's National Park. Chief engineer of the project, Ma Liang, said: "We use a  method of gluing together every panel to tighten the area between them. The thickness of every glass panel is 1.5 centimetres." They then took the Volvo XC90 SUV to the bridge with 11 passengers inside of it and drove it across the bridge, amounting to two tons. Some of the glass panels did shatter under the sledgehammering and the car driving over them but the panels are easily replaced. The chief design engineer on the project said that the bridge can withstand up to 100 MPH winds.
method of gluing together every panel to tighten the area between them. The thickness of every glass panel is 1.5 centimetres." They then took the Volvo XC90 SUV to the bridge with 11 passengers inside of it and drove it across the bridge, amounting to two tons. Some of the glass panels did shatter under the sledgehammering and the car driving over them but the panels are easily replaced. The chief design engineer on the project said that the bridge can withstand up to 100 MPH winds.
The bridge can take the weight of 800 people and will be opening in July. It was supposed to be opened in May, however, weather conditions slowed the engineers down. The man behind the design of the bridge was Israeli designer, Haim Dotan. The bridge cost approximately $37.4 million to construct. Dotan said he wanted to build a bridge that was second in beauty to the nature that the area is known for. The film Avatar was filmed in the canyon.
to be opened in May, however, weather conditions slowed the engineers down. The man behind the design of the bridge was Israeli designer, Haim Dotan. The bridge cost approximately $37.4 million to construct. Dotan said he wanted to build a bridge that was second in beauty to the nature that the area is known for. The film Avatar was filmed in the canyon.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
What is a dark warehouse? It's not a warehouse with its lights off if that's what you're wondering. No, the dark warehouse, or otherwise known as the "lights-out facility", is a factory that runs completely through automated means without any human intervention. Warehouses are opting in for self-driving forklifts, robots equipped with vision cameras, automatic storage and retrieval systems and more. Adidas recently announced a lights-out facility in Germany that would see robots in charge of manufacturing shoes.
Other factories that currently use fully automated systems include cold storage and freezer warehouses where food is frozen and stored. And soon, electronics companies will be using dark warehouses in the manufacturing of electronic devices. The truth is, humans don't need to do those jobs anymore. A hand-tailored cell phone doesn't make anyone jump out of their seats with pride and joy. But a hand tailored Rolls-Royce is a different thing.
 However, lights out facilities are becoming more and more sought after in the industrial world. "A lights-out facility is more possible in less-variable parts of logistics, where people are moving a large portion of the same types of objects," said Matt Engle, an employee for Cognex Corp, a company that specializes in vision systems for factory automation.
However, lights out facilities are becoming more and more sought after in the industrial world. "A lights-out facility is more possible in less-variable parts of logistics, where people are moving a large portion of the same types of objects," said Matt Engle, an employee for Cognex Corp, a company that specializes in vision systems for factory automation.
The dark warehouse is becoming a goal for some factories. The efficiency of a fully automated factory is becoming somewhat of a bragging right for some companies. However, if it isn't cost-effective, then is it truly worth it? The answer to that question lies in co-bot (collaborative robots) technology. Cobots are cheaper than fully automated industrial robots and cost small and medium-sized enterprises - who want to go into automation - much less. However, collaborative robotics alludes to the involvement of human instruction. Thereby, eliminating the truly dark warehouse.
However, for big industrial facilities that are looking to fully automating and going 'dark', DC Velocity has compiled a comprehensive three-point checklist that companies can follow in their pursuit for fully automated systems:
- Automated storage and retrieval systems: facilities that handle high volumes of inventory moving and out of storage
- High-speed sorting equipment
- Warehouse robotics: guided by wireless instruction from a warehouse management system or warehouse execution system
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
Engineers have to work in teams. It's seldom that an engineer won't have to face a team dynamic at some point. The problem some people have is behaving accordingly when working with a team. You either do well at teamwork or you don't. The issue is, sometimes it is unavoidable. An engineer might end up working with other hot-headed engineers and suddenly a conflict arises. The shocking fact is that sometimes conflict might be a good thing. All you have to do is read Steve Jobs' biography to see how many times he clashed with his fellow engineering pals but look at Apple today. So yes, conflict can be good, but sometimes, conflict can derail an entire project.
 Scott Dietzen, the CEO of Pure Storage, a company that lends itself to all-flash solutions for demanding business and IT problems works with engineering-types. He recently wrote a Top 10 list of the top 10 things you need to do to be a successful engineer. It was published on Forbes' website. The first one was, an engineer should choose meaningful problems. The second one was, build or join an outstanding team. The question is, whether or not that outstanding team will survive a conflict that arises. Is conflict necessary in an 'outstanding' team? Is being part of a team the deciding factor in making someone a good engineer?
Scott Dietzen, the CEO of Pure Storage, a company that lends itself to all-flash solutions for demanding business and IT problems works with engineering-types. He recently wrote a Top 10 list of the top 10 things you need to do to be a successful engineer. It was published on Forbes' website. The first one was, an engineer should choose meaningful problems. The second one was, build or join an outstanding team. The question is, whether or not that outstanding team will survive a conflict that arises. Is conflict necessary in an 'outstanding' team? Is being part of a team the deciding factor in making someone a good engineer?
"It's an issue we have all the time and let's face it conflict is actually a good thing," says the Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institute of Technology, Steve Mackay. He opens up about the conflict prevalent in the engineering industry in his video series the Engineering News Network. "Whenever you have a conflict in your team, the trick is always to deal with the problem as quickly as possible and also to try and focus on the issue, not the person. So, focus on the issue, try and deal with the issue, dissect it very carefully and try and listen carefully to all parties," he added. He also says the action and decision on a certain issue should be swift as well," he added.
Mackay ends his video off with a quote from Garth Brooks. The quote reads: "The greatest conflicts are not between two people but between one person and himself."
Paul J Breaux at the Southwest Research Insitute wrote a guide to handling conflict in engineering teams that was published in the IEEE Xplore Digital Library. He wrote: "Conflict must be managed both locally and globally to assure the success of any engineering organization in its target industry. How an engineering organization manages conflict can directly impact its success or failure." He alludes to the fact that ignoring conflict is not an option.
Dietzen's other principles one should stick to - if they want to be a good engineer - are:
- Work hard
- Tell your story well
- Be optimistic
- Be realistic
- Be contrarian
- Trust your instincts
- It's a marathon, not a sprint
- Have fun
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
Australia, The United States, and Britain. Who is winning the renewable energy race? Who is doing more to secure green energy in their country? The answer is Germany. They have installed and are achieving 38301 MWp (Mega Watt peak) with photovoltaic devices. They have strategies in place to ensure that their country could run fully renewable energy by 2030. However, how close are the other superpowers and forward thinking countries? Those aforementioned countries that are considered to be big players in the renewable energy game. Let's take a look.
 Australia's Labor Government has established a Strategic Industries Taskforce to further the renewable energy conversation in the country. The taskforce wants to set up a Strategic Industries Reserve Fund that would see AUD $300 million to encourage renewable energy in "emissions intensive industries". This would include modernizing companies that are still operating with a big carbon footprint. The money will also be funneled into research in STEM fields to further investigate ways of making Australia's energy reach its renewable energy goals.
Australia's Labor Government has established a Strategic Industries Taskforce to further the renewable energy conversation in the country. The taskforce wants to set up a Strategic Industries Reserve Fund that would see AUD $300 million to encourage renewable energy in "emissions intensive industries". This would include modernizing companies that are still operating with a big carbon footprint. The money will also be funneled into research in STEM fields to further investigate ways of making Australia's energy reach its renewable energy goals.
Bill Shorten, the Opposition Leader for the Labor Party, spoke to media recently, saying: "Renewable energy is not just a fringe industry anymore. It is a key strategy in delivering jobs in Australia delivering investment into Australian industry. That is why we are prioritising our goal of 50 percent of our energy mix by 2030 will be derived from renewable energy sources such as these remarkable solar farms [referring to the Royalla Solar Farms]."
The United States are set to commit to a new clean power goal at a summit being held in Ottawa this week. Countries set to co-sign the bill are Canada and Mexico as well. They're calling it...and wait for it, it's worth it...The Three Amigos Summit. The summit will see the three countries agreeing to power their country through renewable means by up to 50% by the year 2025. A senior advisor in Barack Obama's camp said that the goals are aggressive but they are certain the three countries will be able to do it, making it a continent-wide agreement. According to The Guardian, a third of America's power is already being produced from renewable energy sources. Interestingly, Canada already produces 81% of its energy through renewable means.
And now for the inevitable news. Britain has been told that the exit from the European Union will amount to less renewable energy technology making its way into the country. The offshore wind industry is rumored to be impacted by the Brexit as well. After the Brexit results were unveiled, Siemens halted wind power investment in the UK due to uncertainty in the market. Dong Energy is also one of the bigger investors in UK offshore wind. Their spokesperson told the Guardian: "We will await clarity over the implications of the vote to leave the European Union. However, we don't believe that UK energy policy is dependent on EU membership." Therefore, the UK should say a collective, "Whew!" What is apparent, however, is that time will tell what the Brexit's impact on British energy policies is. Hopefully, for the engineers who work in the industry's sake, everything will be fine. It depends on the change in leadership and what those leaders have in mind for renewable energy in the UK, a country who was tipped to be the dark horse in the renewable energy game before the Brexit.
Source: Renew Economy / The Guardian
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
We know it's going to play a big part in our future, but how big are we talking here? Lithium seems to be on everyone's lips these days due to being in the driver's seat in the push for renewable energy. Needless to say, it powers most home electronics as it is. It is also leading the charge in home energy storage units. So what does the demand for lithium look like?
Experts say that as of 2015, the global lithium supply was approximately at 160,000 tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE). Those are the ones we are using every day of our lives which power the lithium-ion batteries, that are also making their way into electric vehicles.
 Francis Weldin, executive technical director at a company named Dakota Minerals Ltd was interviewed in a recent report on global lithium demand. He says that for every 1% of new electric vehicles making their way to market, 70,000 tonnes of lithium is in demand. These numbers were originally published by Goldman Sachs, who called lithium-ion the new gasoline, showing just how much demand has grown. So, needless to say, the numbers aren't inspiring much confidence. Sodium-ion batteries, anyone?
Francis Weldin, executive technical director at a company named Dakota Minerals Ltd was interviewed in a recent report on global lithium demand. He says that for every 1% of new electric vehicles making their way to market, 70,000 tonnes of lithium is in demand. These numbers were originally published by Goldman Sachs, who called lithium-ion the new gasoline, showing just how much demand has grown. So, needless to say, the numbers aren't inspiring much confidence. Sodium-ion batteries, anyone?
According to ABC News, only five lithium mines have been fully developed in the last 20 years due to the low demand. However, then Elon Musk and his soon-to-launch Tesla Gigafactory hit the scene and is using lithium-ion propaganda to instil the anxious feeling that everyone should have a lithium-ion battery in their car and in the house, or be left in the Stone Age. Musk's factory, if successful, will be the world leader in lithium battery power producing.
