Developments
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Additive manufacturing is the process of manufacturing a material object through layer-by-layer technology enabled by computer-aided design technology. Or at least it used to be. A new kind of rapid prototyping is on the rise. Rapid prototyping is a useful process for scientists and engineers alike, who use 3D printing technology to rapidly manufacture objects for both theoretical and practical uses. Rapid prototyping allows for the creation of models and parts that could be used in engineering applications. In some applications, it used to take an idea and display it as a working model or prototype. A tool for engineers to envision what the end product of something might look like, or actually manufacture a tool necessary for their projects, or even produce the product they are going to be selling.
According to T.S. Srivatsan and T.S. Sudarshan's book: Additive Manufacturing: Innovations, Advances, and Applications, rapid prototyping has achieved for big successes in the development of products:
1. Reductions in both time and costs
2. Enhanced human interaction
3. Possibility of creating any shape that would otherwise be difficult to produce
4. A shortened development cycle
However, the technology has progressed to the point where rapid prototyping could forever be changed. In 2015, Michael Breme, the head of Audi's tool design, described how 3D printing was benefitting their business. He said: "It enables us to produce the parts faster

and more cost-effectively. For example, with a 3D printer, we don't have any waste like we would with metal cutting, which means we're faster and more effective." However, back in 2015, there was only one problem with 3D printers. They weren't fast.
The 3D printing start-up company, Carbon, has received $81 million in funding from global investors this year. The investors include BMW Group, General Electric, Nikon and JSR Corp, amongst others. The company now has $222 million in funding that it will use to further their particular kind of 3D printing. The company utilizes Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP). Their printer, the Carbon M1 printer produces a solid object from a small tub of liquid plastic through new stereolithography (SLA) rapid prototyping technology. They're making rapid prototyping even more rapid.
How do they do it?
Well, what this printer does differently to other printers is all in the ultraviolet (UV) light projector. The projector purportedly 'projects' what the end product should look like and then pulls it out of the liquid polymer (resin). Instead of a laser physically redefining the CAD (computer-aided design) pattern over and over again, the CLIP technology uses UV light and oxygen to produce a mechanically sound object without the need for layer-by-layer technology. As a result, a chemical process known as photopolymerization occurs.
The CEO of Carbon, Joseph DeSimone, said: "This product lays the groundwork for addressing major gaps in additive manufacturing as we work with our customers to continually innovate and push the boundaries of product design and production."
Carbon says their method of rapid prototyping is one hundred times faster than conventional printers available on the market today.
Speaking of the 3D printing market. The rapid prototyping materials (the actual resins used to print) market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 26.8% from 2016 to 2021. Markets and Markets estimate that the rapid prototyping materials market will reach USD 903.8 million by 2021. According to another report by Wohlers Associates, the entire 3D printing market will peak at $10 billion by 2017. They also confirmed that last year, 278,000 desktop 3D printers were purchased, showing that 3D printing is also becoming popular among hobbyists.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Engineers in North Dakota, in the United States, are embroiled in a stop-start construction build of what would be the Dakota Access Pipeline. Due to citizen pressures in the form of protesting, the project has been halted by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit. Meaning, that a federal court under the Obama administration has stopped the pipeline progressing, for now. Obama previously completely canceled a pipeline that was meant to run from Canada to Texas, named the Keystone XL Pipeline.
The engineers in North Dakota are from a company named Dakota Access, who are made up of Energy Transfer Partners. They have been assembling the pipeline that is to span four states wide. It will reportedly cost $3.8 billion and will transport 470,000 barrels of "light sweet crude oil" from North Dakota, all the way to Patoka, Illinois, twenty-four hours a day.
The engineers say the project will create 8,000 to 12,000 new local jobs during construction. They also

say that the pipeline will lead to millions "in state and local revenues" for the states it spans across. There's just one problem, however. The proposed pipeline reportedly cuts through land sacred to the Lakȟóta people ; indigenous peoples of the Great Plains of North America. The Rock Sioux Tribe also expressed concerns that it could impact the drinking water in the nearby areas where they are stationed.
The engineers have also tried to assure the public that a pipeline is the safest way to transport crude oil. However, the tribes and the local protestors are concerned about hypothetical leaks or accidents that might befall the pipeline, leading to oil spills. In the past, oil would be transported by rail, which led to fiery derailments.
The BBC confirms that the protests linked to the North Dakota pipeline have brought together the largest Native American gathering in 100 years. Dave Archambault II from the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe, who are protesting against the pipeline said: "It is a pipeline that is threatening the lives of people, lives of my tribe as well as millions down the river. It threatens the ancestral sites that are  significant to our tribe."
significant to our tribe."
The Energy Transfer Partners are not backing down. They say they are committed to completing the pipeline's construction and are imploring the Obama administration to lift their moratorium so that they can continue building the Dakota Access Pipeline.
One thing the engineers are right about is how important pipelines have been to American energy production. On their website, Dakota Access write: "Pipelines play a vital role in our daily lives and provide critical links between the sources of energy in production fields and end-users or consumers. Without pipelines, the majority of the United States would not have access to American oil and natural gas..."
However, the continued fight to cut fossil-fuel emissions, around the world, has meant that pipeline systems in oil and natural gas have seen some criticism. Whether or not the Dakota Access Pipeline's construction will continue remains to be seen.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
What do nanotechnology, polyethylene (plastic), and clothing have in common? Well, they can all be combined to make clothing that helps the person wearing it stay cool, especially in hotter climates. Listen up, engineers who work in high-temperature workplaces! Engineers at Stanford University have created a plastic-based material that can be "woven" into items of clothing. The researchers published their findings in the Science journal, under the title: Radiative human body cooling by nanoporous polyethylene textile.

The plastic textile reportedly cools the body in two ways. According to the researchers, the textile is made from a nanostructure that allows the same kind of perspiration evaporation that normal clothes do. However, it also allows body heat, in the form of infrared radiation, to pass through and out of the clothing which is something that normal clothing doesn't do.
What do they plan to do with this newly made textile? Well, it could cut down energy costs because there will be less dependence on air-conditioning systems. Or at least, that's what the engineers would like. Yi Cui, an associate professor of materials science and engineering and the man at the helm of the project at Stanford said: "If you can cool the person rather than the building where they work or live, that will save energy."
Shanhui Fan, a professor of electrical engineering said: "Forty to 60 percent of our body heat is dissipated as infrared radiation when we are sitting in an office. But until now there has been little or no research on designing the thermal radiation characteristics of textiles."
Have we finally reached the breakthrough this Sasol ad hypothesized so many years back?
How did they do it?
In classic nano-engineering fashion, the researchers brought engineering disciplines from all corners together to develop their textile. Working with polyethylene they tested different variants. Eventually, they discovered a variant that was commonly used in batteries. The engineers then treated the variant with chemical processes, until the variant allowed water vapor molecules to be evaporated. The engineers indicated that the water evaporates through "nanopores" in the plastic, which makes the fabric breathable. What they found is that the plastic with, nanostructures built-in will ensure that body heat escapes the clothing. It will also "scatter" any heat that is trying to make it into the clothing.
The material allegedly makes the wearer 36 Fahrenheit (2.7 celcius) cooler in body temperature than conventional clothing. The engineers say this difference in heat could prevent someone from having to turn on a fan or an air-conditioner. Moreover, the engineers say they will keep on working on the material and improve it.
How much will it cost if it does make it to the market? Cui said: "If you want to make a textile, you have to be able to make huge volumes inexpensively." Therefore, the engineers are going to try and keep the cost as low as possible so that it could be affordable to the consumer public.
"In hindsight, some of what we've done looks very simple, but it's because a few have really been looking at engineering the radiation characteristics of textiles," Cui added.
Source: Stanford News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Internet-less African towns will have to wait for their internet connections a little longer. A satellite belonging to Facebook - for the purposes of supplying the internet to sub-Saharan Africa - was destroyed by an exploding SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Thursday. There were no injuries reported, however, there were reports of the ground rumbling in areas miles away from the blast site. The estimated losses were said to be $200 million.
Those looking for answers as to what caused the explosion anxiously waited to hear from SpaceX CEO Elon Musk. He tweeted:
Loss of Falcon vehicle today during propellant fill operation. Originated around upper stage oxygen tank. Cause still unknown. More soon.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) September 1, 2016
CEO of Facebook Mark Zuckerberg, who, at the time, had made his way from Nigeria and into Kenya on business, took to his platform to express his dismay. He said:
As I'm here in Africa, I'm deeply disappointed to hear that SpaceX's launch failure destroyed our satellite that would have provided connectivity to so many entrepreneurs and everyone else across the continent.
Fortunately, we have developed other technologies like Aquila that will connect people as well. We remain committed to our mission of connecting everyone, and we will keep working until everyone has the opportunities this satellite would have provided.
Zuckerberg, of course, talking about their solar powered, internet-via-drone project that Facebook's engineers have been testing earlier this year.
The explosion comes at the wrong time for SpaceX. After a host of unsuccessful rocket landings, they finally started to get things right with their Falcon 9. The engineers successfully managed to land the Falcon 9 on a barge in the sea after launching, twice. However, in June 2015, a rocket meant to deliver supplies to the International Space Station also went up in flames. Then, yesterday's explosion occurs and adds to the growing list of embarrassing mishaps SpaceX has been seeing.
SpaceX has also announced that it will work with NASA to perform an unmanned mission to Mars by 2018. Stephanie Martin, the spokeswoman for the Kennedy Space Center, unfortunately, had to talk about what effects this blast would have on the future Mars missions. She said: "It is too early to know what impacts there would be (with the manned flights) and it would be inappropriate to speculate at this time. NASA remains confident in its commercial partners, including SpaceX."
The engineers from SpaceX confirmed that the incident took place at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral, and will now ground any further projects until they know what caused the explosion for sure. They reportedly had another launch planned for Saturday, but that will reportedly not go forward until engineers can say what really caused the Falcon 9's explosion.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
In the mere eight months that 2016 has seen, industrial robotics has been a hot topic. Electronics companies, even shoe factories, are now fully automating some of their more repetitive tasks, prioritizing the efficiency of a robot above the efficiency of a human being. China has called on the expertise of German engineering to try and equip their factories with the very best industrial robots, and Barack Obama has been informing steel workers that jobs that have been replaced by automated systems might never come back. There hasn't been a better time for industrial companies to own industrial robots than now.
Whose market is it anyways?
 It's all about the industrial robot, it seems. Something no one expected, however, was that non-industrial robots would surge forward in the markets and overtake the market size that industrial robotics have been enjoying. According to a report by a research company who specialize in robotics - Tractica - industrial robots will only see 41% of total robotics revenue, whereas they currently hold 50%. The other 59% will belong to non-industrial robotics. The report was entitled Robotics Market Forecasts.
It's all about the industrial robot, it seems. Something no one expected, however, was that non-industrial robots would surge forward in the markets and overtake the market size that industrial robotics have been enjoying. According to a report by a research company who specialize in robotics - Tractica - industrial robots will only see 41% of total robotics revenue, whereas they currently hold 50%. The other 59% will belong to non-industrial robotics. The report was entitled Robotics Market Forecasts.
Tractica defines these non-industrial robots as consumer robots, enterprise robots, military robots, unmanned aerial vehicles, and autonomous vehicles. The director of research at Tractica , Aditya Kaul, said: "The definition of a robot is in flux and traditional robot manufacturers that have been building and supplying robots for decades have seen this industry undergo a dramatic transformation in the past few years."
Considered in this context, it is not surprising to see why non-industrial robots are doing so well. The FAA published new guidelines for unmanned aerial vehicles this year, in a move they say could produce 100,000 new jobs and generate $82 billion for the American economy. Home assistant robots are also slowly making their way to the market, as well. We focused on ASUS's Zenbo Robot recently. A robot that will be joining a host of new automated technologies for the home.
Furthermore, Tractica estimates that the robotics industry will grow from $34.1 billion in 2016 to $226.2 billion by 2021, solidifying a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 46%.
Industrial engineers, fear not
One novel idea that would see industrial robots gaining in the market, is using industrial robots for non-industrial applications. As these engineers have shown, industrial robots could even be used as the next generation of tattoo artists. The video show's the world's first tattoo performed by an industrial robot. After months of preparation, the engineers tirelessly worked to show that even industrial robots, in their robustness, can be precise enough to delicately work on a human object.
ABB Robotics have also outlined what the most popular applications for industrial robotics are. These applications will be keeping industrial robotics in the market due to their practicality, industrial companies have seen their usefulness. ABB has supplied many industrial engineering companies their robots, building more automated operations all over the world. Their top 10 list is as follows:
- Arc welding
- Spot welding
- Materials welding
- Machine tending
- Painting
- Picking, packing and palletizing
- Assembly
- Mechanical cutting grinding, deburring and polishing
- Gluing, adhesive sealing and spraying materials
- Other processes (inspection, waterjet cutting, soldering)
Source: Tractica
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
It was bound to happen at some point. The Federal Aviation Administration - more widely known as the FAA - have begun their crackdown on lithium-ion batteries. This proverbial shot across the bow from the FAA is a warning to engineering companies developing and utilizing lithium-ion batteries, to tighten up battery safety. 36 months ago, what are being called "fire-prone" lithium-ion batteries caught fire on a Boeing 787, alerting the public to the fact that some lithium-ion batteries could suffer from being susceptible to a process known as "thermal runaway". In this process, the heat inside and outside of a lithium battery stretches past what it can handle, whereafter the batteries become flammable.
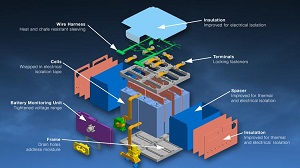
Boeing's engineers were scrutinized for the batteries catching fire and were encouraged to redesign the batteries. The aircraft uses the lithium-ion battery for backup power. Now, the batteries are stored in "fireproof containers" (pictured left) that ensure, if a fire does break out, it prevents it from escaping into the plane. Ventilation tubes are now also in place, so that if any chemical explosion occurs, the fumes are transferred to the outside of the aircraft.
According to the Wall Street Journal, the FAA have delivered their safety guidelines for the 737 passenger jets and the 767 cargo jets to Boeing. The new terms suggest that Boeings' battery design should "eliminate the potential for uncontrolled failures". If uncontrolled failure does happen, the FAA warns that the company should take the necessary steps to ensure that any onboard passengers will remain safe. The safety regulations are not only directed at Boeing alone, the FAA is hoping that all aircraft companies will abide by their new guidelines.
However, Airbus disagrees with the new guidelines, in terms of the metal casing for the backup lithium-ion batteries. The FAA is suggesting Airbus fit their A350 aircraft with the precautionary mechanism, but the company seems reluctant to sign off on the idea. They've been saying "no" since last September. The company maintains that its batteries are smaller and safer than Boeing's and won't need the fireproof containers.
It was Airbus's Executive Vice President of Engineering Charles Champion, in an interview to Flight Global, who said: "If you start to put a huge coffin around the battery system in place then you lose all the benefit of the lithium-ion battery." Airbus utilize batteries built by Saft, a world leader in renewable energy technology that was recently bought by Total S.A.
 Fire-prone lithium batteries are nothing new. The United States's Consumer Product Safety Commission reported that by July 2016, up to $2 million in property damage - as a result of 60 fires - were caused by so-called "hoverboard" technologies (pictured left). The multicell lithium battery packs within the hoverboards - that house 20 lithium ion cells per board - have been declared as a fire hazard. Once the lithium batteries inside surpass their heat thresholds, they tend to catch fire. If one catches fire, all of them follow.
Fire-prone lithium batteries are nothing new. The United States's Consumer Product Safety Commission reported that by July 2016, up to $2 million in property damage - as a result of 60 fires - were caused by so-called "hoverboard" technologies (pictured left). The multicell lithium battery packs within the hoverboards - that house 20 lithium ion cells per board - have been declared as a fire hazard. Once the lithium batteries inside surpass their heat thresholds, they tend to catch fire. If one catches fire, all of them follow.
"After months of excellent, round-the-clock work by our engineers, investigators and compliance officers, CPSC has secured the recall of more than a half-million hoverboards by 10 different companies," said CPSC Chairman Elliot Kaye.
Source: Wall Street Journal
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Engineers use emojis too. Except they see them graphically represented on a piece of software that isn't a chatting platform, but rather, a software that is showing how happy an industrial facility is. By happy, we mean, how efficient and how streamlined an industrial process is going -- which in turn makes an engineer happy. We are talking of course about the Human Machine Interface that displays data in facilities all around the world. Humans need to see data presented to them in ways they would understand. That is why Human Machine Interfaces are important.
Why do we need HMIs?
 Engineers need HMIs to show exactly how the industrial control systems - the SCADA systems, the PLCs and more - are operating. The HMI will even show the engineer when security parameters have been breached. HMIs are important to the efficiency of an industrial operation, thanks to virtualization.
Engineers need HMIs to show exactly how the industrial control systems - the SCADA systems, the PLCs and more - are operating. The HMI will even show the engineer when security parameters have been breached. HMIs are important to the efficiency of an industrial operation, thanks to virtualization.
Virtualization of industrial operations will be a very important feature in a future that will see another layer of added interconnectivity thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT). The data that would be available to engineers with these updated systems will ensure that industrial facilities perform faster and more efficiently in the future. This is due to the real-time nature of the HMI software that would display the industrial processes of the facility immediately.
Modern industrial facilities are growing. The amount of hardware in the industrial facilities including the number of remote devices that need to work in cohesion with the hardware. It requires a system to unify the data input sources so that everyone on the facility is on the same page. This is where the HMI software comes in.
For instance, Wonderware's InTouch platform is used in one-third of the world's industrial facilities. It includes graphical representations of general machine security, the working machinery systems within a factory, a number of times a button had been pressed and many more applications.
Some PLCs (programmable logic controllers) come with HMIs in a package deal these days. Those are integrated HMIs, but you also get non-integrated HMI solutions that an engineer can use in his/her industrial facility.
Continued innovation
As the Internet of Things continues its mission of getting the world to embrace the fourth industrial revolution (Industrie 4.0), engineers will be working with human-machine interfaces more than ever before.
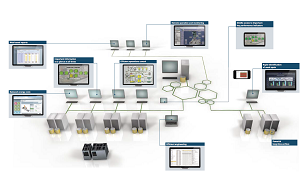 Siemens' SIMATIC WinCC V7 is another HMI solution that advertises fewer downtimes for industrial facilities, rapid access to data, and the fast integration of existing hardware. The retrofitting of HMI software to already-existing SCADA systems is something engineers are looking for in industrial facilities that cannot afford to update the entire system. It also unifies all of the systems and allows for employees of an industrial facility to see the compiled and real-time data that keeps them all on the same page. The business side of an industrial operation instantly benefits from the HMI's virtualization of operational data.
Siemens' SIMATIC WinCC V7 is another HMI solution that advertises fewer downtimes for industrial facilities, rapid access to data, and the fast integration of existing hardware. The retrofitting of HMI software to already-existing SCADA systems is something engineers are looking for in industrial facilities that cannot afford to update the entire system. It also unifies all of the systems and allows for employees of an industrial facility to see the compiled and real-time data that keeps them all on the same page. The business side of an industrial operation instantly benefits from the HMI's virtualization of operational data.
Cybersecurity of SCADA systems and other ICS systems rely on HMI interfaces so that engineers are aware when systems have been targeted, or if there is an operational issue in industrial facilities. HMI is central to the SCADA databases' visual representation as well. Furthermore, the HMI can display the operational data in graphs and other graphical representations. With the number of remote operators, with the added gigabytes of data that will be observed by industrial machinery, cybersecurity for ICS is absolutely necessary. HMI assists and makes this process easier thanks to the visualisation of networks and systems.
To become more knowledgeable and proficient in HMI system competency, engineers or technologists can get their professional certificate of competency in Wonderware InTouch HMI through the Engineering Institue of Technology. The course will teach HMI applications from scratch through online e-learning. Designing graphics and animations, including the configuring of alarm systems for security purposes, are also included in the course. Follow the link to read more about it.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
It was just the other day that Switzerland opened the longest railway tunnel in the world. Now, Norway is planning the world's first underwater tube-shaped tunnel. A masterpiece of structural engineering that will consist of two 1,200 meters (4,000 ft) concrete tubes that will lie 30 meters below the surface of the Norwegian sea. The tunnel will connect the city of Kristiansand to the city of Trondheim. Norway already has the record for the largest road tunnel in the world ;The Lærdal Tunnel is 15.23 miles long (24.51-kilometers). It looks like they're on their way to another world-first record.

According to Wired, if you were to drive from Kristiansand to Trondheim it would take you 21 hours on the roads that already exist. Not to mention, the number of ferries you would have to take due to Norway's notorious fjords and difficult to navigate mountainous areas. There are 7 ferry rides that need to happen to complete the journey from Kristiansand to Trondheim. The tunnels are set to make the journey a tad more streamlined. The engineers behind the project say that the new underwater tunnels could eliminate 10 hours of travel time once built. Norway will be funding the project, with a handsome $25 billion. Construction is expected to be completed by 2035.

The tunnel will be held up by pontoons, that would be secured with trusses to keep them in one place. The engineers confirmed that going underwater by 60 to 100 feet would ensure that should storms happen, the floating tunnel would be safe.
Arianna Minoretti, a senior civil structural engineer from the Norwegian Public Roads Administration (NPRA) says that they might also bolt the tunnels to the bedrock to ensure further stability. "Having this connection means that people there do not have to wait for a helicopter to go to the hospital." She also says that driving through the tunnel, to a driver, would feel like any other tunnel.
The NPRA also maintain that the original scenery will not be disrupted so those who still wish to make the journey the long way around will still be able to do so. However, those who want to shave some time off of their travel times will find the tunnels very useful. The idea of the underwater tunnels might also inspire other countries to follow suit with similar tunnel designs once the success of the Norwegian tunnels is shown.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
With two weeks to go, the Rio Olympics' grim outlook continues. The Australian Olympics team has a bone to pick with the civil engineers that constructed the Athletes Village. They have complained that the village is "not safe or ready" to live in. The complaints range from blocked toilets to exposed electrical wiring. The Aussies have refused to live in the apartments and have rather opted for hotels in the surrounding area until their building is ready. The Australian team's head of mission, Kitty Chiller, did not mince any words when talking to the media.
"Problems include blocked toilets, leaking pipes, exposed wiring, darkened stairwells where no lighting has been installed and dirty floors in need of a massive clean. This is my fifth Olympic Games, I have never experienced a Village in this lack of state of readiness at this point in time," Chiller said in a statement. She did, however, say that the rest of the Village looked to be one of the more beautiful villages seen in recent history.

Mayor of Rio de Janiero, Eduardo Paes has refuted the claims and has hit back at the Australians. He has said that Rio's village is "more beautiful and better" than Australia's village that was built when they hosted the 2000 Olympics in Sydney. However, the Australians maintain that the Rio Village is barely habitable.
Mahe Drysdale is an olympian on the Kiwi rowing team for New Zealand this year and has moved into the Village. He took to Instagram with the photo you can see to your left, saying: "All is good, few finishing touches still to be made but when you arrive at 5am on opening day you can't expect it to be perfect."
Similarly, the South African men's under-23 football team landed in Rio and reported that their specific apartments were up to standard. Rio de Janiero will see 15,000 to 18,000 athletes descending upon the Athletes Village and hopes to have it fully ready before the opening ceremony of the Olympics, on August 6th. It is said to be the biggest Athletes Village in the history of the Games. Once the Olympics is finished, the apartments will be put on sale and advertised to the Brazillian public.
To get a clearer picture of the engineering endeavours Brazil has seen on the back of hosting another large-scale sporting event, José Roberto Bernasconi, the president of Brazil's architecture and engineering union spoke about the country's great achievements in engineering. He spoke to the Huffington Post earlier this year, saying: "Rio went through a transformation after it was decided that it would host the Games. There was a great change in mobility and urban infrastructure with the recovery of downtown Rio, the demolition of the elevated expressway, and the Museum of Tomorrow. Those are extraordinary man-made works, combined with the city's natural beauty. It is a gain."
Nonetheless, the engineers who have designed and constructed the buildings on the lead up to the Olympic Games will be heavily scrutinized if something goes wrong in the upcoming weeks. However, it seems that the initial reports of unhabitable conditions in the Athletes Village will be handled come opening day. The only thing left to say is: "Game on." To see more of the Athletes Village, take a look at this video compiled by RT:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Want to be a successful engineer? Have a master plan. Or better yet, have two master plans. Elon Musk, the CEO of SpaceX, Tesla Motors and co-founder of SolarCity, OpenAI and PayPal has released his second master plan. The master plans refer to the feats of engineering he hopes to achieve in the new future. Basically, a vision and mission statement as if he was sat in a job interview and asked: So, what do you want to achieve in the next ten years?
Musk says that ten years ago he penned his first master plan. And it looked something like this:
- Create a low volume car, which would necessarily be expensive
- Use that money to develop a medium volume car at a lower price
- Use that money to create an affordable, high volume car
And...- Provide solar power. No kidding, this has literally been on our website for 10 years.
 Now, Musk has released his Master Plan: Part Deux.
Now, Musk has released his Master Plan: Part Deux.
Firstly, Musk wants to create a "smoothly integrated and beautiful solar-roof-with-battery product that looks good". This is already in progress. Tesla and SolarCity have joined forces that will join up the efforts of both companies and see them integrating their current products into one ecosystem of solar technology. This will encourage more work into sending the Powerwall technology into a global marketplace.