Goldman Sachs further projected that lithium-ion batteries' use in electric vehicles alone would grow 11-fold, making the demand reach 300,000 tonnes by 2025. Elon Musk isn't the only philanthropist wanting to get his hands on the world's lithium production, China is interested too. A study conducted by Infiniti Research Limited entitled Global Lithium Market 2016-2020 estimates that the electric vehicle market in China. The demand for EVs in China will grow the market at a CAGR of 7.84%, making the country a contender for lithium-ion battery usage. All we know is the more lithium mining that occurs the more there will be for the world, and that's what engineers are working towards. A world powered by renewable energy with the assistance of lithium-ion technology.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
A cyber-takedown of the Ukranian electricity grid in December of 2015 has sent the cybersecurity industry spiralling. Since then, governments across the globe have been equipping themselves with cybersecurity firms that will try to ensure a takedown of a similar nature doesn't occur. What is apparent is that governments need some pretty efficient firewalls to ensure that criminals can't take down their country's power grids with complex lines of code. Industrial control systems being interceptable by outside forces poses a big risk for the future of ensuring the safety of grids. It's all about the smart-grid now, but is it smart enough to ensure that hackers don't take them down?
The United States' Office of Electricity Delivery & Energy Reliability said: "Addressing cybersecurity is critical to enhancing the security and reliability of the nation's electric grid. Ensuring a resilient electric grid is particularly important since it is arguably the most complex and critical infrastructure that other sectors depend upon to deliver essential services."
 So what have the US government done to secure that a virtual takedown doesn't happen? They put the U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team (ICS-CERT) to work and learned from the loopholes that allowed hackers to take down the Ukranian power grid.
So what have the US government done to secure that a virtual takedown doesn't happen? They put the U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team (ICS-CERT) to work and learned from the loopholes that allowed hackers to take down the Ukranian power grid.
Robert Lee, a former cyber warfare operations office for the U.S. Air Force spoke to Spectrum, saying: "Everything about this attack was repeatable in the United States. While their security wasn't awesome, it definitely wasn't below the industry standards."
America has a Critical Infrastructure Protection standard that protects the country's important SCADA systems. But professionals are saying more powerful firewalls are needed to make sure the SCADA systems never get touched. Experts warn that the more "smart meters, electric car chargers, rooftop solar installation, and other intelligent devices" open the grid up for attack.
DNP3 protocols allowing communications across substations and field devices are the entry points that need to be continually monitored for potential hacking. Using open source extensions like DNP3 SCADA, the utility can set up alarms. Alarms enable utilities to monitor intrusion on a network that is in the process of being hacked. However, experts say the willingness of utilites to embrace DNP3-compatible extensions that monitor intrusion have only been adopted by four or five utilities in the US. Experts also warn that not enough utilities are taking cybersecurity seriously.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
Engineering failures continue to plague African countries. Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana have been under heavy scrutiny by both its people and its governments due to unsafe civil engineering practices that have left many dead in the last few years. In Nigeria, the lack of a structural engineer was one of the reasons given for the collapse of the Synagogue Church of All Nations that left 115 people dead. In Kenya, after the collapse of a six-storey building, the Deputy Governer of Nairobi said that seventy percent of buildings in the country are erected without proper certification. There is an engineering ethics problem in Africa, but nothing is being done to change it.
Ghanaian publication, Graphic Online, has berated their president, John Dramani Mahama for not doing anything about the annual floods that occur in Accura due to what the publication claims are 'engineering failures'. They wrote: "Mr President, we appeal to you apply the whip on your appointees, especially metropolitan, municipal and district chief executives who fail to use the statutory authority of their assemblies to compel the people to respect the laws."
 The engineering experts in Ghana have said that Accra is located in low-lying areas that are susceptible to flooding due to where the houses had been constructed in the first place. Furthermore, the draining systems are overcrowded with rubbish due to the residents who dump their rubbish into the drainage systems. The experts are saying a proper, effective drainage system is needed and then the city can address problems with litter and other issues. The publication thinks that underground drainage systems would be better for the area because open drain systems have been a target for the city to turn the drain into a landfill.
The engineering experts in Ghana have said that Accra is located in low-lying areas that are susceptible to flooding due to where the houses had been constructed in the first place. Furthermore, the draining systems are overcrowded with rubbish due to the residents who dump their rubbish into the drainage systems. The experts are saying a proper, effective drainage system is needed and then the city can address problems with litter and other issues. The publication thinks that underground drainage systems would be better for the area because open drain systems have been a target for the city to turn the drain into a landfill.
However, whoever first constructed the drains must have known that at some point there was going to be a problem with waste management. Why would they build it in any case? It becomes an ethics issue. From the process of awarding the contracts to construction companies to the unethical building of unsafe drainage networks and buildings around Africa.
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institue of Technology, Steve Mackay has broached the topic of engineering ethics in the latest episode of his YouTube series, Engineering News Network. He said: "Ethics for engineers means engineers in the fulfillment of their professional duties shall uphold paramount the safety, health and welfare of their fellow citizens. That should be the highest possible consideration. It's a very expensive process if you want to rip the system but ethics is something that we as engineers and technical professionals have to do all the time."
Mackay outlines what the American Society of Civil Engineers believes are the fundamentals of ethical engineering. They're something that engineering entities in Africa should be focused on, but regrettably, are mostly ignoring.
- Hold safety, health and welfare of your fellow citizen in high regard
- Only work in areas where you are competent. Don't build bridges if you're an electronics design engineer for circuit boards. Focus on your areas of competence
- Be truthful and objective in everything you do. Be honest, tell the truth and be objective when you communicate and talk to others.
- Try and hold the highest professional standards in whatever you do. Don't take shortcuts, don't go for the cheap and nasty approach.
- Avoid conflicts of interest
- Ensure that your professional reputation is built on real, objective successes.
- Have zero tolerance for fraud, corruption, bribery. Say no.
- Always focus on enhancing your skills
- Details
- Written by: Steve Mackay
- Category: Blog - Steve Mackay
As we know – engineering professionals often hugely underestimate their contribution and role in industry and society. Safety in the workplace especially when it comes to electricity is something we have to constantly keep our eye on and can continue to make a huge contribution.
Dear Colleagues
As we know – engineering professionals often hugely underestimate their contribution and role in industry and society. Safety in the workplace especially when it comes to electricity is something we have to constantly keep our eye on and can continue to make a huge contribution.
Engineering professionals should be proud
As engineers and technical people we are proud to make things happen and but it’s important that in this desire to produce an outcome, the technical solutions properly take into account:
- The relevant technical and safety requirements of a statutory nature (the legal requirements, contained in Acts, Regulations and referenced technical standards/codes);
- The possible need for additional measures to protect people and property (moral issues that arise because simple compliance with local laws may not deliver an adequately safe outcome for people and property – this is where issues such as good risk management and “good industry practice” come into play); and
- The wider corporate responsibility and also the impact on corporate image (and thus shareholder value) should a major deficiency with the outcome become evident. For example, the capacity and means for ensuring the ongoing safety of facilities in the long term need to be considered, where relevant.
An Energy Safety checklist
I believe these three issues need to be seen as part of the “energy safety checklist” that practitioners apply as part of their work, in their endeavour for continuous improvement, whether working on infrastructure (e.g. electricity or gas transmission lines, power stations etc) or industry installations (of mine sites, process plants or large buildings).
Massive Energy Safety failures
There have been some very newsworthy energy safety failures in recent times and two come to mind (besides the Gulf of Mexico rig explosion, of course). Firstly during early June 2010 there was a substation explosion and fire in Dhaka, Bangladesh which resulted in the death of at least 117 people and many more injured people, as the substation was next to a building storing various flammable chemicals. Secondly, during August 2010 it was announced that British Petroleum had agreed to pay a record OSH law fine of US$51m for failing to correct safety hazards at its Texas City oil refinery after an explosion killed 15 workers in 2005. The latter failure to comply is now not only costing BP a huge amount of money, but is also seriously hurting the company’s image and credibility.
Safety short cuts are expensive
It highlights that taking safety shortcuts to save some dollars doesn’t really save money in the long run. It also highlights that engineers should not be afraid to make sure the right information goes “up the line” to CEOs and also the directors of company boards, since many now take pride in reporting corporate performance through a triple bottom line – known as people, planet & profit.
Thanks to Al Koenig for this useful commentary.
In undertaking your day-to-day work, especially as far as safety is concerned, Howard Newton sagely observed: People forget how fast you did a job - but they remember how well you did it.
Yours in engineering learning
Steve
Mackay’s Musings – 28th June’16 #606
780, 293 readers – www.eit.edu.au/cms/news/blog-steve-mackay
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration that involves multiple telecommunications companies who were behind the expansion of third-generation (3G) mobile phone system technology. The collaboration now wants to focus its efforts on Industrie 4.0 and focus on communication for the Internet of Things. This involves working on fifth generation technology. The group has released the first specifications for a new radio technology that will be ready to be used in devices by June 2018.
They will be finalising the architecture of systems that will run on fifth-generation communications by December of 2016. The result will be narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) supporting two-way communications that will have low throughput and will be able to function on low-cost devices. Furthermore, the technology will be able to support up to 150,000 devices per single cellular cell. The release will also be able to run alongside existing 2G and LTE networking. This means, finally, GPRS will be quicker as well. Don't you just hate it when your phone barely manages to get internet on GPRS? Now, Release 13 allows for a 20db link budget improvement that will see GPRS perform better under terrible conditions.
 Dino Flore, chairman of 3GPP said: "It took us only nine months to standardise the new technology after the study phase. Once again 3GPP demonstrated the ability to quickly respond to the emerging market needs."
Dino Flore, chairman of 3GPP said: "It took us only nine months to standardise the new technology after the study phase. Once again 3GPP demonstrated the ability to quickly respond to the emerging market needs."
Meanwhile, a company named u-blox has released a chip that will be compatible with 3GPP Release 13 (the new 5G standard) that will assist with communications in "smart buildings and cities, utilities metering, white goods, asset tracking, and agricultural and environmental monitoring." It is being considered the world's first cellular NB-Iot (Narrowband) technology. The chip will be the first one to be used by industry leaders Vodafone, Huawei and more. It will be the standard for NB-IoT and the future of the 5G world. It is called SARA-N2 module
Vodafone will be using NB-IoT as soon as 2017. The technology will go by the name LTE-Advanced Pro.
Alex Sinclair, CTO of the GSMA, said: "We are pleased that the industry has moved so quickly to adopt them and that they have now been ratified by 3GPP. Mobile operators have already started a number of pilots around the world and this agreement over common standards will help accelerate the development of commercial solutions and ensure they are in market much faster, providing customers with more choice."
The Internet of Things is going to need lightning-speed communications between devices and this standardisation of communications technology is a good step forward.
Source: PR Newswire
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
The world is moving at a fast pace in the twenty-first century. It's easy to have mastered the skills necessary to do a job, just to find yourself years down the road with a whole set of new skills you have to learn to remain employable to a company. It happens in many engineering industries due to how technology is constantly updated, software changes, hardware gets replaced, a robot takes the repetitive task you used to do. etcetera. You could even be fresh out of high school not knowing where to start on your road to becoming an engineer. Perhaps a MOOC could be your saving grace.
 MOOC is short for Massive Open Online Course. A free online course that is offered by top universities that introduce students to the type of work that tertiary level institutions teach or lets you brush up on your skills that you might require for a certain type of job. To find a list of MOOCs that specialize in Engineering, you can look at this website: MOOC LIST.
MOOC is short for Massive Open Online Course. A free online course that is offered by top universities that introduce students to the type of work that tertiary level institutions teach or lets you brush up on your skills that you might require for a certain type of job. To find a list of MOOCs that specialize in Engineering, you can look at this website: MOOC LIST.