Then, Tesla will be expanding into the freight truck world, developing what Musk calls the Tesla Semi. Musk says they will engineer freight trucks that reduce the cost of cargo transportation with engineers who worked on the Model S. Which means we would be looking at trucks that are powered by lithium-ion technology and would potentially be self-driving. The third item on Musk's new master plan was to secure self-driving mini buses as well. The company will also be working on pick-up trucks, adding to their long line of electric vehicles.
"As the technology matures, all Tesla vehicles will have the hardware necessary to be fully self-driving with fail-operational capability, meaning that any given system in the car could break and your car will still drive itself safely. It is important to emphasize that refinement and validation of the software will take much longer than putting in place the cameras, radar, sonar and computing hardware," Musk said.
This cautious nature of the language chosen by Musk here is on the back of incidents that relate to the AutoPilot software already inside their vehicles. One of Tesla's vehicles recently caused a fatal accident. However, Musk is still adamant that self-driving technology is the way to go and once their software is ten times safer than human drivers, they will take it out of the beta phase.
The final part of Musk's renewed master plan is to make sure that the electric vehicles they produce lead to a world where the consumer gets money back for providing energy to the grid. He simply calls it: sharing. It's not a new idea for energy management industries, however, it is a rarely practiced one due to the scarcity of electric vehicles. Nonetheless, the way it will work is, consumers will be able to opt-in to a Tesla shared fleet. This would be done by simply using an app that would then begin sharing some of the capacity of a charged lithium-ion battery, i.e. providing energy to the grid. Musk says: "Since most cars are only in use by their owner for 4% to 10% of the day, the fundamental economic utility of a truly self-driving car is likely to be several times that of a car which is not."
In summary, Elon Musks's Master Plan: Part Deux:
Create stunning solar roofs with seamlessly integrated battery storage
Expand the electric vehicle product line to address all major segments
Develop a self-driving capability that is 10X safer than manual via massive fleet learning
Enable your car to make money for you when you aren't using it
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Residential energy storage systems have seen a major uptake in Australia. LG Chem has said that Australia's interest in energy storage systems has signalled a "critical solar decade" for the country. 2016, in the first seven months, has been the biggest year for Australian residential home batteries due to entire suburbs receiving subsidised energy storage systems. 200 houses in Canberra received discounted Tesla PowerWalls in a pilot program that emphasized Australia's willingness to adopt residential energy systems.
Onwards and upwards, Tesla has announced that a second residential microgrid is being set up in  Australia. According to Seeking Alpha, a development named "Merri-green" in Melbourne will be receiving twenty Tesla PowerWalls connected to rooftop solar photovoltaic technologies. A single house's setup is said to be approximately $7400+ for the entire solar PV, storage unit, and energy management link.
Australia. According to Seeking Alpha, a development named "Merri-green" in Melbourne will be receiving twenty Tesla PowerWalls connected to rooftop solar photovoltaic technologies. A single house's setup is said to be approximately $7400+ for the entire solar PV, storage unit, and energy management link.
Earlier in April, PV-Magazine revealed that 170,000 households in West Australia would see rooftop photovoltaic energy solutions installed this year. The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) says that entire suburb microgrids present a unique opportunity for energy retailers, developers, and consumers alike - where everyone benefits. The microgrids will also supply energy to utility grids, selling energy back to the grid, which then gives consumers pay back benefits to renting out apartments and houses with rooftop PV solutions. Recent reports by GTM Research indicate that Australia's energy storage market would have grown by 37-fold between 2015 and 2020.
Australia aims to achieve 100% renewable energy by 2020. One of the ways they are trying to do this is by implementing dozens of microgrid solutions to entire suburbs. The country already has 5 gigawatts of energy produced by rooftop solar PV technologies. Australia is reportedly also used as the "testing field" for 27 battery suppliers, making the country one of the most important players in the energy storage industry.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Ever had a cell phone overheat when using a battery-heavy application like the GPS or playing a CPU-intensive game? Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have announced that they have perfected a 'sand' that could be used to cool down electronic devices. Electronic devices tend to run at high temperatures. What kind of sand are we talking about here? Silicon dioxide nanoparticles that are covered with a "high dielectric constant polymer". The researchers explain that the cooling effect is produced by the electromagnetic properties that arise once the silicon dioxide particles collaborate to ensure conductivity.

"We have shown for the first time that you can take a packed nanoparticle bed that would typically act as an insulator and by causing light to couple strongly into the material by engineering a high dielectric constant medium like water or ethylene glycol at the surfaces, you can turn the nanoparticle bed into a conductor," said Baratunde Cola, an associate professor at George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering.
The researchers published their findings in the Material Horizons journal, under the title High thermal in polaritonic SiO2 nanoparticle beds.
In summary, the researchers used ethylene glycol to coat the silicon dioxide nanoparticles with so that it turned into a conductor which increased heat transfer by 20-fold. Thus, the electromagnetic effect the nanoparticles have minimizes the amount of heat being produced.
"You could basically take an electronic device, pack these ethylene glycol-coated nanoparticles in the air space, and it would be useful as a heat dissipation material that at the same time, won't conduct electricity," Cola added.
The coated particles have a sand-like texture to them, hence the assertion that a sand could be used to cool electronic devices down. The researchers say there is still some work to be done due to ethylene glycol easily being evaporated, however, the research will continue until the heat dissipation inside devices is secured. The researchers also say that the coated nanoparticles would be an inexpensive way of ensuring heat is absorbed within electronics and is easy to produce. Sounds like a win for engineering.
Source: GA Tech News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Bridges need to be sturdy. It's just one of those things. If you don't build a sturdy bridge, what were you building one for, in the first place? A former researcher at the University of Warwick thinks that she may have perfected the method for building the perfect bridge. People are using the word 'indestructible'. The researchers attached to the product say a production method called 'form finding' could build a bridge that has no weak points. To get a clearer picture of what form finding structures are, we have to go back to 2008. Researchers at MIT wrote a report on Form-finding structures. They said that form-finding structures are "inherently characterized by the interaction of geometry and forces, the unique of long span dome, shell, and membrane structures."

However, it is a little more complicated than that. The structures are more inspired by nature than anything else. They're not your conventional structures. According to retired professor from the University of Warwick's School of Engineering, Wanda Lewis, form-finding methods will build indestructible bridges.
In a statement posted on the University of Warwick's website, Professor Lewis was quoted, saying: "Nature's design principles cannot be matched by conventional engineering design. Aesthetics is an important aspect of any design, and we have been programmed to view some shapes, such as circular arches or spherical domes as aesthetic."
According to Lewis, using a mathematical model to determine arch-shapes, the bridge will be held in place by pure compression and tension with zero bending stresses. Lewis published her works in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A, under the title Mathematical Model of a moment-less arch. world's first ultra-rigid indestructible bridge can be built.
The retired engineer allegedly did an experiment with a piece of fabric that lay in its natural shape, which was then frozen and inverted into a rigid object. Lewis then found the coordinates of the shape through computation and measured the gravitational forces of the object. What she found was that this upside frozen-in-place fabric arch caused a moment-less arch that was able to handle downward forces (see picture above).
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Self-driving technology will never stop being a hot topic until it is perfected and fully integrated into our society. Until then, engineers are having to grapple with the shortcomings of the technology to figure out how to create a fully safe, efficient, self-driving car. On June 30th, Tesla's Autopilot feature failed to notice a trailer in the way of a freeway, causing a fatal crash. Now, the National Highway Transportation Safety Administration has announced that it will be investigating all of Tesla's vehicles that have the 'Autopilot Technology Package'. The investigations could have ramifications on all automakers and engineers at companies who are trying to secure automated driving for vehicles.
Nonetheless, the investigations into Tesla didn't deter Audi and Nissan from announcing their own self-driving technology packages. Audi announced their self-driving car, Jack, to media in 2012, but are ready to implement the technology into the latest models. The car will notify a driver when the automated processes switch on inside the car, once the car is driving on the freeway. The car uses twenty sensors - stationed around the vehicle - which help it circumnavigate through traffic. The car has been shown off before, however, Audi's Senior Engineer Kaushik Raghu and President of Audi America, Scott Keogh, told CNBC that Audi will be launching another self-driving car in 2018. The car will reportedly control 60 to 70 percent of the driving of the vehicle. The Audi A7 already equipped with the self-driving technology has been driven on the world's fastest highway - The Autobahn - before.

Then it was Nissan's turn to show their new offering off. The company's new Serena vehicle would be equipped with their attempt at a self-driving technology called Nissan ProPILOT. A self-driving minivan - don't tell the soccer moms. The car will go on sale in Japan in August. Nissan - much like Tesla and Audi- are stressing that the system is not fully able to drive the vehicle to point A to point B right now, but will relieve some stresses during heavy peak time traffic.
"The point is it's not fully autonomous driving, but driver assistance technology, so it can't handle everything for you," Hideyuki Sakamoto, Nissan's executive vice president, said.
Based on the video Nissan has released, the camera technology in the vehicle will keep a car in the center of a lane and maintain whatever speed it might need to ensure the safety of the passengers inside the car. By 2018, Nissan says it wants to move towards highway multi-lane driving with ProPILOT. By 2020, the company wants a fully automated car that does not need a driver to control.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Does the future success of the Internet of Things lie in the collaborations between companies joining their expertise together for a one-size-fits-all approach to IoT? IBM and Cisco think so. The two companies are joining forces to bring a cloud-based IoT-connected workplace kit available. IBM would be bringing their artificial intelligence supercomputer, Watson, to the table. Cisco would be bringing their connectivity equipment and data producing apps.
 Cisco's hardware will work alongside Watson software to produce IoT analytics data for industrial and other enterprise operations that will have real-time data ready for analysis. The companies say that the solution will bring new collaborative tools that will see employee efficiency increasing. Cisco's Edge Analytics software ensures that data is shown in a virtualization that is easy to peruse so that engineers know exactly how efficiently a system is working, Using IBM's Watson and connections APIs as well as Cisco Spark and WebEx APIs, the companies have produced a fully integrated IoT system.
Cisco's hardware will work alongside Watson software to produce IoT analytics data for industrial and other enterprise operations that will have real-time data ready for analysis. The companies say that the solution will bring new collaborative tools that will see employee efficiency increasing. Cisco's Edge Analytics software ensures that data is shown in a virtualization that is easy to peruse so that engineers know exactly how efficiently a system is working, Using IBM's Watson and connections APIs as well as Cisco Spark and WebEx APIs, the companies have produced a fully integrated IoT system.
"While we have a focus on Watson as a cloud-based system, for certain clients with remote or autonomous operations we need something else. Shipping, mining, and many factories all operate at the edge of the computer network, where bandwidth might be expensive or unreliable," said Harriet Green, general manager at IBM's Watson IoT, Commerce, and Education department. This means, offshore drilling facilities can now have an IoT-connected solution that exists in its own cloud network that can display analytics on demand without having to take that data back to the shore.
The companies say that their solution will take away repetitive tasks that employees usually get distracted by, by automating those processes. Mundane tasks can now be done with the cloud-based solution. Which means, scheduling, note-taking and meetings can also be done on an integrated online platform within an enterprise.
“With our combined technology strengths and understanding of how teams get work done, IBM and Cisco can deliver the next generation of collaboration tools needed to cultivate innovation and drive productivity. By incorporating analytics and cognitive technologies into these solutions, we expect them to be able to learn what is important, in context, and take the right actions on behalf of the user," said Inhi Cho, the General Manager of IBM Collaboration Solutions.
Source: IBM
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Australia's clean energy storage market is growing at a speed that other countries are struggling to keep up with. The market has always been forward thinking and proactive. Now, South Korean company, LG Chem is using Australia as their platform, to launch their new battery storage solution. LG Chem's energy storage units have already been previewed but are finally ready to launch to consumers.
The company had initially announced that it would make 600 Residental Energy Storage Units (RESU6.4EX) available to "local distributors" in Australia, last year. Now, the company is saying it will have produced 3,000 units in 2016 and will continue to produce more energy storage units in 2017.  This signals that the company is entering the market and is here to stay. They are convinced that the energy storage market will be growing in the upcoming years. The company has been quoted saying that Australia is in a "critical solar decade".
This signals that the company is entering the market and is here to stay. They are convinced that the energy storage market will be growing in the upcoming years. The company has been quoted saying that Australia is in a "critical solar decade".
"We see a quiet solar revolution brewing and we strongly believe that LG Chem will be at the forefront of this transformation to help unlock the true value of solar storage and better enable the ecosystem. We welcome competition too. We are positive that when more people adopt the RESU6.4EX in Australia, the market will appreciate the quality, efficiency and cost competitiveness of our offering," said Changwan Choi, LG Chem's manager of Australian business development.
The battery storage units start at 3.2kWh versions and can be stacked to reach outputs of 9.6kWh and 12kWh in energy storage. The unit weighs only 132lbs (60 kg). The rumor that currently exists is that LG Chem's battery is the most affordable battery on the market, according to the dollar to kilowatt-hour conversion. The battery will reportedly cost close to $8,000.
LG Chem says their new energy storage units are lightweight and conveniently compact. The batteries are also stackable and connectable so that a stronger megawatt output can be achieved. The company claims to have the largest manufacturing facility in the world and are certain that that will drive the prices of their battery storage units down. They will also integrate their battery technology into utility and business operations as well.
Volkswagen has also been rumored to be working with LG Chem in a joint venture that could see their cars being powered by the battery technology. The auto manufacturer could be looking to put batteries into between 2 million and 3 million vehicles by 2025. According to Bloomberg, four Asian companies including Panasonic and LG Chem own 80% of the battery market in Asian-Pacific territories.
"Batery technology is a key competence for electric mobility, which will see its breakthrough toward a mass market in coming years," Volkswagen said in a statement.
Now for the engineers that are interested in installing one of LG Chem's home storage units, there is already an installation video for it:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Want to go work in Singapore? According to veteran engineers, Singapore's engineers are flocking to other industries. This has caused a shortage of engineers in key industries that require them, most notably in telecommunications and railway engineering applications. The dean of the engineering faculty at the National University of Singapore, Professor Chua Kee Chaing, has said there is a lack of engineering talent in critical infrastructure industries such as broadband and power networks. There has been a host of train breakdowns due to power issues across Singapore.
 The problem, according to Singapore's Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong, is the tertiary engineering education in the country. At the 50th anniversary celebration of the Institution of Engineers Singapore, the PM warned of the dire situation the country was experiencing.
The problem, according to Singapore's Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong, is the tertiary engineering education in the country. At the 50th anniversary celebration of the Institution of Engineers Singapore, the PM warned of the dire situation the country was experiencing.
Experts have suggested that other industries are needing the expertise of engineers. Finance and business industries have been luring students in with higher salaries, leaving critical infrastructure industries without engineers. A better pay cheque is a significant factor that could see prospective engineers lending their skill sets elsewhere, taking on other professions.
"Other factors include the lack of effective career planning and job rotation. For instance, not all engineers want to remain engineers, but may want to become senior managers," said the president of the Institution of Engineers Singapore, Edwin Khew. He added that banks could probably pay engineers 30 percent more than critical infrastructure industries.
Professor Chua also mentions that infrastructure industries are not able to produce the same salaries as banking and finance industries.
According to the Straits Times, even when engineering was chosen as a field of study, the students still landed in banking-related jobs. Engineering students in Singapore have confirmed that no matter what their qualifications were, some industries were just hiring to hire, as long as qualifications were held. Veteran engineers are now saying that government needs to pump more money into engineering salaries in critical infrastructure so that there is not a lack of engineers in industries that need them the most.
"A lot of students I talk to say they want to do good in society. Maybe we don't do our outreach well enough. For example, when engineers bring clean water technology to underdeveloped economies, eliminating diseases, the impact is tremendous. Increasingly, we want our students to go out to more disadvantaged communities," Prof Chua concluded.
Source: The Straits Times
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Advanced Microgrid Solutions (AMS) is a company that integrates clean renewable energy into buildings through supplying energy storage units. Their solutions ensure that businesses use less utility grid energy. The company operates out of San Francisco, California. They are teaming up with Macquarie Group, an investment banking, and diversified financial services group. Macquarie will be supplying the energy giant $200 million to kick-start new energy storage projects.
 Chief Executive of AMS, Susan Kennedy, says the funding will ensure that large infrastructure development in energy storage will take place as a result. The projects will see California getting energy storage technologies. The first projects for the two companies will be building 300 megawatt-hour energy producing facilities. According to Clean Technica,the global annual storage market last year reached 700 megawatt-hours. Therefore, the facilities that will be built as a result of the collaboration are going to be quite sizeable. AMS have been taking business office space into the hybrid future. Using Tesla PowerWalls, the company powers buildings through alternative methods, leading to less grid demand. The energy storage market is expected to grow to a demand of 14 GWh by 2020. Thus, deals like these need to become more frequent if the world is to keep up with stationary storage market demand.
Chief Executive of AMS, Susan Kennedy, says the funding will ensure that large infrastructure development in energy storage will take place as a result. The projects will see California getting energy storage technologies. The first projects for the two companies will be building 300 megawatt-hour energy producing facilities. According to Clean Technica,the global annual storage market last year reached 700 megawatt-hours. Therefore, the facilities that will be built as a result of the collaboration are going to be quite sizeable. AMS have been taking business office space into the hybrid future. Using Tesla PowerWalls, the company powers buildings through alternative methods, leading to less grid demand. The energy storage market is expected to grow to a demand of 14 GWh by 2020. Thus, deals like these need to become more frequent if the world is to keep up with stationary storage market demand.
Rob Kupchak, the head of US Power, Utilities and Renewables for Macquarie Capital said: "AMS's focus on contracted, grid-scale energy storage projects stands out amongst developers forging a path in the energy storage space. The next decade is likely to see huge changes in the mix of energy consumed across the globe, and we see energy storage rapidly emerging as a growth market in the next generation of energy infrastructure."
A month ago, Bloomberg's New Energy Finance New Energy Outlook Report 2016 report was released and indicated that the energy storage market would be valued at $250 billion by 2040. The report indicated that the falling prices of lithium and the falling price of battery technology would mean the market would grow considerably.
"Macquarie Capital is the gold standard for investment in critical infrastructure. Combining our innovative designs and technology with Macquarie's development and financing expertise will enable us to deliver best-in-class storage solutions and build tomorrow's energy grid," said Kelly Warner, President of AMS.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial workers have to operate some heavy machinery and carry some heavy equipment. Now, a new glove that makes it easier to do those things is here. Engineers from General Motors have shown off a new innovation they have been working on for quite some time. A robotic glove turned industrial glove. The glove is a collaborative project between General Motors and NASA. The glove is called the RoboGlove. It was a joint venture between GM and NASA that took nine years to perfect. The gloves were initially designed for the use of the Robonaut 2 that works aboard the International Space Station. The gloves were designed four years ago but are now being re-purposed for industrial operations.
 Marty Linn, GM's Principal Engineer of Robotics, said: "This was really inspired by the work that was done on the hands of R-2. The unique thing about R-2 is its hands and its ability to manipulate objects and to do work. We've taken the same sort of technology, the tendon driven actuators and the sensors and translated that from the robot into a glove that a human operator could wear."
Marty Linn, GM's Principal Engineer of Robotics, said: "This was really inspired by the work that was done on the hands of R-2. The unique thing about R-2 is its hands and its ability to manipulate objects and to do work. We've taken the same sort of technology, the tendon driven actuators and the sensors and translated that from the robot into a glove that a human operator could wear."
The gloves will be used by workers with the purpose of reducing the amount of fatigue that occurs in heavy lifting and working with tools. The technology was trademarked under the name 'SEM' which translates to Soft Extra Muscle technology. Another company that wants to utilize the technology is Bioservo Technologies. They intend to use the glove for biomedical and industrial purposes.
In a statement, Tomas War, CEO of Bioservo Technologies, said: "Combining the best of three worlds – space technology from NASA, engineering from GM and 'medtech from Bioservo – in a new industrial glove could lead to industrial scale use of the technology."
"This glove provides additional grip force on the order of ten pounds to be able to help the operator do their job longer and better," Linn added. The engineers say the gloves have a grasp force that makes industrial heavy-lifting much easier. It significantly reduces the force a worker needs to exert in industrial operations.
To see how the RoboGlove could be used in the industrial world, take a look at the video below:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Research group Gartner tell us that 6.4 billion devices are soon to be connected to the Internet of Things this year. That will be 30 percent more than 2015. This would mean that 5 million devices will be connected to the internet every single day. In 2020, the number is expected to grow to 20.8 billion connected things. Some of these devices will be connected to the Industrial Internet of Things. IIoT-connected devices will ensure that industrial automation reaches new heights, redefining industrial operations and leading to new levels of efficiency.
 Honeywell has launched a new programmable logic controller (PLC) called the ControlEdge. It is equipped to deal with the IIoT and ensure that industrial devices all work in tandem with unprecedented efficiency. With built-in cybersecurity, the PLC promises to capitalize on the IIoT and take industry into what has been defined as Industrie 4.0.
Honeywell has launched a new programmable logic controller (PLC) called the ControlEdge. It is equipped to deal with the IIoT and ensure that industrial devices all work in tandem with unprecedented efficiency. With built-in cybersecurity, the PLC promises to capitalize on the IIoT and take industry into what has been defined as Industrie 4.0.
Andrew Brodie, Global Controls Leader, in a roundtable discussion on the future of IIoT, said: "IIoT has the potential to be the most significant development in automation systems since the introduction of distributed control systems. It offers a wide range of potential uses and benefits, enabling business to leverage the vast amount of data provided by modern automation and control systems."
He lists the benefits of an IIoT-controlled set up within an industrial operation. He summarizes the huge advantages:
- Providing operations personnel with improved remote monitoring
- Diagnostic and asset management capabilities
- Enhancing data collection - even in the most dispersed enterprises
- Improved decisions about the actual health of assets
- Reducing the time and effort for configuration and commissioning
- Minimizing the need to troubleshoot device issues in the field
- Bringing new production fields online faster and improving collaboration across the company
Honeywell says their new PLC will assist industrial operations with all of the aforementioned necessities. Access to immediate data makes this PLC a productive tool that engineers can work with. The company has sold the Experion PKS automation systems to industrial operators, most notably to an Oil and Gas company named Kuban in Russia. The automation systems will assist with performance and promises to cut costs. The automation system employs the ControlEdge PLC, which reportedly assists with secured connectivity and integration with multiple devices across vendors. It also ensures that industrial operations can continue at an efficient level in an uncertain shift towards IIoT-connected warehouses, factories and industrial complexes.
The embedded security reportedly reduces the risk for the companies who employ the PLC. The PLC boots with something called 'Safeboot'. This scans industrial systems for any unauthorized software before industrial operations continue to ensure that no dangerous software is imposing on the systems. The PLC also has a firewall that ensures security.
Robert Alston, a cyber security technical lead at Honeywell, in a roundtable discussion on IIoT-connected PLCs, said: "Honeywell offers Industrial cybersecurity solutions and managed services that help protect the availability, safety, and reliability of industrial control systems and site operations."
Source: Honeywell
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Transparency Market Research has issued a new report on the global supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems market. They have been tracking the market since 2014 and will continue to do so until 2020. The report is titled 'Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, and Forecast 2020'. SCADA systems run all of the major players in industry. They're used in substations, oil and gas, water distribution, telecommunications, manufacturing, the list goes on. They are brutally important to industrial operations.
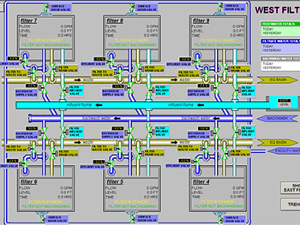 The report says that the market was valued at $23 billion in 2013. By 2020, the report estimates the market will reach a value of $32.7 billion by 2020. This would mean the market would have a compound annual growth rate of 5% between 2014 and 2020.
The report says that the market was valued at $23 billion in 2013. By 2020, the report estimates the market will reach a value of $32.7 billion by 2020. This would mean the market would have a compound annual growth rate of 5% between 2014 and 2020.
To indicate how important SCADA systems are to the future of industrial control systems, a recent report by BCC Research can be quoted. They say the industrial robotics market will be valued at $31.5 billion by 2021.
What industries are utilizing SCADA systems to their full potentials in the current market? First of all, the electric power generation sector, powering smart grids and turning cities into efficient energy consuming territories. The report says countries that have been incorporating smart-energy with SCADA systems are India and China. Then oil and gas, manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications, food and beverage, water and wastewater, and transportation. The report says substations and energy applications account for 17.7% of the market in 2013. That number will undoubtedly grow due to the amount of energy-producing applications that are being invented in the smart-grid age.
The United States was found to be the top buyer in the market due to having 38.8% of the market share. The market share has been explained by the U.S's craving for automation within factories, and the energy sector growing rapidly. Furthermore, the U.S.'s oil and gas sectors are still very active. All of these industries require SCADA systems.
Asia Pacific areas were the second biggest market for SCADA systems. China's investment into industrial automation will see the SCADA systems market growing as well. Europe was third and the rest of the world followed after that.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The global smart energy market will see seven vendors rising up above the rest, to capitalize on the new era of clean energy production with an added layer of digitization as the Industrial Internet of Things. The seven leading vendors were determined by a study done by Technavio, which considered energy companies that provided services in "smart-grid, HEMS, digital oil fields" and leading solar technologies, all in the name of clean and smart energy production. The efficiency of these power companies was also considered. Technavio estimates that these seven vendors will lead the market from 2016 to 2020. Thus, we begin our series titled Global Smart Energy 2016 to 2020 and catch up with these seven energy companies to see the work they are doing in energy sectors and to see what qualifies them as the top vendors for global smart energy.
Landis + Gyr
It's easy to see why Landis + Gyr are word leaders in global smart energy production. The company has provided a host of countries smart electricity technologies. Their slogan is, "manage energy better," and it is clear to see they do that through giving the consumer the power. They offer a host of smart metering technologies to ensure that the consumer knows and understands how much electricity is being used, and how much can be saved.