In South Africa, students recently led a protest against the hiking of university admission fees, which quickly turned into an argument for free tertiary education. Now, The University of the Witswatersrand is offering three new massive open online courses that could get students started on building towards their engineering career. The University will be the first in Africa to offer MOOCs along with with the edX program. The three courses are:
- Research Methods: An Engineering Approach
- Results-Based Project Management: Monitoring and Evaluation
- System Dynamics for Health Sciences
Deputy Vice Chancellor at Wits says: "There is no doubt that there is dire need for more places at South African universities and for access to quality post-school training. Wits is proud to be the first African university on the edX platform, where we offer free online courses unique to South Africa."
It is a good move for the university that is trying to do everything it can to at least offer something to a country that is demanding tertiary education be made free and available to every student. And it is encouraging to see they are engineering-inspired courses. However, if you wanted to, you could also do some MOOCs that get you started through industry big-hitters like MIT, Stanford and more.
The University of New South Wales Australia has also launched their own MOOC, named Through Engineers' Eyes: Engineering Mechanics by Experiment Analysis and Design. The professors behind the MOOC say learning foundational engineering concepts is invaluable to the future studies that a student pursues.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The civil engineering industry is desperately wanting to use automated drone technology in the United States. Current unmanned vehicle laws from the Federal Aviation Administration have limited some of the automated operations that could be run on construction sites, which would perform site monitoring, mapping, and inspection. Now, they are updating the laws but have still left out amendments that would benefit the engineering companies.
Companies in the US that want to use drones, want to implement automated systems. Amazon and Alphabet have both engineered automated drone delivery systems that will not be able to fly under the new FAA regulations. Another regulation that could stunt the growth is the fact that drones would not be able to fly during the hours of the night.
The new laws demand that a drone must always be in "eyeshot" of the pilot controlling it. However, as more and more automated drone delivery systems are proposed, the FAA could alter these laws. This would mean that automated site mapping, monitoring or inspection drones are a pipe dream for now, but so long as a piloted inspection drone can be seen by its pilot, those seem to be allowed for now.
U.S. Transport Secretary Anthony Foxx announced the new regulations on the FAA's website, saying: "We are part of a new era in aviation, and the potential for unmanned aircraft will make it safer and easier to do certain jobs. We look forward to working with the aviation community to support innovation, while maintaining our standards as the safest and most complex airspace in the world."
The FAA says the new regulations could create up to 100,000 new jobs in the industry over the next 10 years. They also say that the money generated by companies using drone technology could top $82 billion, according to their industry estimates.
There are many other uses UAS's could be used for in the engineering community and now that the laws have been altered, those uses can finally come to fruition. However, the lack of support for the automation of those systems sets some industries back. Good news for drone operators whose employment is guaranteed until the FAA decides to review the law on a pilot being necessary.
Automated drones flying pre-planned paths is invaluable to civil engineering industries and the safety of those sites, as shown in this video below:
The new drone laws are summarized
Source: Federal Aviation Administration
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
Heartbreak, dismay, disappointment. Just some of the words that academics are using to express themselves with after the British public decided that the United Kingdom would not remain in the Europe Union. Universities are now saying they anticipate considerable changes in the future of studies in engineering and science.
When the referendum's results were announced the Institution of Engineering and Technology immediately demanded discussions be held to measure what kind of damage a Brexit will have on the engineering industries. The group says the vote comes at an inconvenient time due to the shortage of engineers the country has. They say the vote will impair the economy
 According to a poll, the publication The Independent ran, 56 percent of students believed that leaving the EU would lead to "detrimental effects" on career prospects in the country. What academics are worried about is the loss of the European Union research funding. £687 million ($907 million) is made available for research and a lot of that is used for engineering and science research and innovation.
According to a poll, the publication The Independent ran, 56 percent of students believed that leaving the EU would lead to "detrimental effects" on career prospects in the country. What academics are worried about is the loss of the European Union research funding. £687 million ($907 million) is made available for research and a lot of that is used for engineering and science research and innovation.
President of Universities UK, Julia Goodfellow said: "'Leaving the EU will create significant challenges for universities. Although this is not an outcome that we wished or campaigned for, we respect the decision of the UK electorate. We should remember that leaving the EU will not happen overnight – there will be a gradual exit process with significant opportunities to seek assurances and influence future policy.
However, Patrick Flaherty, Chief Executive of AECOM UK said that due to the fact that no nation has ever left the EU before, the long-term impact couldn't be measured as of yet.
However, students are anxious about what the Brexit means for the high-ranking British universities. Five percent of students in the UK are from EU territories, and the exit could have implications for them, depending on what politicians decide about immigrating students. Universities UK wants to ensure that EU student exchange stays in place.
"Our first priority will be to convince the UK Government to take steps to ensure that staff and students from EU countries can continue to work and study at British universities in the long term, and to promote the UK as a welcoming destination for the brightest and best minds. They make a powerful contribution to university research and teaching and have a positive impact on the British economy and society. We will also prioritise securing opportunities for our researchers and students to access vital pan-European programmes and build new global networks," Goodfellow concluded, in her statement after the Brexit results were published.
Source: Universities UK
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The European Union has been reading some Isaac Asimov novels, it seems. The expansion of industrial robotics has made the EU question whether or not to finally give robots the "electronic persons" classification. We are seeing robots in factories around the world furthering the fourth industrial revolution and slowly making their way into households around the world. The fact of the matter cannot be denied, robots being considered "electronic persons" is soon not going to be the stuff of science-fiction novels anymore.
The draft document by the Legal Affairs Committee of the EU to give intelligent robots that title "electronic persons" has gotten the engineers who develop and equip factories with these 'robotic persons', talking. VDMA, a German engineering association, says this is the kind of overeager chatter that will slow the fourth industrial revolution down. The European Union are trying to force regulation on technologies that they assume already exists, says VDMA chief executive Thilo Brodtmann.
 VDMA robotics and automation head Patrick Schwarzkopf told Reuters that a legal framework for electronic persons should only be happening in the next 50 years and not in the next ten years. "We think it would be very bureaucratic and would stunt the development of robotics," he said.
VDMA robotics and automation head Patrick Schwarzkopf told Reuters that a legal framework for electronic persons should only be happening in the next 50 years and not in the next ten years. "We think it would be very bureaucratic and would stunt the development of robotics," he said.
The draft proposal has come after news that factories all over the world are continually replacing human workers with a robotic workforce. The rise in industrial automation is something that Europe does quite well, and in Germany specifically. Perhaps that is why the EU wants to jump on the issue so quickly.
The activist behind the proposal is an MP Mady Delvaux. She was interviewed by the EU's actual website, saying that robots need a classification of some sort because of the many different kinds of robots that exist today, i.e. service robots, industrial robots, drones, cars, etc. She said: "There are various reasons for this. We need a new European standardisation. We also need to consider liability, the protection of personal data and the prevention of hacking...The US, China, Korea and Japan have very ambitious projects. If we do not create the legal framework for the development of robotics, our market will be invaded by robots from the outside. Also, the European Parliament will be the first parliament in the world to discuss and create such a legal framework." She also alludes to the fact that the robot revolution will "destroy certain kinds of jobs" but is confident that Europe will be creating new ones to counteract the loss of employment.
Other robot manufacturers like Kuka have also rubbished the claims that an "electronic persons" classification for robots is necessary right now and would rather delay the process to see where robotics lands up in the upcoming years.
Here is the entire draft report on the recommendations to the commission on Civil Law Rules on Robotics
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
The engineering world wants hard-earned academic qualifications. It's no lie. A degree from a well-known, respected university can get you a job. However, do you have experience? This is where engineering apprenticeships come in. A student studying towards their Masters Engineering levels could see themselves taking part in an apprenticeship and equipping themselves with even more engineering skills which will lead to a lucrative career. Learning practical skills in an industry-specific apprenticeship will give you invaluable background information and skills that will equip you to go further and do more in the career you are building towards.
Engineering UK said in 2013 that there would be a demand for 69,000 qualified people in an engineering apprenticeship positions from the years 2010-2020. However, only 27,000 apprentices get their qualifications per year in the UK. The bigger picture is that by 2020, the UK expects to have seen 1.86 million jobs to have been made available in the engineering industry.
 Furthermore, there is the nasty business of seeing the gender imbalance statistics in engineering apprenticeships. The issue of men outnumbering women in engineering is unavoidable these days, and it obviously affects the apprenticeship numbers as well. The Young Women's Trust compiled a report that revealed there are 25 male apprentices in a program and only one female. They have also highlighted that men apprentices get paid more than female apprentices. Aecom has also recently warned the industry that the gender gap needs to be addressed due to less than 8% of manufacturing and engineering technology apprenticeship programs being given to women candidates. Those numbers were made public by the Department for Business, Innovation & Skills in the UK.
Furthermore, there is the nasty business of seeing the gender imbalance statistics in engineering apprenticeships. The issue of men outnumbering women in engineering is unavoidable these days, and it obviously affects the apprenticeship numbers as well. The Young Women's Trust compiled a report that revealed there are 25 male apprentices in a program and only one female. They have also highlighted that men apprentices get paid more than female apprentices. Aecom has also recently warned the industry that the gender gap needs to be addressed due to less than 8% of manufacturing and engineering technology apprenticeship programs being given to women candidates. Those numbers were made public by the Department for Business, Innovation & Skills in the UK.
Mark Gale, campaigns manager at Young Women's Trust said: "We know that for engineering there's such a massive skills requirement over the next few years. Currently, one in five schoolchildren would have to become an engineer to fill that gap." Their findings also showed that 16% of female apprentices were able to find work once completing their apprenticeships. "So despite all that investment in trying to get young women into science, technology, engineering and maths workplaces, it's not really having an impact."
There has been a renewed effort to include more women in the industry, especially in apprenticeship positions and to remove any discrimination that is prevalent in engineering workplaces. Now, that Britain has just gone through with an exit from the European Union, apprenticeships will be very important to the future skills teaching in the sector. An engineering firm called Dawson Shanahan has seen the need to train younger engineers so that longevity can be achieved.
Les Reeves, joint managing director of Dawson Shanahan said: "At a time when the engineering skills gap is continuing to grow, effectively training young people is key to preventing a decline in manufacturing in the UK and protecting our economy. Giving young people the skills they need to be at the cutting edge of our industry and the job market is vital for their future and for the future of engineering in the UK."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
I can sometimes be seen on a rod but I'm not a fish. I can be forked but I'm not a tongue. I'm bright but I'm not the sun. I'm electric but I don't have any wires. I'm seen during a storm but I'm not a cloud. What am I? Seeing as though it's Friday, I'll let you off the hook and give you the answer. It's lightning.
In this article, two industries that seem to produce conductive elements that attract lightning, will be focused on. However, here is a list of just some of the objects that need earthing and grounding:
- Standby generators
- LV and HV supply systems
- Technical Earthing for equipment sensitive to fault currents
- Transformers
- Feeder Pillars
- Telecommunications Systems
- Wind Farms
- Deep drilled boreholes with conductive aggregates
- Rail and tram earthing
- And many more
Wind turbines are behind a lot of the clean energy production that is sticking to governmental agreements to minimize the amount of greenhouse gases, especially in Europe. Ensuring the turbines aren't hit by lightning is an enormous undertaking due to the very pole-like nature the turbines have, including the electromagnetic fields the turbines produce. They are a glaring target for lightning. Reports of damaged blades and the electronic equipment inside the turbines have been seen in the industry due to bad grounding practices.