 They have a global portfolio that encourages increased efficiency in energy management. In the Netherlands, they have installed smart street lighting to ensure lights are only being used when brutally necessary. They have installed smart-grid technologies including large-scale battery and PV technologies in Japan and the United States. In Estonia, they have installed 630,000 residential metering points to ensure consumers get the right amount of electricity based on how much they have paid.
They have a global portfolio that encourages increased efficiency in energy management. In the Netherlands, they have installed smart street lighting to ensure lights are only being used when brutally necessary. They have installed smart-grid technologies including large-scale battery and PV technologies in Japan and the United States. In Estonia, they have installed 630,000 residential metering points to ensure consumers get the right amount of electricity based on how much they have paid.
In Slovenia, the company employs what they call a "virtual power plant" that supplies 60MW to the cyber-grid. The transmission system operator installs the virtual cyber-grid which assists with regulating and balancing power that gets sent to industrial and consumer-based demands.
In France, a $77.8 million project has ensured that Landis + Gyr's smart meters make their way into French customers' houses. The meters are built in an automated factory based on engineers' designs. The money for the project was provided by the European Regional Development Fund, that is ensuring the smart metering technology makes it further into France.
“Landis+Gyr is proud to have been selected by ERDF as one of the main suppliers for this ambitious programme to bring smart meter technology across France”, said Andreas Umbach, Landis+Gyr’s President and CEO.“We look forward to helping them realize the goal of empowering their customers to better manage their energy consumption.”
The deal sets the record for the world's largest smart metering rollout.
The company also assists cities in becoming smarter. In Yokohama City, Japan, Landis + Gyr is in charge of making the city smarter, energy wise. They have installed home energy management systems, central management systems for smart grids, electric vehicle charging stations and SCADA systems that keeps an eye on the energy production of the city. The company also supplies advanced metering options to Denmark, Rome, Spanish customers. They also specialize in smart gas technologies in Britain.
Source: Landis + Gyr
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Twinkie is America's snack. Or, at least it used to be. If anything, it is a wonderfully engineered bit of a pastry for people who desire a cake with a bit of stuffing - or is that icing? Regardless, the company who make Twinkies, Hostess, almost went bankrupt twice. Just imagine if you were an American living in a world without Twinkies. In 2013, as Hostess admitted to bankruptcy due to employee and union "arrangements", the company was bought by another company named Apollo. Now, the company is going public and is valued at $2.3 billion. How did they turn it around? The answer is: Automation.
The company now at the helm of the Twinkies brand has let go of most of their employees. Five years  ago the company had 8,000 employees, now they have 1,170. The money that would've gone to those other 6,830 people was spent on revamping their industrial machinery and industrial ovens. $130 million was pumped into automation, making the company re-fire ovens that used to be used by 22,000 workers (in 40 bakeries) when the company was in its heyday.
ago the company had 8,000 employees, now they have 1,170. The money that would've gone to those other 6,830 people was spent on revamping their industrial machinery and industrial ovens. $130 million was pumped into automation, making the company re-fire ovens that used to be used by 22,000 workers (in 40 bakeries) when the company was in its heyday.
A robotic takeover of food industries is not a foreign idea and is happening every day. Hostess was crippled by employing humans. According to Forbes, the company had 372 bargaining contracts for workers, 5,500 delivery routes and "a vast production system" all headed up by humans. Now, with letting go of 94% of their employees and employing automated industrial food technology, they have saved the company.
The new factories that Twinkies are made in use a $20 million piece of automation tech called the Auto-Bake system. The industrial ovens use state-of-the-art PLC (programmable logic controller) systems to fully automate the production line. Robotic arms are also used to package the Twinkies into boxes and ensure that 1 million Twinkies make it out of the factory per day. That's 400 million a year. That was a year ago, the CEOs want to now employ a second Auto-Bake system and double the output. This would ensure that they produce more Twinkies than ever before in history.
Back in May, former CEO of McDonalds Ed Rensi said: "I was at the National Restaurant Show yesterday and if you look at the robotic devices that are coming into the restaurant industry -- it's cheaper to buy a $35,000 robotic arm than it is to hire an employee who's inefficient making $15 an hour bagging French fries -- it's nonsense and it's very destructive and it's inflationary and it's going to cause a job loss across [the United States] like you're not going to believe."
The harsh criticism of the food industry by Rensi can explain why it is is more lucrative for Hostess to employ robotic employees instead of union-affiliated employees that sent the company into a death-spiral years before.
To see how the Auto-Bake system works, take a look at the video below:
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The global smart energy market will see seven vendors rising up above the rest, to capitalize on the new era of clean energy production with an added layer of digitization as the Industrial Internet of Things. The seven leading vendors were determined by a study done by Technavio, which considered energy companies that provided services in "smart-grid, HEMS, digital oil fields" and leading solar technologies, all in the name of clean and smart energy production. The efficiency of these power companies was also considered. Technavio estimates that these seven vendors will lead the market from 2016 to 2020. Thus, we begin our series titled Global Smart Energy 2016 to 2020 and catch up with these seven energy companies to see the work they are doing in energy sectors and to see what qualifies them as the top vendors for global smart energy.
ABB
The hottest town in Australia is said to be Marble Bar. It is in the Pilbara region in north-western Australia. The town set a record when the temperature reached 100oF and stayed there for 160 consecutive days. So, needless to say, the town get's a lot of sun. It seems to be the perfect spot for solar panels.
ABB supply microgrid solutions - named ABB Microgrid Plus technology- that combine the power of diesel generators and the power of solar panels. It ensures that mining operations and endeavours of the like are mostly powered by renewable energy. The ABB engineers say that the town can now be powered by renewable energy 60% of the time, with their microgrid applications. The solar array supplies 320 kilowatts to the town, whilst the diesel generators supply 320 kilowatts.
 "Traditionally, we would have had a diesel power station here, supplying the grid. In a microgrid you've got multiple sources of energy, in this case here, you've got solar power plus the diesel. The goal here is for our microgrid control system to minimize the diesel and maximise the solar," said Heath Lang, a senior engineer from ABB.
"Traditionally, we would have had a diesel power station here, supplying the grid. In a microgrid you've got multiple sources of energy, in this case here, you've got solar power plus the diesel. The goal here is for our microgrid control system to minimize the diesel and maximise the solar," said Heath Lang, a senior engineer from ABB.
ABB say that they have 80 similar installations operating all over the world. In the case of Marble Bar, the town saves 40% of the diesel fuel it would have used (240,000 litres of diesel fuel) if they didn't have the solar panels. This microgrid solution ensures that 1,100 tonnes of greenhouse gases are avoided.
ABB's Microgrid Solutions are bringing clean, renewable power to remote, hard-to-reach places in the world. They estimate there are 1.3 billion people living in remote parts of the world, and those are the ones they want to reach.
"ABB's unique microgrid solutions enable very high levels of wind and solar power penetration in isolated diesel-powered grids. This solution calculates the most economical power configuration, ensuring a proper balance of supply and demand that maximizes renewable energy integration, providing for up to 100% renewable penetration and the highest level of stability and reliability," ABB said in a statement.
Their solution can be used for microgrid communities (much like Marble Bar), integrated solutions for businesses or microgrids for industry applications like mining operations etcetera.
Source: ABB
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A recent report by Research and Markets indicated that wind and solar generated 77 percent of the global renewable energy in 2015. The American Wind Energy Association says that wind energy currently powers up to 20 million homes in the United States. Wind farms are gaining popularity all over the world, equipped with row upon row of wind turbines. Even companies like Walmart now have stakes in wind farms that generate some of the electricity they power their buildings with. Ikea has also invested into clean renewable technologies to power their stores.
 So, the demand for wind turbine technology is high. Siemens is one of the top 10 manufacturers and have just announced a new offshore wind turbine. The new turbine is named the SWT-8.0-154 and uses Siemens' direct drive wind turbine technology. The technology is used in both onshore and offshore applications. When the direct drive technology was announced in 2011, the engineers said that they had revolutionized the entire wind market.
So, the demand for wind turbine technology is high. Siemens is one of the top 10 manufacturers and have just announced a new offshore wind turbine. The new turbine is named the SWT-8.0-154 and uses Siemens' direct drive wind turbine technology. The technology is used in both onshore and offshore applications. When the direct drive technology was announced in 2011, the engineers said that they had revolutionized the entire wind market.
Siemens says installations of the new turbine will kick off in early 2017. The turbine will produce 10% more energy annual energy production due to being an 8MW model. This is a step up from their 7MW model. Siemens currently operate 1,240 direct-drive onshore turbines and 150 offshore turbines.
Michael Hannibal, CEO for Offshore at Siemens' Wind Power and Renewables Division said: "We are relentlessly working on the levelized cost of energy, and the offshore direct drive platform enables us to do this with the lowest possible risk. With the same proven reliability as our successful 6 and 7MW models, the SWT-8.0-154 will be the new benchmark for gearless offshore wind technology on the market."

Siemens' direct drive technology is respected as one of the more innovative wind turbine technologies available today. However, what about a wind turbine with twelve blades?
The twelve-bladed behemoth has been proposed by a company named Vestas. The company needs to prove to investors that twelve blades are better than three and can equate to more efficiency. The company has had the proposal on ice whilst they figured out how a twelve-bladed turbine would actually work. The worry is that if one set of blades stops working or an internal error occurs, then the entire thing will stop functioning.
 Perhaps the answer isn't more blades, but, maybe longer blades. A wind energy firm named Adwen and LM Wind Power have created the world's longest wind turbine blade. The blade is 88.4 meters long and will fit on Adwen's own AD 8-180, 8MW, wind turbine.
Perhaps the answer isn't more blades, but, maybe longer blades. A wind energy firm named Adwen and LM Wind Power have created the world's longest wind turbine blade. The blade is 88.4 meters long and will fit on Adwen's own AD 8-180, 8MW, wind turbine.
Roel Schuring, the CTO of LM Wind Power said: "The rotor is the motor and to put it simply, longer blades extract more energy from the wind. Increasing the annual energy production from each offshore wind turbine is a key driver to reduce the levelized cost of offshore wind energy which is decisive for a large-scale deployment. The blade is the single most influential component for increasing energy yields and its design and aerodynamic features can make a huge difference for the turbine's power production."
Source: Clean Technica
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The safety helmet seems to be the worldwide symbol for engineers. If you go to Google Images and type the word 'engineers', almost every single image that comes back is of people with hard hats on. To an average joe, engineers wear hard hats in their occupations. However, a new report indicates that engineers are tired of the hard hat as the worldwide symbol for engineering. Engineers want the symbol to be changed in educational works that emphasize the stereotype that all engineers wear hard hats.
 The report is known as the Sainsbury Management Fellows' 2016 Hard Hat Index that measures the number of times a hard hat appears in editorials or advertisements. In 2014, the Hard Hat Index saw a 20% increase in the number of hard hats in "key engineering publications". In 2014, hard hats were featured in 229 advertisements and 143 editorials.
The report is known as the Sainsbury Management Fellows' 2016 Hard Hat Index that measures the number of times a hard hat appears in editorials or advertisements. In 2014, the Hard Hat Index saw a 20% increase in the number of hard hats in "key engineering publications". In 2014, hard hats were featured in 229 advertisements and 143 editorials.
SMF say they invented the Index to show how pervasive the use of hard hats has become in "influential media". They believe that the image "limits the profile of engineers". So, has the Index worked and minimized the amount of stereotypical hard hats in mainstream media? The answer is: No. This year alone, hard hats have appeared 257 times in engineering media. The number is the highest it has been since the SMF Index was launched in 2013. The current Index shows that images of hard hats have risen 39% since 2013.
The President of SMF, David Falzani said: "The Hard Hat Index points out how the engineering community is choosing to represent itself in terms of image and emotional value. Generations Y and X are far more image and brand conscious than before. Image and emotional value are vital in our ability to attract, inspire, recruit and retain bright young people. This is a serious national challenge which we must all embrace."
SMF actually conducted a workshop with engineering graduates to discuss the use of the hard hat as a symbolic image for engineering. In the group of respondents, there were seventy students from the Royal Academy of Engineering. They showed the students 30 different advertisements that featured hard hats in them. Only 20 percent of the ads received positive feedback. Meaning, engineers feel underrepresented by advertising of engineers.
The question that remains is how to visually show what an engineer looks like. The multiple industries engineering caters to makes it impossible to secure one image.
"The Hard Hat Index is therefore designed to highlight how our industry is representing itself. It is disappointing to see that despite the question of the engineering brand being debated in the engineering media over the last 18 months, the hard hat representation in editorial is on the increase. This begs the question whether our industry is open to reinvention in order to persuade the public that engineering is an exciting, dynamic and rewarding profession," Falzani said.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Industrial control system cybersecurity continues to be an elusive concept to companies who have not made advancements in securing company assets that are connected to the internet. The guys at Automation World have you covered, though. They have compiled a very simple 3 principle approach to protecting your industrial operations that will or do function with the Industrial Internet of Things.