Wind Farm Bop writes that there are 3 main characteristics of an earthing system:
- Ensure that living beings in the vicinity of the earthing system are not exposed to dangerous potentials
- Retain system voltages within reasonable limits in case of faults
- Provide a sufficiently low impedance
He further says mechanical technology solutions for grounding wind turbines has a bigger failure rate than other more solid grounding applications such as exothermic or compression grounding technology. Exothermic grounding technology is able to survive vibrations and disturbances, whereas mechanical technology can shake and come loose.
A new solution to grounding wind turbines has been an invention out of Spain named the Halo Lightning Suppressor. It deionizes the space around an electricity generating turbine. The technology boasts a 100% guarantee that lightning will be avoided.
 Jay Kothari, the president of EMP Solutions - the company who has developed the Halo Lightning Suppressor - has underlined the problems wind turbines have. He said: “The first issue is the problem caused by atmospheric lightning, and second, because the turbine is spinning, it generates its own electrical field. So you have the static from the turbine as well. The solution is to deionize the air passing overhead and dissipate the static charge generated by the spinning blades. For that, we install a unit inside the tower to pull some the static electricity off the blades and send it to ground. And we install a unit on top of the turbine to dissipate the charges generated by the storm cloud. The two devices provide a huge area of protection. A single device can protect a 100-m radius or about 337,000 ft2 of space."
Jay Kothari, the president of EMP Solutions - the company who has developed the Halo Lightning Suppressor - has underlined the problems wind turbines have. He said: “The first issue is the problem caused by atmospheric lightning, and second, because the turbine is spinning, it generates its own electrical field. So you have the static from the turbine as well. The solution is to deionize the air passing overhead and dissipate the static charge generated by the spinning blades. For that, we install a unit inside the tower to pull some the static electricity off the blades and send it to ground. And we install a unit on top of the turbine to dissipate the charges generated by the storm cloud. The two devices provide a huge area of protection. A single device can protect a 100-m radius or about 337,000 ft2 of space."
Therefore, instead of trying to predict where lightning is going to strike, EMP Solutions tries to ensure that lightning doesn't strike at all. However, the company does admit lightning areas prone to lightning do require ground earthing systems regardless of their 'wonder-tool' that claims to undercut lightning.
Meuller also gives a nod to the grounding work that telecoms do in their fight against lightning. Data communications and telecommunication industries religiously ground their equipment and do it well. Something that could be shaking up the need for grounding in data communications and telecommunications is the introduction of fiber technologies.
The Dean of Engineering at the Engineering Institue of Technology, Steve Mackay, in a new episode of the Engineering News Network has spoken out against the myths of lightning. Talking about fiber, Mackay said: "If you're ever working with daily communications systems in lightning prone areas, always try and use fiber. Fiber gets rid of all the problems because fiber, of course, doesn't conduct lightning and of course, is immune to any electromagnetic interference. So, it's a really good solution." Mackay further warns that the misconception of lightning not striking twice is also a nonsensical myth due to the Empire State Building being struck multiple times a year, and emphasizing that lightning is unpredictable in that way.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Robots are expensive. Some companies can overlook the fact that installing industrial robots would be an expensive endeavor because they have the funds available. But, what about start-up companies that can't exactly put down a lot of money for industrial robotics? The International Federation of Robotics has said that by 2018, there will be 2.3 million industrial robots at work. However, that number could be adjusted upwards if robotics becomes affordable by then.
This would be possible with collaborative robots, or 'cobots'. These are industrial collaborative machines that are cheaper to buy than a full-fledged industrial robotic setup  but helps with factory efficiency. The average price for one is $24,000 but there are some that go for $10,000. So, the prices aren't bad for small companies who want to get into manufacturing or automate some of their assembly lines. The cheaper collaborative robots are single arms that do repetitive tasks like picking and placing or packaging. And they are becoming more attractive to companies and fast.
but helps with factory efficiency. The average price for one is $24,000 but there are some that go for $10,000. So, the prices aren't bad for small companies who want to get into manufacturing or automate some of their assembly lines. The cheaper collaborative robots are single arms that do repetitive tasks like picking and placing or packaging. And they are becoming more attractive to companies and fast.
The cobot market itself, according to Barclays, was sitting at $116 million last year, but will shoot up to $11.5 billion by 2025. Speaking to Reuters, Stefan Lampa, the head of robotics at Germany's Kuka spoke about collaborative robots: "By 2020 it will be a game-changer"
The leader in collaborative robotics sales is Universal Robotics, who say they are doubling the number of sales yearly due to the fresh demand for collaborative robots.
Collaborative robots are seeing a massive sales hike in not only the manufacturing industries but also the food industry. Barclays released their report that showed the UK would be spending $1.6 billion on automation in the next year. The report says that beverage and food companies would see "productivity improvements" of 25% and would also see jobs being creation despite more automation being implemented. This relates to the fact that more collaborative robots are being purchased that still make space for humans within jobs.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
The results are in. The British public has decided that they want to leave the European Union. The vote to leave the EU won by 51.9%, compared to the 48.1% who voted to 'remain'. The result will now ensure that the opinions of those who warned that engineering and science industries were in trouble if a 'leave' vote went through, will be given another read through.
In Support of 'REMAIN'
Roland Berger says that UK exports rake in GBP390 billion annually and that engineering industries are in charge of 44% of those exports. Their data tells them that a 'leave' vote would damage foreign investment into the country which could hurt their export numbers. The group says that foreign direct investment has produced up to 84,000 jobs in 2015 alone and that the exit of the EU will ensure that the UK doesn't produce these kinds of numbers again.
 Roland Berger said: "Leaving the EU would on balance be expected to have a damaging effect on both international trade terms and FDI attractiveness, particularly in the near term. Politicians, academics, and economists can merrily debate the long term, and the consensus is that the long term will be damaged also, sadly the near term is the one we are living in. The Engineering sector requires continuous investment decisions if it is to retain its international position, and so will shrink throughout this near term; indeed we are already seeing these effects.”
Roland Berger said: "Leaving the EU would on balance be expected to have a damaging effect on both international trade terms and FDI attractiveness, particularly in the near term. Politicians, academics, and economists can merrily debate the long term, and the consensus is that the long term will be damaged also, sadly the near term is the one we are living in. The Engineering sector requires continuous investment decisions if it is to retain its international position, and so will shrink throughout this near term; indeed we are already seeing these effects.”
We also recently reported that Rolls-Royce was against a Brexit. The company - who are very respected in the automotive engineering industry - said that investment decisions would be put on hold if the vote went through.
In support of 'LEAVE'
Sir James Dyson was one of the engineering experts that showed his support for a 'leave' vote and is probably quite pleased with today's historic results. This year, Dyson opened the Dyson Center for Engineering Design at Cambridge University. The center cost $11.6 million to build and will ensure that students have A-grade facilities to design and engineer new products in.
 Dyson thinks leaving the EU would lead to "more wealth and more jobs" despite what the 'remain' camp says. He said: "When the Remain campaign tells us no one will trade with us if we leave the EU, sorry, it's absolute cobblers." He spoke of the trade imbalances with the EU that are already bad but further pokes at the EU's free movement of people beliefs. He says that Britain isn't getting the kind of engineering professionals they need.
Dyson thinks leaving the EU would lead to "more wealth and more jobs" despite what the 'remain' camp says. He said: "When the Remain campaign tells us no one will trade with us if we leave the EU, sorry, it's absolute cobblers." He spoke of the trade imbalances with the EU that are already bad but further pokes at the EU's free movement of people beliefs. He says that Britain isn't getting the kind of engineering professionals they need.
"We're not allowed to employ them unless they're from the EU. At the moment, if we want to hire a foreign engineer, it takes four and a half months to go through the Home Office procedure. It's crazy," Dyson told the Telegraph. "It's just that on this issue I think they're fundamentally wrong. I don't just mean from the business point of view, I mean from the point of view of sovereignty and our whole ability to govern ourselves. We will create more wealth and more jobs by being outside the EU than we will within it and we will be in control of our destiny. And control, I think, is the most important thing in life and business."
Dealing with Brexit
After the Brexit result was unveiled, it was the automotive engineering industry that was quickest to reply.
Aston Martin is not defeatist about the referendum. They believe their exports may be boosted by the move. Chief Executive Andy Palmer said:
"We acknowledge the decision and the rule of democracy. Aston Martin will now orientate its business to deliver our mid-term plan in the context of the exit and the market volatility that may exist during the period of transition. As the UK could now be subeject to new trade tarriff barriers, we also ancitipate the need for additional productivity and efficiency in the medium term."
Ford also broached the subject, saying:
We will continue working toward this goal with key stakeholders in the UK and across the other Member States and EU institutions to ensure they understand our concerns which mirror those of the majority of the UK and European auto industry.
While Ford will take whatever action is needed to ensure that our European business remains competitive and keeps to the path toward sustainable profitability, we have made no changes to our current investment plans and will not do so unless there is clear evidence that action is not needed.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Getting your professional certificate in 3D printing and design could take you many places. After all, additive manufacturing is becoming an important part of a lot of industrial endeavours in the world of engineering today. However, the biomedical field is always an interesting one when it works in tandem with 3D printing. We've seen everything from artificial arms to tracheas get printed and used for biomedical purposes. But now bioprinting has taken another step forward. And it's got to do with stem cell research.
Researchers from the University of Bristol have developed a material named bio-ink. The 'ink' lays the material foundation for stem cell growth to be facilitated. Thereafter, living tissue can be 3D printed. The revelations come from the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine who have published their findings in the Wiley Online Library under the title: 3D Bioprinting Using a Templated Porous Bio-ink.
 To explain, Dr Adam Perriman, from the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, said: "Designing the new bio-ink was extremely challenging. You need a material that is printable, strong enough to maintain its shape when immersed in nutrients, and that is not harmful to the cells. We managed to do this, but there was a lot of trial and error before we cracked the final formulation. The special bio-ink formulation was extruded from a retrofitted benchtop 3D printer, as a liquid that transformed to a gel at 37°C, which allowed construction of complex living 3D architectures."
To explain, Dr Adam Perriman, from the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, said: "Designing the new bio-ink was extremely challenging. You need a material that is printable, strong enough to maintain its shape when immersed in nutrients, and that is not harmful to the cells. We managed to do this, but there was a lot of trial and error before we cracked the final formulation. The special bio-ink formulation was extruded from a retrofitted benchtop 3D printer, as a liquid that transformed to a gel at 37°C, which allowed construction of complex living 3D architectures."
The bio-ink consisted of polymers extracted from seaweed and another unnamed synthetic polymer. The seaweed polymer is reportedly the answer to sustaining cell nutrients once they are heated up to the specific temperature.
"What was really astonishing for us was when the cell nutrients were introduced, the synthetic polymer was completely expelled from the 3D structure, leaving only the stem cells and the natural seaweed polymer. This, in turn, created microscopic pores in the structure, which provided more effective nutrient access for the stem cells,” Perriman concluded.
The printing of complex tissue structures could see the future of printed body parts actually becoming more than fiction. This would add even more uses to the already impressive feat of engineering that is the 3D printer.
How about it engineers? Want to get your hands on some bio-ink and develop something that could improve the engineering world through 3D printing?
Source: PHYS
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
BMW have finally revealed that they intend to get into the energy storage system market and compete against manufacturers like Tesla, Daimler (Mercedes Benz) and Nissan. BMW will be repurposing their i3 model batteries for home storage systems once the batteries have served their purpose inside the car. Once an electric vehicle has used a percentage of a lithium-ion battery's recharge cycles, it is illegal to keep it inside a car, however, the battery retains enough of its power to act as a solar energy storage unit for households. Nissan will be putting their Leaf vehicle's batteries on walls once they are past their prime as well.