One of the issues for industrial operations is that attacks can be performed on the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. A study by Booz Allen Hamilton showed that the US Department of Homeland Security dealt with 295 industrial incidents in 2015. Energy utility companies  were the most heavily attacked. Other companies included manufacturing facilities in the car, electrical and metal industries. The utilities said the attacks were by ransomware criminals that tried to access their enterprise networks. The director of Industrial Security at Booz Allen says enterprise networks are the first to get hacked. Once enterprise networks have been accessed, the actual operational technology of an industrial operation is targeted. Once the operational technology is targeted, things like SCADA systems and other industrial control systems are at the mercy of hackers. The report indicated that more hacking incidents happened in 2015 than any other year, however, 2016 could eclipse that statistic.
were the most heavily attacked. Other companies included manufacturing facilities in the car, electrical and metal industries. The utilities said the attacks were by ransomware criminals that tried to access their enterprise networks. The director of Industrial Security at Booz Allen says enterprise networks are the first to get hacked. Once enterprise networks have been accessed, the actual operational technology of an industrial operation is targeted. Once the operational technology is targeted, things like SCADA systems and other industrial control systems are at the mercy of hackers. The report indicated that more hacking incidents happened in 2015 than any other year, however, 2016 could eclipse that statistic.
Automation World's 3 point policy for securing industrial systems with cybersecurity is as follows:
- A top-down security approach with centrally-defined plant-wide policies that are automated to ensure consistent shieldign of all field assets.
- A focus on security essentials, i.e. securing what matters and doing the basic things right, repeatedly, to shield industrial assets from risk.
- Prioritize protection of field assets, which are key for production safety and integrity.
Eli Mahal, who wrote the three point cybersecurity policy, works for a cybersecurity company named Next Nine. He says: "Both the NIST framework and NERC-CIP v5 say that asset identification is foundational for knowing what must be protected. A comprehensive and up-to-date asset inventory is vital to developing and maintaining an appropriate defense of an industrial network and infrastructure. The owner/operator needs clear visibility into what devices are on the network; what they communicate with and how; the characteristics of the devices; and the presence of any known vulnerabilities.
Some companies believe that employing air-gapped industrial equipment is the answer. This would include using equipment that has never been exposed to the internet or a previous network. This is not a viable option due to the Industrial Internet of Things surging forward and bringing in a new era of efficiency for industrial operations.
However, those companies shouldn't have to worry because now there is a gap in the market for private cybersecurity firms. Post-Quantum, a cybersecurity firm in the United Kingdom just secured $10.4 million of investment. The company specializes in cybersecurity for "enterprises and organizations", which include: banks, government, and healthcare. Another company this week named Darktrace secured funding of $65 million, and another company named SecurityScoreCard received $20 million. The cyber-protection of industries has never been more lucrative for engineers than it has been today.
"Organizations should address the security essentials and focus on doing the basic things right, such as applying qualified operating system patches and anti-virus signatures, collecting and analyzing devices logs, and scanning IP address ranges to look for unexpected changes," Mahal concluded.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Australia's construction market is doing quite well. In the Performance of Construction Index, Australia rose by 6.5 points in June, giving them an average score of 53.2. Their score in May was 46.7. A healthy score is above 50.0 which separates the line of expansion versus contraction. Therefore, Australia's construction is looking healthy. Recent reports indicate that the Australian construction industry has taken a dip since March 2013. Sourceable confirmed that construction activity had dropped by 25 percent since 2013 when it was at its peak. Nonetheless, the latest construction numbers are quite surprising.
 The numbers were crunched by the Ai Group, as usual, delivering the news that Australia's construction industry was at the highest level in ten months. The report showed that all construction subsectors (house building, commercial buildings, and engineering construction) have improved in June. Expert analysts say they haven't seen this impressive of a turnaround in many years. They say the improvement could be signaling further improvements in the months in the remainder in the year.
The numbers were crunched by the Ai Group, as usual, delivering the news that Australia's construction industry was at the highest level in ten months. The report showed that all construction subsectors (house building, commercial buildings, and engineering construction) have improved in June. Expert analysts say they haven't seen this impressive of a turnaround in many years. They say the improvement could be signaling further improvements in the months in the remainder in the year.
The AiG manufacturing index reported more worrying numbers, however. Manufacturing in Australia fell to 51 from 53.4 in April, during May. However, being above the 50 mark means manufacturing is still expanding in the country, which is a good sign. Australia has not dipped below the 50 mark since September 2006.
"The residential sub-sectors of house and apartment building were the standout performers," said Peter Burn, the head of public policy at Ai Group. However, the commercial engineering construction has been seeing drops in new orders. House and residential is carrying all of the weight for the construction industry in Australia.
A country that couldn't brag as much, was Germany. Their Purchasing Managers' Index fell from 52.7 in May to 50.4 in June. Despite the drop, Germany has been faring well. Oliver Kolodseike, an economist at Markit said: "The recovery in Germany’s construction sector appears to be losing its legs at the end of the second quarter, with latest survey results pointing to a marked slowdown in growth of German building activity. The PMI is now close to a level that is normally consistent with a stagnation of construction output, dragged down by declines in both commercial building and civil engineering activity. Although housing shortages and the inflow of refugees should help maintain growth of residential building activity in the near-term, companies were the least optimistic about their future since the end of last year."
Source: The Construction Index
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The global smart energy market will see seven vendors rising up above the rest, to capitalize on the new era of clean energy production with an added layer of digitization as the Industrial Internet of Things. The seven leading vendors were determined by a study done by Technavio, which considered energy companies that provided services in "smart-grid, HEMS, digital oil fields" and leading solar technologies, all in the name of clean and smart energy production. The efficiency of these power companies was also considered. Technavio estimates that these seven vendors will lead the market from 2016 to 2020. Thus, we begin our series titled Global Smart Energy 2016 to 2020 and catch up with these seven energy companies to see the work they are doing in energy sectors and to see what qualifies them as the top vendors for global smart energy.
Itron
Itron is a company that will play a big part in Internet of Things connected smart grids in the near future. The company provides end-to-end smart grid and smart distribution solutions for electric, natural gas and water applications. The company says that in the current global energy market, more needs to be done than just securing a smart-grid. They believe that with the oncoming interconnectedness from the Internet of Things will ensure that a new smart distribution system can be created.
They are coining a new term pertaining to global smart energy. They're calling it the 'Active Grid'. This grid layout will combine the smart grid and smart distribution solutions in one well-oiled machine. The company explains that clean renewable energy, safe gas delivery, and efficient water distribution working in tandem with each other and with the digital connection of the Internet of Things will help the company provide efficiency and reduce waste. The company says through combining these solutions, the smart-cities and the smart utilities of the future can be born.
 "Smart grids are no longer enough. While they collect and move more data than ever, in today's fast-paced world, more data doesn't mean better outcomes. We need a grid and distribution networks that are more than smart. With the right technology and analysis, applied in the right places, we can create something beyond the smart-grid. We can create the Active Grid," Itron said in a promotional video.
"Smart grids are no longer enough. While they collect and move more data than ever, in today's fast-paced world, more data doesn't mean better outcomes. We need a grid and distribution networks that are more than smart. With the right technology and analysis, applied in the right places, we can create something beyond the smart-grid. We can create the Active Grid," Itron said in a promotional video.
Itron outlines a simple three-point plan for their proposal of the Active Grid:
- A network fueled by an open, standards-based and the interactive network that uses intelligent technology. This would relate to Industrial Internet of Things connected technologies.
- Automation with devices, sensors, routers, and applications will make real-time analysis and the making of decisions far easier. No unnecessary data will apply.
- Machine to machine learning and problem-solving that makes sense. However, the active grid will have human intervention where necessary.
The company says an active grid connected to the Internet of Things and connecting distribution systems to an eco-system of interconnectivity will mean that problems and outages will be detected 50 percent faster. Smart metering, smart cities, connected by a smart distribution system is Itron's aim for a future with cleaner energy, cleaner water and an efficiently run country.
Source: Itron
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A wearable. A word that has a very simple definition. It is an item/s that can be worn. When we think about wearables, we think about the current applications available in the media; smart-watches, head-mounted VR gear etc. However, wearable technology has become valuable to engineering industries. Wearables for industrial operations, coupled with modern day automation with the Internet of Things , will ensure that everyone attached to a project or a factory - or even a mine - will all be on the same page with data that is freely and immediately available.
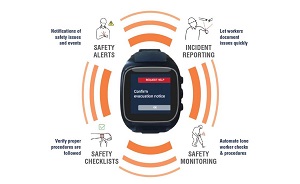
A 3D real-time industrial operations dashboard is available from a company named Vandrico Inc. The company currently shows off how it interconnects miners and engineers, but can also be used for other industrial endeavors. It connects all the engineers and workers attached to an industrial operation across platforms. Smart watches, smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The company calls it Real-Time Operational Intelligence. As an example, Vandrico shows off their smartwatch technology, which accounts for on-site safety. Once a fire alarm goes off at an industrial operation, the smart watch can ask questions like: "Are you safe?", "Is everyone near you safe?" This way a fire or industrial problem can be quickly contained and lives can be saved. This assists with site security and safety, something that engineers need to focus on as they begin a project and whilst the project is ongoing. Their safety-smart-watches were announced last year, with the help of a company named Illumiti. They call the watch the MineSafe smartwatch, which also assists with the response-time of life-threatening situations in mines. It could ensure that safety in mines is paramount, especially in a mine collapse.
According to the companies the full list of uses the smartwatch has are:
- Safety alerts: Notifications of safety issues and events
- Incident Reporting: Let workers document issues quickly
- Safety monitoring: Automate lone worker checks & procedures
- Safety checklists: Verify proper procedures are followed
The company says their wearable technology would be able to save mines millions and could even save lives.
IoT-connected dashboards for industrial operations could be the most useful way of keeping a close eye on the efficiency of a workforce, and can give engineers a good idea of how far a project is.
Vandrico says their platform can be used for many different applications:
- Virtual barricades: Alert miners that they are near an unsafe area and prevent them from going there
- Lone worker: Individual miner and engineer tracking for safety check-ins and immediate ramifications for missed check-ins
- Real-Time Safety Reminder & Safety Forensic Logs
- Real-Time Incident Reporting: Any injuries can be reported immediately. Any mine maintenance issues can be reported instantly
- Mementos: The miners can deliver voice notes or text messages to other workers that would improve efficiency.
- Automated coordination of work orders: A checklist of what needs to happen during the day. A virtual "to-do" list.
Source: Vandrico
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Amazon has announced the winner of a competition held to find the next big warehouse/factory robot arm picker. Teaming up with Germany's RoboCup, Amazon urged engineers to create robot item-pickers in a competition that "aimed to strengthen the ties between industrial and academic robotic communities. The winners would receive $25,000 for first place, $10,000 for second and $5,000 for third. Amazon is currently investigating how to further automate their packaging plants and automate their delivery systems as well.
 Tye Brady, the chief technologist at Amazon Robotics told the BBC: "Our vision is humans and robots working shoulder to shoulder. It was inspiring to see 16 top teams with so many different approaches to the same problem, and we also saw the advancements robotic technology has made since last year."
Tye Brady, the chief technologist at Amazon Robotics told the BBC: "Our vision is humans and robots working shoulder to shoulder. It was inspiring to see 16 top teams with so many different approaches to the same problem, and we also saw the advancements robotic technology has made since last year."
The top 3 were:
- Team Delft (Dutch team) - First place
- NimbRo picking - Second Place
- MIT - Third Place
The teams had to demonstrate sophisticated tasks that included a host of products strewn inside a box that the robot arm picker had to pick up. Team Delft's robot was able to successfully complete a pick in 30 seconds, cementing them as the winner of the competition. The items included some of Amazon's very own products, including clothing, DVD boxes, and bottles of water. It is clear Amazon wants to see which system they might be able to employ in their own factories. Amazon recently purchased Kiva Robotics for $775 million and has started to employ automated processes in their factories. Bloomberg confirms that Amazon utilizes 30,000 of the Kiva robots in its warehouses. Employing picker and packer robots would further automate warehouses that are already seeing a lot of automation. The Kiva robots will allegedly save Amazon $2.8 billion alone.
Team Delft's robot appears to use a suction gripper to lift the items and keep them attached to the robotic arm. It then releases the object into the box it has been programmed to store the objects in. The robots use artificial intelligence to learn how to pick and place more efficiently as it works. According to The Verge, Team Delft's robot has a failure rate of 16.7 percent.
The competition emphasises how advancements of robotics have led to the replacement of humans. The repetitive nature of picking and stowing will now be done by robotics instead of being done by humans.
Source: The Guardian
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Another day, another robotics market research report. Robotics is an immensely important engineering industry that has the power to influence many other industries. Robotics has forever changed the industrial world. BCC Research, an industrial research firm, has published their latest investigation into Robotics: Technologies and Global Markets.