The product was announced at BMW's very own electric vehicle facility in Montreal, Canada. The company pointed out that their offerings stand out above the crowd due to being a repurposed car battery and not a full battery pack like Tesla has developed. The technology has recently been branded 'car-to-grid' technology.
The unit gets its electricity from solar panels and is able to provide that electricity to households during peak hours to save consumers some of their hard-earned cash once the cost of energy provided by the grid is at its highest. It can also power the household once an outage occurs. Along with PV module and the storage unit, you get the converter and equipment that will all be inclusive in the installation rates.
How much juice are we talking here? BMW will be selling stackable 22-kWh or 33-kWh packs. This would definitely be able to power most of the appliances in a house for a 24 hour period. The average household in the United States uses 30kWh per day. BMW also confirm that the battery can be used to charge electric vehicles.
Cliff Fietzek, manager of Connected eMobility at BMW USA, said: "The remarkable advantage for BMW customers in using BMW i3 batteries as a plug and play storage application is the ability to tap into an alternative resource for residential and commercial backup power, thus using renewable energy much more efficiently and enabling additional revenues from the energy market."
An update to our wall of competitors is in order:
| Tesla PowerWall | Mercedes | Nissan xStorage | BMW |
| Stores 6.4kWh | Stores 2.5kWh | Stores 4.2kWh | TBD |
| Storage stacking: 9 PowerWalls can be connected to equal 58kWh | Storage stacking: 8 Mercedes batteries to equal 20kWh | Storage stacking: 8 batteries to equal 20kWh | Storage stacking: 22kwH or 33kwH |
| Price: Up to $7,000 each including installation | Price: Up to $10,000 each including installation | Price: $4,500 each including installation | TBD |
Source: Autoblog
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
Industrial control systems need to be protected in a world where automation opens avenues for criminals to exploit them. Air gapped SCADA systems will become more and more difficult to stick to in the era where the Internet of Things is striving to connect and automate industrial control systems. There is just no escaping the fact that networks will have to be connected to a cloud-based solution that could enable cyber criminals.
Last year, only 24 percent of engineers who took part in a survey by SANS Information Security believed that there were moderate to severe attacks on industrial control systems. This year, 67 percent of the engineers agree that the situation is becoming dire.
 Derek Harp, the director of industrial control systems global programs at Bethesda said: "It's a trend driven by a problem that's been getting worse. There are more incidents being reported, and more awareness at the senior levels of the companies about what their exposures are."
Derek Harp, the director of industrial control systems global programs at Bethesda said: "It's a trend driven by a problem that's been getting worse. There are more incidents being reported, and more awareness at the senior levels of the companies about what their exposures are."
Bengt Gregory-Brown, a SANS Information Security analyst said: "Control systems are increasingly integrated with IT networks and assets, offering more breach opportunities and attack surfaces in the ICS environment. Unfortunately, we are not seeing a commensurate improvement in the efforts or outcomes of ICS and SCADA security."
Now, industrial security professionals are saying that there is no information sharing across the industry concerning the safeguarding of industrial control systems. Respondents to a study pertaining to information-sharing partnerships have revealed that
"Knowledge is a big problem here. There are a lot of undetected problems. It's widely held that most systems have had some sort of probing, but it's really hard to know if someone was there," Harp said.
These sorts of probings are now the interest of private cybersecurity firms that will attempt to prevent attacks by cyber-criminals who are trying to brute force access to control industrial control systems.
Harp says that their study data indicates that there is a lot of misunderstanding in the industry in terms of ignorance of underlying software being targeted by cybercriminals. He said: "We find the lack of concern with this ubiquitous communication mechanism connecting IT and ICS assets troubling, as it is often targeted by bad actors. Attackers use it to pivot from the business network into the ICS."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The Internet of Things is growing at an exponential rate, faster than some companies can keep up. The Internet of Things also emphasizes the need for faster internet connections. The impending future interconnectivity of 50 billion devices around the world has inspired a slew of 5G network tests in the United States, in attempts to handle the speed necessary to facilitate the Internet of Things. Faster internet speeds will be good for the Internet of Things so data and analytics can be quickly calculated and ready for data analysts to peruse.
However, there has been a kink in the wire that has been slowing IoT data and analytics analysis down. The problem lies within the sensors a certain IoT setup contains. For example, a factory could have industrial robots and automated machines that have thousands of sensors within its manufacturing. Those sensors are responsible for monitoring how the machines are working and allow for the data to be exported and perused by the analysts. Researchers at the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) say they have developed a "flexible, generic data-fusion software" that will allow the data from all Internet of Things connected sensors to be shown at once.

Another challenge that could slow down the process of making sense of IoT sensor data, are the formats that they could be encrypted in. Finding a one-fits-all answer to communication protocols is what GTRI are trying to do.
The FUSE data-fusion software has been developed to serve the following purposes:
- Providing users with online forms that let them define the sources they need in the form of “domains” – abstract descriptions of how the targeted data interrelate;
- Gathering incoming raw data according to user specifications and mapping them into the specified domains. The data can then be transformed and manipulated using “tasks,” which are user-defined JavaScript functions or legacy software that run inside the FUSE service;
- Displaying the processed data to users on-screen via an interactive data visualization, exploration and analysis dashboard that supports most data types including numeric, logical, and text data. Users can also devise their own custom dashboards or other interfaces.
"One of the advantages of FUSE is that it can be broken up and distributed to accommodate any sensor and server architecture. So it can grow and change as a business, facility or campus changes over time," Adams concluded.
The researchers at Georgia Tech are trying to automate the processes behind perusing data of automated systems, which would make every element of the Internet of Things more efficient. Now, there are still manual processes that need to be followed with acquiring the data produced by the sensors in an IoT setup. FUSE would be assisting with this, and could be an invaluable addition to automated setups.
Source: Georgia Tech News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
Industrial robot sales have skyrocketed in the last two years. In 2015, 248,00 robots were sold globally. That number was 12 percent up from the previous year and made it a record year for industrial robotic purchases. By 2018, 2.3 million industrial robots will be employed in the world. These figures are according to The International Federation of Robotics in a study named 2016 World Robotic Statistics.
Based on geographical positioning, the IFR conducted a study on which continents and countries spent the most money on industrial robotics in 2015. The results were as follows:
- Europe in 2015: 50,000 units ; 10% up from the previous year
- America in 2015: 37,000 units ; 15% up from the previous year
- Mexico in 2015: 5,500 units ; Sales more than doubled in one year
- Asia in 2015: 156,000 units ; 16% from the previous year
China's industrial robotics sales grew by 17% compared to the previous year and are actively trying to secure the sales of industrial robotics companies. Recently, Chinese companies tried to buy German-run Kuka Robotics to further cement China as the leader in industrial robotics.
The industries that reported the most sales in industrial robotics were:
- The automotive industry: 95,000 units purchased in 2015
- Metal industry: 63% more purchases than 2014
- Plastics and rubber industry: 40% more robots purchased in 2015
- Electronics industry: 16% rise in industrial robot purchasing
The President of the International Federation of Robotics said: "The wave of digital transformation and automation will continue to drive the robotics boom forward until 2018. Revolutionary developments in IT connected with all aspects of the Internet of Things and new networked services are changing the producing industries fundamentally. Machines, logistics, and production plants are merging into integrated cyber-physical systems. The aim is to use smart factories to work more flexibly, more cost-efficiently and more productively."
Why is there a big jump in the sale of industrial robots? The Head of Robotics for ABB, Per Vegard Nerseth: "People today don't want to do dull, dirty, dangerous and delicate jobs anymore, so many companies see when the older generation of factory workers retire they really struggle to get hold of people who wants to take up on those jobs."
The elimination of repetitive tasks at industrial level was recently highlighted when Foxconn retrenched 65,000 human workers and replaced them with industrial robots. Companies want humans to work on higher-value elements in their jobs and minimize the amount of work that could easily be done by a robot. Therefore, the industrial robotics sales numbers for 2016 could be astronomical.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
When getting your qualifications in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, it is easy to lose track of skills that could be easily attainable that might assist your job hunt in the future. There are a number of engineering experts that are warning students to further explore entrepreneurial and business skills that might complement their engineering degrees.
In the United Kingdom, in Newcastle, STEM experts are trying to implement a student-focused course named The Hunter's Smart Specialisation Strategy. The strategy tries to fuse both STEM careers and entrepreneurship, as well as digital literacy, in an attempt to grow the skill sets of STEM  career professionals.
career professionals.
The Massachusetts Insitute of Technology (MIT) also recently launched entrepreneurship courses that specifically teach engineers entrepreneurial skills for the closing of business deals. The course is called Entrepreneurial Negotiations: The MIT Way.
Moreover, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign's College of Engineering have also launched a program that sees business-savvy skills being taught to engineering students. The university wants to launch the course by this September. The program will focus on "Innovation, Leadership and Engineering Entrepreneurship."
"We lead the pack in entrepreneurship and by creating this degree we are recognizing that innovation leadership and engineering entrepreneurship are not just satellite, extracurricular activities but we bring them front and center. Students can come to Illinois, engage their passions, and receive mentorship, education and guidance as they part in our highly entrepreneurial ecosystem on campus," said Andreas Cangellaris, dean of engineering at UIUC.
UIUC have high-ranking engineering alumni who have gone on to start build and contribute to companies like PayPal and YouTube.
Sydney Morning Herald contributor Tony Featherstone has also commented on the need for entrepreneurship education in Australia amidst a shortage of mathematics education and entrepreneurship education. He writes:
Australia needs more scientists who think like entrepreneurs, information technology students who can turn their software into a fast-growth growth ventures, mathematicians who can turn algorithms into commercial ventures, and engineers who can build big businesses. But it will take generational change to achieve it and the push must start at school.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Photovoltaic cells are not reaching their full potential. Recently, we reported on a method that could lead to more efficient photovoltaic cells from the University of Utah. The revelations included subjecting semiconductors to light sources before the manufacturing process. This reportedly, allowed semiconductors to work more efficiently, especially for applications in solar technology.
The improvement of solar technology will be important in the photovoltaic cell industry in the next few years. Increasing solar efficiency is paramount to the future of renewable energy. The University of Utah's work is largely theoretical as it stands. A sure-fire solution to making solar panels more efficient is needed, here and now.
 "The problem occurs in series-connected solar panels (which is one of the most common ways of connecting solar panels for distributed PV systems) when solar modules are experiencing varying levels of irradiation or temperature. This can result from sporadic cloud, dust accumulation on the PV panels, or uneven air ventilation. In these instances, the current generated by each module is different," said Masdar Insitute Research Engineer Omair Khan.
"The problem occurs in series-connected solar panels (which is one of the most common ways of connecting solar panels for distributed PV systems) when solar modules are experiencing varying levels of irradiation or temperature. This can result from sporadic cloud, dust accumulation on the PV panels, or uneven air ventilation. In these instances, the current generated by each module is different," said Masdar Insitute Research Engineer Omair Khan.
The engineers say that low-performing photovoltaic panels covered by shade cause panels that are exposed to the electricity giving sun to produce less energy. Therefore, the engineers came up with a novel solution.
 The device was developed by Khan and the Masdar Institue of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. The device connects the solar panels and optimizes their output. The device takes the series-connected solar panels and feeds each of them independently instead of the usual load-share, photovoltaic panels are synonymous for.
The device was developed by Khan and the Masdar Institue of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. The device connects the solar panels and optimizes their output. The device takes the series-connected solar panels and feeds each of them independently instead of the usual load-share, photovoltaic panels are synonymous for.
"The low performing solar modules affect the energy output of the entire string of solar panels, as the maximum power output is governed by the lowest current in the system. This means that if one solar module is shaded and thus generating a low current, and is connected in series to several good, high-performing modules, then the high-performing modules cannot operate at higher currents," Khan said.
The device undercuts the "lowest current" limitation prevalent in photovoltaic cells today and rather uses the strongest output a panel may be receiving.
"By employing a dedicated converter to independently perform maximum power point tracking on each submodule, rather than the string of modules as a whole, means that the operating point of each submodule has no effect on the rest of the submodules in the system. Each converter extracts the maximum power possible from each submodule, thus maximizing the PV system's energy-efficiency," Khan concluded.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
We've all seen them. A video that is sped up by about 2 times its normal rate, showing an industrial robot performing some sort of complicated task. The main issue is the speed at which the robot is actually operating at. Industrial robotics can't be fully implemented if what we're left with are slow robots working at a slow pace. That's where motion planning comes in. Researchers at Duke University explain: "Motion planning is the problem of finding a path to move a robot from its current position to some goal position without colliding with any obstacles."
Essentially, collision detection software needs to be built into the robot's processor so that it knows what to avoid and what to pick up. The processor has collision detecting circuits, according to an engineer which assisted in the building of the chip.

"Although motion planning has been studied for decades, existing techniques take seconds on general purpose CPUs and hundreds of milliseconds on power-hungry GPUs to create a single plan. This is a major obstacle to the practical use of robots in unstructured environments as there are often long delays between the desire to execute a motion, and actually having a plan to execute," said the researchers in their video.
The researchers are trying to save the day with the processor they have developed. They have published their findings in a journal titled Robot Motion Planning on a Chip. They claim they are able to speed up the motion planning three times over and say that it would use 20 percent less power than robots do for motion planning as it is. The researchers have tested a robot arm out on their motion planning chip and have revealed that the motion planning takes less than a millisecond to motion plan.
The researchers use multiple Microsoft Kinects put in four different locations around a robotic arm, which then calculates 3D volumes in its path, which are called voxels. The algorithm then calculates what is considered an object due to a pre-existing instruction and avoids anything that it is programmed to avoid.
As a result, the robot looks to be working as quick as a human would in terms of noticing what obstacles are in its way, and circumnavigating around them to obtain the item it is looking for. In other words, it is motion planning in real time much like a human brain would. Of course, it isn't completely full-proof yet but the research indicates that robots will be extra efficient in the future.
Watch the video below to see the impressive engineering feats that the engineers over at Duke Robotics have perfected:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
A company named ShanghaiRanking Consultancy has conducted a study, singling out the best universities for different kinds of engineering. As expected, American universities posted high results, however, other countries were found to be climbing the ladder. The report's name was the Global Raking of Academic Subjects for 2016. The study evaluated more than 350 universities and colleges.
The research took a look at the top 30 universities per engineering qualification, but here we will just recap the top 5. However, the six universities mentioned the most in the study were:
- University of California, Berkeley
- Massachusetts Insitute of Technology (MIT)
- Stanford University
- ETH Zurich
- Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne
- Tsinghua University
Presumably, these are the universities that, if you studied engineering in, you could also look forward to a fruitful career in the engineering industry.
 Most of the statistical data that the results are generated from are from Elsevier, who is a world-leader in providing scientific, technical and medical information. Their Director of Content and Analytics M'hamed El Aisati said: "With students, researchers and other stakeholders taking a closer look at universities' performance and reputations, ShangaiRanking Consultancy is taking an important step by providing a specific ranking for engineering." He further went on to say it is a good ranking system so that the "competitive position" of the universities could be realized.
Most of the statistical data that the results are generated from are from Elsevier, who is a world-leader in providing scientific, technical and medical information. Their Director of Content and Analytics M'hamed El Aisati said: "With students, researchers and other stakeholders taking a closer look at universities' performance and reputations, ShangaiRanking Consultancy is taking an important step by providing a specific ranking for engineering." He further went on to say it is a good ranking system so that the "competitive position" of the universities could be realized.
Top 5 universities for chemical engineering
| Rank | Institution | Country |
| 1 | Massachusetts Insitute of Technology | United States |
| 2 | Stanford University | United States |
| 3 | University of California, Berkeley | United States |
| 4 | National University of Singapore | Singapore |
| 5 | University of Tokyo |
Japan |
- 31 U.S. universities in the top 100 for chemical engineering
Top 5 universities for civil engineering
| Rank | Institution | Country |
| 1 | Purdue University | United States |
| 2 | Technical University of Denmark | Denmark |
| 3 | Tsinghua University | China |
| 4 | Hong Kong Polytechnic University | China- Hong Kong |
| 5 | Tongji University | China |
- Civil engineering has the lowest number of universities ranked due to low output
Top 5 universities for electrical and electronic engineering
| Rank | Institution | Country |
| 1 | Stanford University | United States |
| 2 | Massachussets Institute of Technology (MIT) | United States |
| 3 | University of California, Berkeley | United States |
| 4 | Nanyang Technological University | Singapore |
| 5 | Georgia Institute of Technology | United States |
- 45 of the top 100 universities in electrical and electronic engineering are from the United States
- Total of 937 universities ranked.
Top 5 universities for energy science and engineering
| Rank | Institution | Country |
| 1 | Tsinghua University | China |
| 2 | Technical University of Denmark | Denmark |
| 3 | National University of Singapore | Singapore |
| 4 | Imperial College London | United Kingdom |
| 5 | Nanyang Technological University | Singapore |
Top 5 universities for mechanical engineering
| Rank | Institution | Country |
| 1 | Massachusetts Insitute of Technology | United States |
| 2 | Stanford University | United States |
| 3 | University of Cambridge | United Kingdom |
| 4 | Northwestern University | United States |
| 5 | Georgia Institute of Technology | United States |
- United States universities most prevalent
- United Kingdom also high-ranking
Source: Shangai Ranking
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Researchers from Swansea University could be sitting on a gold mine. The team has just been awarded £25,000 (about $37,000) from the Worshipful Company of Armourers and Brasiers. What? Who are we worshipping? The researchers have apparently made breakthroughs in corrosion inhibitors that prevent rust and corrosion, especially on steel products. They have developed this inhibitor to address the issue of a previous inhibitor which will be banned from the EU in 2019. That specific inhibitor is named "hexavalent chromate".
Hexavalent chromium is being banned for health reasons. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration in the U.S. the chromium is unsafe to work with. OHSA said: "The evidence in the record for rulemaking indicates that workers exposed to Cr(VI) are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer. The record also indicates that occupational exposure to Cr(VI) may result in asthma, and damage to the nasal epithelia and skin."

So, the University of Swansea's breakthrough that can be coated onto steel products to prevent their degradation is coming at the best time possible for the steel industry.
The researchers reportedly used aggressive electrolyte anions that were implemented into the coating. The coating then reacts and triggers a release of an inhibitor. They say the alternative they have come up with can be considered a "smart release coating" that outperforms hexavalent chromate.
Professor Gaint Williams, who is at the helm of the team at the University of Swansea's College of Engineering, said: "This is a significant breakthrough, showing a smarter and safer way of reducing corrosion. The new product is environmentally sound, economical, and outperforms the market leader in laboratory tests. It illustrates that Swansea, with its close links between research and industry, remains at the heart of innovation in steel."
The steel market is reportedly worth £3 billion ($4.4 billion) in Europe alone. Therefore, the corrosion inhibitor could make the researchers quite a bit of money based on coming up with a safer alternative to what steel is coated with today.
"The system has been shown to prevent the onset of corrosion for over 24 hours compared to less than two hours for the current market leader. We also have been able to demonstrate that the rate of corrosion can be slowed down significantly once it has started. This is by far the best result seen in 15 years of research on this topic," said Patrick Dodds, a doctoral student at the Univeristy of Swansea.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
A pair of bills has been passed in Congress that will see America's Homeland Security and cybersecurity engineers working together for the betterment of the cybersecurity situation prevalent in the world today. The interesting distinction to be made here is to notice that Homeland Security will be working with private sector cybersecurity firms. Private security network engineers are understanding more about automation, control and SCADA systems than engineers within the American government. The U.S. actively wants to avoid entire substations being taken down by hackers ; a scenario which has actually happened in countries like the Ukraine. The second bill passed was an act named the Rapid Innovation Act which would see the American government making funds available to research and development for emerging technologies. Smells like the Internet of Things.
Congressman John Ratcliffe said: "With these growing cyber threats posing significant danger to our homeland and infrastructure, it is critical that our government keep pace by actively working with the private sector to find solutions to protect our network."
 Australian tech companies are also seeing the adoption of private network security firms. NEC Australia says that it will be building an AU$4.38 million Global Security Intel Centre (GSIC) that will police the Internet of Things to add an extra layer of cybersecurity to countries or companies that want in. With 50 billion devices connected to the internet by 2020, cybersecurity is one of the most important industries to either study in or invest in.
Australian tech companies are also seeing the adoption of private network security firms. NEC Australia says that it will be building an AU$4.38 million Global Security Intel Centre (GSIC) that will police the Internet of Things to add an extra layer of cybersecurity to countries or companies that want in. With 50 billion devices connected to the internet by 2020, cybersecurity is one of the most important industries to either study in or invest in.
One of the biggest targets for cybersecurity is currently banking. Recently, in May, a gang of Japanese criminals made off with $13 million in cash over three hours. They used counterfeit credit cards from a well-known South African bank and were able to steal the money through cybersecurity loopholes. The heist had South Africa's central bank warning local banks to invest into cybersecurity. This is not an isolated incident, these sorts of cybersecurity stories are happening globally.
An insider source said: "They were smart in selecting Japan. They found a badly protected ATM network in a low-risk country, guessing that the fraud analytics software would not automatically block the transactions."
Leonhard Weese, a contributor for Forbes, thinks authenticating users and encryption is the answer to protecting the banks. What kind of system could possible authenticate a user and ensure a level of unbreakable encryption? Bitcoin, of course.
He writes:
Bitcoin uses a method, widely available for decades, called "assymetric encryption", to authenticate the owners of keys. These keys are a pair of mathematically linked numbers. One functions like a key and is private, ergo never leaving the owner's computer. The other can be understood as a lock. It can be safely handed around and publicized without risking a loss of these funds.
Source: The Hill / Forbes
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Photovoltaic installations are all the rage in 2016 but are they cost-effective and efficient? Right now, getting a storage system could be a little bit of the price range of most consumers. If households want to shave their peak-time energy bills, getting a storage system makes sense, however, if there is no subsidization for storage systems, you could expect to part with $3,000 for a Tesla PowerWall. The price goes higher in other countries due to shipping costs and general installation of any sort of storage system for individual households.
Three United Kingdom research organizations noticed this problem and have all banded together to develop a solution to the price tag on storage. The organizations - of which one includes the assistance of The University of Warwick - agreed to lend their top engineers to build sodium-ion cells that would serve as low-cost
alternative to lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion's development is ongoing and is becoming one of the standards for powering vehicles, energy storage systems and still used for powering electronics.The researchers are certain that their sodium alternative would be 30% less expensive to produce.
Faradion's CEO Francis Massin, said: "This partnership with Moxia Technology and WMG offers a great opportunity not just for Faradion, but for global CO2 reduction. Solar energy storage is an important growth market of the next five years and this partnership means that the UK has the opportunity to be at the forefront of the technology development."