The report focuses on six different industries that robotics have been most prominent in:
- Industrial robots
- Professional service robots
- Military robots
- Domestic service robots
- Security robots
- Space robots
 The researchers say the robotics market reached $24.9 billion in 2015 and is expected to earn up to $25.9 billion by the end of 2016. In 2021, the researchers estimate that robotics would have earned $31.5 billion, which would translate into a compound annual growth rate of 4%. The biggest market, that will hold $12 billion of the $31.5 billion will be the Asia-Pacific market. Not surprising, seeing as though China is actively seeking to purchase robotics companies as recently seen with Midea Group buying stakes in Germany's Kuka Robotics.
The researchers say the robotics market reached $24.9 billion in 2015 and is expected to earn up to $25.9 billion by the end of 2016. In 2021, the researchers estimate that robotics would have earned $31.5 billion, which would translate into a compound annual growth rate of 4%. The biggest market, that will hold $12 billion of the $31.5 billion will be the Asia-Pacific market. Not surprising, seeing as though China is actively seeking to purchase robotics companies as recently seen with Midea Group buying stakes in Germany's Kuka Robotics.
Professional service robotics made up 30% of the global robotics market in 2015. Of that 30 percent, the industries that had the most service robots were:
- Healthcare: More than 50 percent
- Aerospace manufacturing: 10%
- Education and research: 6%
- Governmental service robots: 6% The rest: Food, pharmaceutical, agricultural, construction, consumer products, fuel processing etc
James Wilson, a BCC Research analyst attached to the report, said: "In the most generic sense, collaboration is when multiple workers perform tasks on the same work piece. Collaboration is familiar to those who create information products, the most common of which are financial instruments including car loans and mortgages in which computers, not comptometers, calculate payment schedules. A machine capable of sharing workspace with humans and simultaneously working on the same work piece represented the opening of a new industrial era in which robots were seen less as tools and more as a co-worker."
According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, the sales in industrial robotics were also published, representing the other 70% of the robotics market:.
The industries that reported the most sales in industrial robotics were:
- The automotive industry: 95,000 units purchased in 2015
- Metal industry: 63% more purchases than 2014
- Plastics and rubber industry: 40% more robots purchased in 2015
- Electronics industry: 16% rise in industrial robot purchasing
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The global smart energy market will see seven vendors rising up above the rest, to capitalize on the new era of clean energy production with an added layer of digitization as the Industrial Internet of Things. The seven leading vendors were determined by a study done by Technavio, which considered energy companies that provided services in "smart-grid, HEMS, digital oil fields" and leading solar technologies, all in the name of clean and smart energy production. The efficiency of these power companies was also considered. Technavio estimates that these seven vendors will lead the market from 2016 to 2020. Thus, we begin our series titled Global Smart Energy 2016 to 2020 and catch up with these seven energy companies to see the work they are doing in energy sectors and to see what qualifies them as the top vendors for global smart energy.
GE Energy (General Electric)
The company has set a Guinness World Record for the most efficient combined-cycle power plant in the world. The plants use steam and gas turbines to produce energy with little to none carbon emissions. Heavy duty gas turbines are being utilized more than ever due to the political discouragement in using fossil fuel technologies. The company, in collaboration with EDF Energy, opened the plant in France on June 17, 2016. The plant is able to achieve full output in 30 minutes, providing energy to those who need it with minimal outages. It converts gas to electricity with 62.22% efficiency. 680,000 homes will be powered by the plant. It's called the HA gas turbine and produces 605 MegaWatts at a low cost. Combined-cycle power plants are able to produce 50 percent more electricity than the conventional power plants utilizing fossil fuels today.
GE recently launched GE Ventures. The "offshoot" of GE announced that they had purchased a stake in a German battery company named Sonnen GmbH. The joint venture between the two companies is a strategic move for GE, who want to create what they call the "utility of the future".
The company has also recently announced IoT-enabled air conditioners that consumers can monitor and change with a smartphone app.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Engineers have to account for noise in modern day engineering. The health of ears need to be protected. In the same breath, engineers need to ensure whatever they are manufacturing doesn't produce enough noise pollution to damage the hearing of consumers. Even the manufacturing machinery needs to abide by certain noise parameters. Engineers these days are told that less noise means healthier workers and makes a manufactured product that much more attractive in sales.
The control of noise lies in the measurement of A-weighted decibels, abbreviated as dBA. A quick measurement chart you can follow:
- Decibels are just audible at 10dBA
- Soft whispering = 30dBA
- A quiet office = 40dBA
- Normal talking voice = 65dBA
- Hand dryers in public restrooms = 80dBA. This is the level at which ear protection becomes necessary.
- Manufacturing machinery = limit of 85dBA - These are noise levels that can cause damage to ears
- A rock concert = 120dBA
- Thunder clap = 130dBA
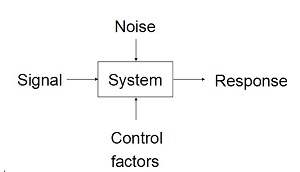
Mackay says that says that some machinery manufacturers are not too keen to cut the noise down, indicating that kitchen appliance manufacturers usually amp up the amount of volume their products produce so that it sounds more powerful to the consumer.
"Noise cancellation is a technology which is employed very widely. But, it really [only] works with short point sources at low frequencies. So, a very large surface operating at a whole spectrum of frequencies is very difficult to apply noise cancellation to," said Mackay.
He also touches on automobile manufacturing, that prides itself on loud cars and loud motorbikes. However, there is an exception. Electric vehicles.
 In 2014, the European Union decreed that in the future, electric vehicles would need to emit an artificial noise that would signal pedestrians and other motorists that they were on the road. This is due to the very quiet nature of electric vehicles. A car powered by batteries won't make much noise at all. The EU is calling the artificial noise generators "Acoustic Vehicle Alerting Systems".
In 2014, the European Union decreed that in the future, electric vehicles would need to emit an artificial noise that would signal pedestrians and other motorists that they were on the road. This is due to the very quiet nature of electric vehicles. A car powered by batteries won't make much noise at all. The EU is calling the artificial noise generators "Acoustic Vehicle Alerting Systems".
Chris Davies, a Liberal Democrat in the European government in 2014, spoke to the Daily Mail, saying: "Quiet electric cars could become a common sight on our roads in years to come but we have to ensure that this doesn't jeopardise the safety of blind and partially-sighted people. ‘The acoustic warning devices will make a sound very similar to that of cars with a regular combustion engine so that people will be able to clearly hear these vehicles, allowing them to judge how safe a road is to cross.
However, in the world of construction and manufacturing, there are still high decibel levels of noise happening which can damage both the hearing of engineers and the manufactured product. Therefore, Mackay says: "In your next engineering design, think about noise. Think about how to reduce the effect on your wonderful clients, you'll probably have a far happier client."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
3D printing - or rather 'additive manufacturing - has seen a boom in the engineering industry recently. We have reported on the multiple ways additive manufacturing is being used in engineering industries. Chinese construction companies are printing 400-square-meter villas in 45 days, mining equipment like longwall shearers have been printed in the mining sector, 3D printing of metal tools, etcetera. It is clear that additive manufacturing - whilst being fairly new to some industries - is here to stay.
In 2015, Michael Breme, the head of Audi tool design described how 3D printing was benefitting their business. He said: "A brand new fascinating technology has made its way to tool making. 3D printing. It enables us to produce the parts faster and more cost-effectively. For example, with a 3D printer, we don't have any waste like we would with metal cutting, which means we're faster and more cost effective." So, 3D printing making its way into engineering is both useful for the speed of production and ensures that costs are minimal as well.
Another novel, innovative way of using current 3D printing technologies that might excite the civil engineering readers, is 3D printing blueprints. Architects are now printing realistic models of blueprint plans and working with design engineers to measure the feasibility of a construction project. This is something that could be eliminated with augmented reality head-mounted technology and AutoCad software, however, it shows impressive dedication from engineers who want to 3D print models of what they could one day be building.
An agricultural engineering company (Wyma Engineering) showed off a 3D printed blueprint of its fruit sorting industrial machine that can be seen to the left of this article. The 3D printer plastic that was used to perform the 3D model blueprint was called Accura Mix. You know, in case you want to get into the business of 3D printing all of your blueprints into models, to make it easier for the engineers to envision what the end product might look like. This way of printing 3D models enables engineers to show project investors the intricate details of a build and give them a clearer picture of what the construction might look like. This would eliminate some of the time spent 3D model building, and probably save some design engineers some sleep.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The Internet of Things. It's a buzzword that won't be getting old anytime soon. The Internet of Things will see everyday objects connected to cloud-based solutions, with the ability to interact with other devices or live alongside each other in an interconnected network. Now, the first country-wide Internet of Things networks are popping up globally.
The Netherlands have become the first country to establish a country-wide network dedicated to the future of connecting cars, smart-grids and smart-city applications to an interconnected cloud.

solution.
The network is being supplied by a telecoms company known as KPN. They are calling it the LoRa network.
Chief Operations Officer and a member of the Board of Management of KPN, Joost Farwerck, in a press release from the company, said: "Last year we identified an increasing demand for low-power network technology for Internet of Things applications. We are responding to this by choosing LoRa, so millions of devices can be connected to the internet in a cost-effective manner. In less than a year, KPN has implemented a network that allows us to satisfy this market demand."
KPN says there are 1.5 million devices ready to be connected to the network. Cisco, a company wanting to capitalize on internet of things technologies, has endorsed the LoRa-like networks by releasing a gateway and an adapter module that would allow their switches to connect to the unlicensed spectrum (LoRa network).
Following suit, South Korea has also launched its own commercial Internet of Things network. The network has been provided by SK Telecom and will reportedly be available for 99% of the country's population. The company says that the new network will assist with delivering data and analytics across cities. Some of the applications include:
- Electricity metering/Management: Keeping accurate track of the amount of electricity being used
- Water Metering/ Management
- Parking space tracking
- Bicycle tracking
- Infrastructure management
- Missing child tracking
The South Korean telecom launched the network six months ahead of the agreed upon date. Seems the Internet of Things just can't be contained. They are also used LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) utilizing LTE-M infrastructure.
Lee Hyung-hee, President of Mobile Network Business at SK Telecom, said: "SK Telecom is proud to announce the nationwide deployment of LoRaWAN as it marks the first important step towards realizing connectivity between infinite number of things, going beyond the traditional role of telecommunications centered on connectivity between people. Going forward, SK Telecom will develop and offer a wide variety of IoT services designed to offer new value for customers, while working closely with partners including SMEs and startups to vitalize the IoT ecosystem."
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A recent report by Markets and Markets focuses on electric substation automation. The report indicated that revenue growth in the market is expected to reach $48.25 billion by 2020. This would mean that a CAGR of 6.71% annually from 2013 to 2018 in the substation automation market. Another report recently released was the Global Substation Automation Market 2016 Industry Trends, Sales, Supply, Demand, Analysis & Forecast to 2021 released by QY Research Group that emphasized many of the same points.
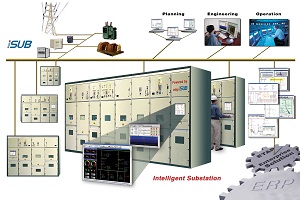
Markets and Markets wrote: "The prominent driver for the electric power substation automation market is the outdated energy infrastructure and growing influence of a smart grid infrastructure that demands a multifunctional solution complying with advanced communication protocols."
Smart-grid technologies were revealed to have produced a quarter of the global energy demand in 2015, according to a recent report.
The key players in the substation automation market were:
- ABB Ltd - Switzerland
- Siemens AG - Germany
- Alstom S.A. - France
- General Electric - United States
- Eaton Corporation - Ireland
- Schweitzer Engg Lab - United States
- Cisco Systems - United States
- Amperion - United States
- Schneider Electric - France
- Ingeteam - Spain
According to a separate report by the International Data Corporation (IDC) energy utilities will be investing $800 million into Internet of Things connected substation automation technologies in 2016. The investments would ensure that older substations retrofit new systems to benefit substations through automation.
The automating of substations will ensure efficiency and reliability of energy supply for utilities. Real-time analytics through Internet of Things connected technologies will also ensure that utilities can measure how efficiently they are providing their services.
IT professionals will also see more employment through utility-funded efforts into cybersecurity for automated systems. Cyber threats are very real in the substation automation market ; hackers and cyber criminals are capitalizing on the network weaknesses of internet-connected substations.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
30 billion Internet-of-Things-connected devices are supposed to up and running by 2020. Some of these connected devices will be in the industrial automation industry, that will ensure manufacturing of goods never dies. But how many were running in 2015? A study conducted by an IoT analyst firm named Berg Insight has given a clear picture of just how many devices were connected. The report indicated that 14.3 million wireless IoT devices were connected in the industrial automation industry in 2015.