Each company brings something different to the table. Faradion brings their sodium know-how. Moixa has a vast knowledge of energy storage and WMG brings some of the best engineers together to work on the newly developed cells.
Faradion was awarded a £38.2 million ($55 million) grant to further develop the sodium-ion batteries back in May. The company is expected to show how the battery could be implemented into electric vehicles by 2018. By 2025, the company estimates that multiple cars across the UK will have sodium-ion batteries installed inside of them.
The question is will sodium-ion be the battery of choice in the future if it remains cheaper than lithium-ion? Lithium batteries seem to have some sort of monopoly over the game now due to manufacturers using it for EVs, storage systems and other applications. However, by 2018 we could see a battle of the batteries.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
Elon Musk has fingers in many pies and those pies have been producing major engineering marvels lately. It's difficult to ignore the engineering endeavors he associates himself with because they are so current and so 'now'. From securing a high-speed tube train to developing the next battery-powered cars to landing a rocket, the list truly does go on.
Musk also has his money in an artificial intelligence company named OpenAI. You guessed it, they develop artificial intelligence. They are actively working on a robot that would assist with "basic housework". The company won't be manufacturing the robot but they will be concerning themselves with the artificial intelligence that would understand what housework is to begin with. The robot that they will most probably test the AI with would be similar to BRETT. The robot is Berkley University's Robot for the Elimination of Tedious Tasks.
Berkely's robot reportedly has the ability to perform housework duties and continue learning about how to do them more efficiently. Through trial and error, the robot eliminates any room for error once it has learned a lesson from grappling with different tasks.
So, will we be communicating with our household robots in our mother tongue and expecting them to reply to us? OpenAI says this will be possible. In a statement, they said: "Today, there are promising algorithms for supervised language tasks such as question answering, syntactic parsing, and machine translation but there aren't any for more advanced linguistic goals, such as the ability to carry a conversation, the ability to fully understand a document, and the ability to follow complex instructions such as natural language."
Further afield, in other Elon Musk news. Tesla, who Musk is the CEO of, is going to buying a company called Solar City. The CEO of Solar City is Elon Musk. The company's modus operandi is in the name, really. They focus on solar power systems for homes, businesses and governments.
"The SolarCity team has built its company into the clear solar industry leader in the residential, commercial and industrial market, with significant scale and growing customer penetration," Tesla Motors wrote in a press statement. The company says they are excited to be a company that offers end-to-end clean energy products. "This would start with the car that you drive and the energy that you use to charge it, and would extend to how everything else in your home or business is powered."
Talking about Tesla Motors, Elon Musk has confirmed that their much-anticipated Model S vehicle will also be able to survive a swim. He said in a tweet: "We *def* don't recommend this, but Model S floats well enough to turn into a boat for short periods of time. Thrust via wheel rotation."
Musk felt he had to address the situation after a video out of Kazhakstan showed that the vehicle had powered through at least a meter of water:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Industrial automation is growing in popularity as the fourth industrial revolution continues to charge ahead into the future. The Robotics Industries Association has reported that in 2015, the demand for industrial robotics grew by 14% and was valued at $1.8 billion. The International Federation of Robotics also chimed in with their projections. They say that by 2018, there will be 1.3 million industrial robots in use around the world.
President of Force Robots, Steve Somes, said: "Collaborative robots are going strong, and you will see a larger role in force sensing and control. Responding to external forces not only makes robots safer collaboration, it also enables more tasks like assembly, grinding and deburring."
Now, in new developments for robotic sensors and cameras, Robotiq has released a vision-guidance system for pick and place robots; the kind of robots you'd find in an industrial factory.The company currently supplies Universal Robots with "2-finger and 3-finger grippers". The camera fits onto a module that surrounds the robots arms and then gives the robot vision, to see what it the shape of something it is picking up. The company says it only takes five minutes to install. Automated location of objects of an object on an assembly line, thanks to the vision guidance system will improve the turnaround time of production, no matter what industry. It would ensure a safer work space as well, for human colleagues using collaborative robots.
Explaining how the Robotiq camera system works, the manufacturing engineer at Continental Automotive, Victor Canton, said: "The Robotiq Camera breaks all the integration barriers that we are used to seeing with vision systems in manufacturing automation. We could think of many pick & place robot tasks that can now be programmed very fast. We will need this solution for upcoming projects with UR robots."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Cement. Can't live without it...can't live without it. Concrete is important in the civil engineering world, but, sustainable, environmentally non-harmful applications of concrete are becoming even more important. However, how do we make cement cooler? Researchers from the Michoacan University of San Nicolás de Hidalgo have the answer. Glow-in-the-dark cement. The researchers have used phosphorescent materials to make the glow-in-the-dark cement which would be more eco-friendly than using normal cement.
How does it work? It absorbs radiation during the day and then lights up at night. It's a phosphorescent cement that acts as an alternative to cement. The researchers explained: "By using additives, scientists are able to prevent the formation of crystals that occur normally during the production of cement, creating a material with a noncrystalline structure - similar to glass - that allows passage of light inside. Varying the proportion of additives added while manufacturing the cement regulates both its luminescent  intensity and colour."
intensity and colour."
The 'cement' could be used in many towns for high visibility and eco-friendliness. The researchers say the cement could be lit-up for 12 hours. The big problem comes with the durability of the cement. Right now, further testing is required. The researchers are looking to the future. They want to hypothetically build entire walkways or bicycle lanes out phosphorescent cement . Additionally, if the cement is eco-friendly, companies may be interested. Minimizing the amount of GHG in the air bodes well for any company or entity, thereby shrinking carbon footprints in the cement industry.
The picture to the left of the article is not phosphorescent cement but stones. The future applications of the cement would be full walkways and bicycle lanes. The stones were positioned in such a way that it resembled Van Gogh's Starry Night, and is nothing more than a small project in the Netherlands.
Source: Futurism
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Education
Dartmouth College has made engineering history. The college has had more women than male graduates in engineering studies. Dartmouth, since 2015, had implemented a quota that saw at least 37 percent of engineering classes consisting of female students. In 2016, the number of female attendees stood at 54 percent of the class. Meaning, more women graduated than men. The United States sees only one-fifth of undergraduate engineering degrees going to women, but Dartmouth has just undercut that fact.
The students are graduating with their bachelor of arts in engineering. Dartmouth's engineering qualifications are not structured like other colleges or universities. Nonetheless, an interest in engineering in females has been a concern, so a bachelor of arts in engineering is progress. Out of 119 graduates in the course, 64 of those were women. The course is a four-year course and a fifth year is available that will focus more on the technical side of engineering. If they opt for the fifth year, they get their Bachelor of Engineering degrees.
The Dean of Engineering at Dartmouth, Joseph Helble, said: "We've been able to attract more students, and especially women, by letting them use engineering to solve real-world challenges. They quickly learn how their creativity and engineering skills can make a difference."
Last week we mentioned the study that outlined the gender gap and the motivations for women who leave engineering. Sexism within the industry was a major concern to the female engineers that took part in the study.
It was also revealed that women account for only 20 percent of undergraduate engineering degrees in the United States, and only 13 percent of the graduated workforce is female. Here's hoping Dartmouth's results cause a domino effect and start inspiring more women to get into engineering.
According to a recent study by CV-Library, 56.6% of 500 female engineers believe that engineering was still perceived to be a male-run industry. However, Randy Atkins, the director of communication for the National Academy of Engineering says this is all going to change. He said: "We're changing the image of engineering to a creative profession, a problem-solving profession. That is resonating with more women, helping them see engineering in a new way."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The world produces a lot of plastic every year. That plastic usually finds it way to landfills. Some of it even lands in our oceans. According to World Watch, the world produces 299 million tons of plastic per year. If you live in Asia, the amount of plastic used by a single person is 20 kilograms per year. Needless to say, there is a lot of polyethylene being used and discarded every day. But once it's discarded, it doesn't serve many purposes. Science fiction kind of changed that when Doc Brown chucked some garbage into his fuel tank in the end of the first Back to the Future movie and powered his vehicle with enough fuel to blast him and Marty McFly into the future. Oh, imagine that, chemical engineers!
The Shangai Institute of Organic Chemistry and the University of California have reportedly developed "efficient and selective degradation of polyethylenes into liquid fuels". The researchers are cognizant of the methods used to produce fuels from plastic today. They, however, say that those methods are low-energy and are not efficient. Additionally, the burning of plastic contributes to harmful emissions. Converting plastic waste into fuel, without creating fossil fuels would be a step forward for  the world.
the world.
The researchers created a process called cross alkane metathesis (CAM). The researchers split the properties of the already manufactured plastic and were left with Ir-H2. They say that splitting of the plastic's properties can then be used with further cross alkane metathesis to produce hydrocarbons that can be used as diesel fuel that is "suitable for transportation". The researchers say the process is highly efficient and inexpensive.
The research implies that plastic and bottles and grocery store plastic bag might be able to be used to make liquid fuel. And we have a lot of those in the world today. You can read the researchers' published works in the Science Advances journal. Their contribution to the journal is titled: Efficient and selective degradation of polyethylenes into liquid fuels and waxes under mild conditions.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Substation design has changed over the years. Now, with the upcoming push for renewable energy, the technology that operates substations needs to keep up with the times or eventually just call it a day. The issue with old substation design? It tends to leave some people in the dark...for hours. Just ask Michigan. 25,000 people were recently subjected to power outages due to unknown reasons. The Executive Director of Public Affairs at Lansing Board of Water & Light Steve Serkaian indicated it was the age of the substation the utility was utilizing.
"When you have a facility that's more than 50 years old, I mean, try driving a vehicle that's more than 50 years old," Serkaian said. That is really the only explanation that might describe most substation failures these days. He further went on to say, "Technology is not flawless."
What do engineers do to guarantee substation design reliability? They build automated systems that can quickly restore power if an unplanned outage occurs. Some utilities use self-healing solutions that assist with some of the challenges they experience today. Newly automated systems have fault detection, isolation, and load restoration (FDIR).
One of these automated solutions is available from ABB Group, who specialize in Automation and Power Technologies. Explaining FDIR, they write: "FDIR enables the utility to quickly identify the location of a fault, isolate it, and restore power during an unplanned outage by rerouting the flow of power on the distribution grid through, unaffected areas."
But the question is, how many utilities have automated systems or reliable, new, technologies that ensure power continues to flow when an unexpected outage occurs? The answer is...not enough. The smart-grid future, some think is here, is a bit further away.
According to Newtons-Evans Research, as of 2014, the number of fully automated substations is significantly lower to substations that have some automation. The number of substations to be built with full automation by the end of this year is also low. The situation is worse in third-world countries where the old technology of eras past is used to supply electricity to their respective towns and cities.
Automated substations would ensure real-time data and analytics and is far more useful than the old substation technology that goes down without an indication of what caused the outages.
The main issue with upgrading substations with automated technology is whether to replace the remote terminal units or just retrofit pre-existing RTUs in the utility. Replacing RTUs might not address the problems some utilities have and can be overly costly, so retrofitting solutions could be implemented.
Miles Dupuis, an engineer from an electrical services company named Cleco Corp, spoke to Utility Products and explained the divide between replacing the legacy RTUs or retrofitting on the old technology. He indicated that there was no comparison between a full RTU replacement versus a retrofitted RTU system. He said: "Using a vendor that allows us to retrofit RTUs in one day while using only one person in the field is far less costly than what other vendors offer. Some solutions offer the option to replace old, outdated RTUs with replacements to modernize your substations ; however, it usually takes three people and two to three days to complete the task, at a much more significant cost."
- Details
- Written by: Steve Mackay
- Category: Blog - Steve Mackay
Perhaps like you, I tend to get somewhat peevish when confronted with yet another ghastly software package or computer interface which is unusable without considerable (indeed mind altering) training. And yet, surely usability is one of our most vital missions or requirements when designing and building a product (or indeed in delivering a service).
Dear Colleagues
Perhaps like you, I tend to get somewhat peevish when confronted with yet another ghastly software package or computer interface which is unusable without considerable (indeed mind altering) training. And yet, surely usability is one of our most vital missions or requirements when designing and building a product (or indeed in delivering a service).
Design for an Orang Utan Brain
I always suggest in our software projects, much to amusement of our programmers, that you should design the (often, software) interface so that even an orang-utan can sensibly use it. As engineering professionals, in our pursuit of efficiency and technical excellence we often lose sight of the key issue that eventually a human will be using our product. Whether it is a chef in a kitchen pressing the button on a mixer, an operator controlling a nuclear reactor or indeed you - trying to grasp how to record a TV program on your new video recorder.
Usability is defined as: ‘the degree to which something—software, hardware, or anything else—is easy to use and a good fit for the people who use it . . . It is whether a product is efficient, effective, and satisfying for those who use it.’ (from the Usability Professionals’ Association).
Steve Jobs was Ruthless
From a computer perspective (as you would expect!), Apple has the highest rating of usability of all computer users (in a recent survey rated at 80%, compared to the pack of computer vendors lurching around at 60%). Steve Jobs of Apple was ruthless in his pursuit of usability – for example, the iPod has a very simple “usable” interface (designed for use by an orang utan!).
User Manuals are Often Ghastly
As some of the old hands would remember, when we design engineers and technicians had designed the product, we sat around with a technical writer and put together a manual and documentation on how to use it. At the same time, we often did a test with a few clients on how they perceived the product and then made some changes to make it more user friendly and usable. As products became more complex, these instruction manuals became larger and more unwieldy. And often required training in how to read the manual and thence the product. The final stage was to place the gigantic product manual on an accompanying CD (supposedly to save paper but really to save the vendor money); which of course no one read. We have now reached the stage, where the software package often has the help facility built into it with no written instructions available (if you are desperate you can search the internet for some manual). Apparently the software will proffer you appropriate help when you need it. Yeah. Right.
Incidents of horrible usability
I can still remember incidents of products of horrible usability. A firm in Boston designed and sold us an expensive sequence events recorder for recording power system protection events which required intricate care in setting up (using a poorly written instruction manual with parts still handwritten). When we reverted back to the original design team for help (technical support had long since abandoned us), their unforgettable rejoinder to us was: ‘Have patience; together we can make a better product’.
Or a supposedly comprehensive SCADA software product which came with a deluge of manuals (relating only to the operating system and nothing on the actual SCADA software).
As we all know (from previous experience) many software vendors simply release their program to the unwary masses without comprehensive testing with the idea that they will let the market be the test bed. This is often due to the costs of development having overshot the budget and the time to completion has also long since been exceeded with the consequent urgent need to get the product to market as soon as possible.
The Science of Usability Components
As Jakob Nielsen remarks - usability has five main components:
- Learnability: How easy is it for users to accomplish basic tasks the first time they encounter the design?
- Efficiency: Once users have learned the design, how quickly can they perform tasks?
- Memorability: When users return to the design after a period of not using it, how easily can they re-establish proficiency?
- Errors: How many errors do users make, how severe are these errors, and how easily can they recover from the errors?
- Satisfaction: How pleasant is it to use the design?
How to improve the usability of our designs
- Probably the quickest way to improve usability is to get hold of some typical independent users (outside your department and indeed your company preferably)
- Get the users to perform typical tasks without any intervention from you
- Observe what the users do / where they succeed / and where they have difficulties. Don't coach or help them; let them work on their own and let them explain the problems.
- Keep iterating the process by improving the usability and let new independent users again test it out
As Donald Norman remarks: Beauty and brains, pleasure and usability — they should go hand in hand.
Thanks to the inimitable Donald Christiansen of the IEEE for a thought provoking article; and Jakob Nielsen on his web site: http://www.useit.com/ (focussing mainly on web usability).
Yours in engineering learning
Steve
Mackay’s Musings – 21st June’16 #605
780, 293 readers – www.eit.edu.au/cms/news/blog-steve-mackay
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
Here is one for the PC master race. The University of California, Davis, is in the news for creating a new 1000-core "kilo-core" processor. Say what? Yes. The university's Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering have created a processing chip that is able to handle 1,000 independent processors. This would be considered the world's first kilo-core processor, the engineers said. Unless there is someone else out there who can take them up on the challenge and prove that something as impressive has already been built. The chip completely destroys the last record that saw only 300 processors on a multi-core chip.
The researchers also ensured that the chip is energy efficient. They say it can be powered by a single AA battery. The researchers showed their creation off at the 2016 Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits.
 Bevan Baas, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC Davis, who was at the helm of the project, said: "To the best of our knowledge, it is the world's first 1000-processor chip and it is the highest clock rate processor ever designed in a university."
Bevan Baas, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC Davis, who was at the helm of the project, said: "To the best of our knowledge, it is the world's first 1000-processor chip and it is the highest clock rate processor ever designed in a university."
So who funded the thing? Unsurprisingly, IBM did.
But how fast does it really go? Baas said that 1,000 processors could handle 115 billion instructions per second. Another benefit of the independent processors being powered individually, the processors could shut themselves off to save battery life when they aren't being utilized.
So what do we do with a kilo-core processor? What can we use it for?
The truth is a lot of processes, however, it wouldn't be consumer-ready (for now) due to a hefty price tag. The team is certain it can be used for "wireless coding/decoding, video processing, encryption" and other large data applications. IBM already has a supercomputer that is on a top 5 list of the fastest computers in the world. Research into these kinds of microchip processors could see their computers becoming even faster.
Source: UC Davis
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Developments
The University of Michigan knows how important nanotechnology is. Engineers all over the world are actively busy with nanotechnology, that can be worn outside of the body, but also exist inside a body. Biomedical applications of nanotechnology have a long list of advantages if perfected. Now, researchers from the university have begun to work an injectable computer that uses radio frequencies to communicate with machinery outside of the body. Fancy having a WiFi connected body?
The engineers say that an injectable computer could help measuring tumor pressure inside the body, as well as other medical applications. At the helm of the project is David Wentzloff, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Michigan. The battery-operated computer was crafted for a project the university was running that encouraged students to build something that could "boost the evolution" of the Internet of Things.

So, what the engineers at the University of Michigan have done, is connected our bodies to the Internet of Things. As facetious as that sounds, it is a legitimate statement for the future of the Internet of Things.
David Blaauw, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Michigan, and another researcher attached to the designing of the injectable computer said: "We have incorporated in our system, a radio. Typically in the past, we've only been able to go a couple centimeters of distance. That's really small. Now, what we've done here is made a new type of antenna that can go much longer distances but is still small enough that it can be put inside a syringe."
Wentzloff said that the computer would be able to definitely measure the pressure of tumors if the computer was injected into a patient. It could also track how well chemotherapy is working inside a patient. He said: "The size of a tumor is directly correlated to the pressure of the tumor. When you are administering chemotherapy, you can use pressure as a way of measuring the progress of the treatment. The primary challenge there is when you inject a device to try and measure the pressure, which scar tissue forms you are not getting a good reading. These millimeter-scaled injectable sensors are a minimally invasive way to measure the pressure inside a cancerous time."
The issue that researchers have had in the past is that the human body absorbs most of the electromagnetic radiation previously making it difficult to connect devices together through radio frequencies. The engineers went to work and produced a radio that can speak to another device by up to a foot outside of the body.
Source: The University of Michigan
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Category: Industry
This Thursday Britain will make a decision. The decision is whether to leave the European Union or remain in the position they currently fulfill. As the day draws closer, engineering experts have unequivocally supported a 'STAY' vote. Experts say that if Britain does leave the European Union, they might be cutting off their noses to spite their face, especially in engineering industries. And the warnings keep streaming in.
"The fact that we source talent from the best universities in continental Europe is to the benefit of the UK economy because they help us to design infrastructure in the country," said Chief Executive of WS Atkins Plc, Uwe Krueger, speaking to Reuters News Agency.
 We have already reported what leaving the EU means for civil engineering due to already spiraling figures in the industry. The data done by market analysts shows that civil engineering activity in the country had slowed down. The Brexit vote has notoriously damaged steel workers' outputs significantly.
We have already reported what leaving the EU means for civil engineering due to already spiraling figures in the industry. The data done by market analysts shows that civil engineering activity in the country had slowed down. The Brexit vote has notoriously damaged steel workers' outputs significantly.
However, now experts like Krueger are warning that A-grade engineering graduates will be last in line when it comes to engineering talent. Rolls-Royce is another engineering company that has said it would be better for their interests if Britain remained in the EU. The company drafted a formal letter that said their stance is that they want to remain 'IN'. Chief executive, Warren East, has been quoted saying that their new engine testing plant could be in danger of losing profits if Britain exit the EU.
He was quoted from a BBC Radio interview: "We're making investment decisions all of the time about where to place different parts of our operation, and uncertainty created by Brexit puts a lot of those decisions on hold and that pause is something that our US competitors don't have to cope with. That's why it's not good for us."
It's not only Britain's own industries that might struggle to recover from the lack of investment after a hypothetical 'OUT' vote. According to the Wall Street Journal, German exports estimations will have to be tweaked if Britain exit the EU.
The president of the Federation of German Wholesale, Foreign Trade, and Services, Anton F. Börner said: "Brexit leads to insecurity and a loss of trust over the years. This is poison for the economy in the UK and in all of Europe."
The fact of the matter is, the polls have been 50/50 in the lead up to the referendum and only by Thursday will we know whether or not to keep focused on how a Brexit could affect engineering in the UK.
Blog - Steve Mackay
EIT's Technical Director, Steve Mackay, enjoys keeping his blog up-to-date with useful tips and current industry matters for his fellow colleagues. He has a loyal and expanding following base reaching over 300,000 people around the world.
Student Stories
In this section you have the opportunity to read and listen to EIT students talking about the reality of the programs. Discussions are wide-ranging and include information about the study commitment required, the value of the qualification in their careers, the relevance of the subject matter, future pathways, and more. They provide valuable feedback for you to take into account before you decide to join one of our programs.
Career Information
Latest career information including industry research, podcasts, blogs, life hacks and general information about how you can make the most out of your career.
Education
Here you will find out more about the latest trends and developments within education worldwide, along with some helpful articles regarding study tips and keeping on track with your studies.
Developments
The latest innovation and inventions from the world of engineering can be found here. Learn about advances in technology and how they can make a real difference within your industry.
Announcements
Keep up to date with the latest announcements from the Engineering Institute of Technology. In this section you can read more about new courses, new recognition from professional bodies, our Excellence in Teaching Award, upcoming free webinars and much more.
Monthly Update
We understand that you may not have time to read all the articles that we post, so our monthly update gives you access to some fascinating articles which cover the best of the months news in a compact format.
Engineering Resources
The key objective of the Engineering Institute of Technology is to provide outstanding practical engineering and technology education. Together with several industry and educational partners we gladly share the following resources and information to assist you along your professional development path. Please note that some of the articles will open a new internet browser tab and redirect you to other partner websites.