The report states that automation networks will grow at a CAGR of 27.7 percent, reaching 62 million Industrial Internet of Things devices by 2021.
The leading technologies that enable the wireless operations of automated factories are currently WiFi and Bluetooth technologies. Recently, an industry-wide architecture for narrowband internet-of-things two-way communication was secured by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project. Making the future of wirelessly connected devices that much quicker and efficient.
Johan Svanberg, a Berg Insight analyst, said: "Wireless communication and industrial IoT solutions can provide integration of different automation systems as well as enterprise systems which enables supply chains to be lean, even with a complex mix of products and output levels. Connected automation solutions also open up the possibility for entirely new business and service models which can give companies a much needed competitive edge in today’s manufacturing landscape."
Digital Trends reports that the three companies wanting to capitalize on Internet of Things infrastructure are Cisco, General Electric, and Verizon.
Business Insider confirmed that the industrial automation will be utilizing the most Internet of Things technologies, followed by government and the consumers coming in at third place. The market has been estimated to reach $6 trillion in the next five years.
Source: Berg Insights
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Research and Markets have released their projections for the growth of global battery energy storage systems pertaining to the smart grid. The report investigates the growth from 2016 to 2020. What the report reveals is that the market for smart grid battery technology will grow at a CAGR of 72.91% from 2016 to 2020. The report was generated through industry analysis which included market analysis and interviewing engineering experts.
 The companies who took part in the report are some of the biggest engineering companies in the world today: Siemens, ABB, Samsung, GE-Alston, Bosch, AES Energy Storage, Bosch, Saft, and more. The report investigates the current market landscape, how batteries are segmenting the marketing, market drivers, impact of those drivers and key leading countries, amongst other things.
The companies who took part in the report are some of the biggest engineering companies in the world today: Siemens, ABB, Samsung, GE-Alston, Bosch, AES Energy Storage, Bosch, Saft, and more. The report investigates the current market landscape, how batteries are segmenting the marketing, market drivers, impact of those drivers and key leading countries, amongst other things.
The research was conducted by Technavio, who said: "With growth in population and increasing urbanization, there has been an increase in power consumption. Excess power consumption has led to power outages in many countries and has also resulted in heavy loads during peak hours. One of the reasons for power outages is the massive loss of electricity during its transmission and distribution from the power plants. The use of smart grid storage technologies enables reduction of such losses and improves the efficiency of power plants."
Lithium-ion batteries are used to store the energy that these renewable technologies generate. The battery market will grow at a CAGR of 72% from 2016 to 2020. Sayani Roy, an analyst at Technavio for smart-grid research, said: "The cost of Li-ion batteries, however, is a big challenge for the industry. Companies are focusing on developing cost-effective Li-ion batteries. The Li-ion battery cost has dropped at an average of 23% per year since 2010, while the energy storage system cost has also dropped at an average of 14% per year. This has led to a total installation cost reduction by 17%."
The global need for power will be increasing the desirability of smart-grid technologies, hence the rise in annual growth percentages. To see physical proof of this growth, REN21 conducted a report named the Renewables 2016 Global Status Report. The account said that 25 percent of global electricity capacity in 2015 was powered by renewable energy technologies.
According to their report, wind and solar made up 77 percent of the smart-grid technology that provided the global renewable energy in 2015. Hydropower was the second biggest contributor. The report also showed that global investment reached a "record level" in 2015. It showed that renewable technologies were fast replacing fossil fuel energy technologies.
Employment in renewables grew - excluding hydroelectric power - to 8.1 million jobs in 2015. Solar industries employed the most engineers, however, hydroelectric power supplied 1.3 million jobs by itself.
Source: Business Wire
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
When designing a substation, engineers have to think about everything. They need to ensure the safety of a substation and need to ensure that at all times they would be able to control any situation that could put substations in danger. However, hurricane weather is one of those 'act-of-god' problems that can't exactly be predicted decades in advance. Therefore, once weather interferes, a different level of safety is exercised. Substation robots.
A utility named FPL, in Florida, have unveiled their substation robots that will ensure power is restored at a quicker rate once a storm hits the state. The robot has a GPS (global positioning 
Bill Orlove, an FPL spokesperson, spoke to Florida Today, saying: "This is the latest tool that we have in our toolkit to help restore service to our customers when the storm passes." He also says that there are 600 substations in FPL's jurisdictional area and says that the robots would assist restoring power to those hard to reach substations.
The utility also plans to use drones to survey the surrounding areas of substations that may have been damaged by a storm.
"So with the substation robot, that will be pre-deployed so it'll be ready to once we're able to access it, the unmanned aircraft system or drone, that would be in an area where we've seen where there may be some damage, we would send people out there to fly it, it would both save us time and efficiencies, make it more efficient for us," Orlove added.
The novel idea could influence other utilities to follow suit and get their hands on their own drones and robots that could restore power to communities during storms, where sending engineers out is impossible.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Thirty football fields in size. 500 metres wide. A marvel of civil engineering. It's the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope, also known as FAST, and the construction is complete. The final touches are happening and it will be fully operational in September. The Xinhua News confirmed that the final 4,4450 panels were positioned in the center of the dish.
Chinese scientists had the idea for the telescope back in 1994, and now it has been completed. Engineer Zhu Boqin immediately began surveying land to decide where the telescope should be built. He eventually found a "round depression

embraced" by hills in China's Guizhou Province and subsequently decided that that was the perfect place. The engineer said that the site's surroundings provided a perfect platform that facilitated the right amount of radio silence for the telescope. There are no towns in a 3-mile radius. The only problem was that the round depression had a village in the middle of it. The residents were relocated in 2009, and then the project really started gaining traction. The telescope is a global collaboration between the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NOAC) and Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO).
What is the telescope being used for?
Survey neutral hydrogen in distant galaxies and detect faint pulsars (highly magnetised balls of neutrons)
More than 2,000 pulsars so far said to have been detected
Improve the chances of detecting low frequency gravitational waves
Help in the search for extraterrestrial life
Source: Xinhua, South China Morning Post
 Talking to CCTV, Yue Youling, associate researcher of National Astronomical Observatories, said: "Understanding the fundamental physics of pulsars will help us understand the Big Bang. Now we only know what happened after the Big Bang, everything before that relies on our calculation. Therefore, there are a lot of uncertainties."
Talking to CCTV, Yue Youling, associate researcher of National Astronomical Observatories, said: "Understanding the fundamental physics of pulsars will help us understand the Big Bang. Now we only know what happened after the Big Bang, everything before that relies on our calculation. Therefore, there are a lot of uncertainties."
It cost a total of $185 million to construct.
NAN Redong is the general engineer and chief scientist on the FAST project. He said: "FAST will enable Chinese astronomers to jump-start many scientific goals, such as surveying the neutral hydrogen in the Milky Way. detecting faint pulsars, and listening to possible signals from other civilizations. It's time for China to have its own big telescope."
That's right. The Chinese want to contact civilizations hidden in the cosmos, or pick up their communications that they have been sending our way. You know, amongst other great uses the telescope offers. Nonetheless, scientists would be nowhere without engineers. They have built one good-looking telescope. and might just built the greatest chat room between civilizations.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Making the switch to renewable energy is slowly becoming easier and easier in a world that desperately desires progress in clean energy markets. Energy consumers want more control. Car manufacturers noticed this and companies like Tesla, BMW, Nissan and more, saw the gap in the market. Car manufacturers want to power homes and power vehicles in one all-inclusive, multi-faceted system. This future, cars manufacturers envision, all depend on lithium technologies. And more companies are jumping on the bandwagon.
Hanergy is the world's leader in thin-film solar power manufacturing and offers a range of solar photovoltaic packages that assist consumers in powering their households, allowing them to move further away from the utility grid. They also specialize in wind and hydropower generation. However, they are jumping into the vehicle game as well. The company has announced plans to release solar- powered electric cars. The cars have thin-film solar panels on the bonnet and on the roof, capturing the energy from the sun, converting it, and storing in lithium-ion batteries. This means that electric vehicle charging stations are essentially not necessary, granted there is enough sun to power the vehicle. However, the vehicle can still be charged via EV charging stations. They're calling it the "zero charge" feature, that they hope to improve in upcoming years.
powered electric cars. The cars have thin-film solar panels on the bonnet and on the roof, capturing the energy from the sun, converting it, and storing in lithium-ion batteries. This means that electric vehicle charging stations are essentially not necessary, granted there is enough sun to power the vehicle. However, the vehicle can still be charged via EV charging stations. They're calling it the "zero charge" feature, that they hope to improve in upcoming years.
The vehicles can currently drive 49 miles on a six-hour solar charge. A full charge via an EV charging station would see the vehicle doing 217 miles on one charge. The company says their current cells convert solar energy at 31.6% and will further increase that to 38% by 2020. By 2025, the company hopes to have 42% conversion and also hope that a fully solar-powered car could be a reality by then.
"Breaking the bottleneck of poor practicality of previous solar-powered vehicles, the four launched by Hanergy are the first full thin-film solar power vehicles that can be commercialised, redefining new energy vehicles," Hanergy said in a statement.
The company is also developing more efficient solar panels that can be put on buses, to make buses more energy efficient and reduce emissions.
Source: China Car News
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Formula E is an auto-racing competition that uses only electric-powered cars. The battery packs inside the vehicles are developed by Williams Advanced Engineering that is housed inside a body shell named the Spark-Renault SRT 01E. The car goes 0 to 60 MPH in 3 seconds and can reach a maximum speed of 140 MPH.
The batteries were updated by Williams Advanced Engineering in what they called the 'season two' battery, a year ago. The engineers have said that they intend to deliver 850kWh of power, making the batteries 25% more effective than the first season of battery packs they designed.
 Now, the company is looking to repurpose the batteries once they have served their time in the Formula E vehicles. This is not a new idea, both Nissan and BMW will be re-using pre-existing lithium batteries once they reach their allotted legal lifespan. However, the lifespan of the lithium batteries used in cars is much longer than the legal lifespan of the vehicles, so they can be re-used once they are taken out of the vehicles. So, they can be re-used to provide energy storage to home units or other grid-balancing applications.
Now, the company is looking to repurpose the batteries once they have served their time in the Formula E vehicles. This is not a new idea, both Nissan and BMW will be re-using pre-existing lithium batteries once they reach their allotted legal lifespan. However, the lifespan of the lithium batteries used in cars is much longer than the legal lifespan of the vehicles, so they can be re-used once they are taken out of the vehicles. So, they can be re-used to provide energy storage to home units or other grid-balancing applications.
Therefore, Williams Advanced Engineering has announced that they will be re-using the batteries from their battery packs for home energy storage. Paul McNamara, the Techincal Director at Williams Advanced Engineering said: "For us, Formula E acts as a proving ground for higher batteries working in harsh environments. We have been able to fully test and validate our cooling systems, charge retention, and module design, and apply this technology to other projects outside of motorsport."
The battery parks hold a degree of fire-proof guarantee due to the work engineers had to do to ensure that the batteries did not explode during high-temperature races. The engineers have said that their batteries cool each and every cell

and control them to perform optimally. This bodes well for the company. Lithium-ion batteries, especially in the home storage unit market, could suffer from thermal runaway, which could cause the batteries to explode. However, McNamara says: "We can measure the battery's performance during each session [the race], and crucially the temperature of each individual cell to monitor how well thermal management is working." Hence, the engineers are confident that these batteries can be used for home energy storage, due to the thermal management and storing capabilities of their batteries.
"The championship really is a point of innovation for electric road cars. We've been able to test and validate various aspects, such as safety requirements, which are important considerations in the creation of electric vehicles. Things such as flammability, cooling, crash testing and potential leaks have all been evaluated in Formula E and now massively influence our design when developing systems for road cars," McNamara added.
All of this points to a more efficient and safer home energy storage unit. The Energy Storage Wars are quick becoming a game dominated by the automobile industry who ensure that their batteries are re-usable and efficient.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
As renewable technologies make their way into our lives, we wonder how we will integrate the newly available technologies with our older technology that we still use to power our homes, our electronics and much more. Ir's hard to imagine calling some sort of firm and asking them to strip your house of its electricity and replace everything with solar cells tomorrow. So what we are left with is buying home energy storage units and saving ourselves some money by using less energy from the old grid in peak times.
Enter, the passive solar building. A building designed with solar energy in mind. A guest blogger for Sturdy Structural defines the passive solar building as a building designed with energy saving elements. We're talking the entire building. From the roof to the walls, to the floors. Solar passive buildings take the climate into consideration, using energy-saving applications to collect any and all energy that the sun is giving to the units.
To see the engineering design principles behind passive solar buildings, check this video out. This uses a house as an example, however, more and more business complexes are building with passive solar technologies in mind:
 Cornell University has also gotten wind of further development in passive solar buildings. The university has seen designs that could make their next dormitories the most energy-efficient dorms in the world. The dorms will be a $115 million project and stand at 26-stories high. The passive solar design will ensure that the building uses 70 to 90 percent less energy than buildings of equal size. The engineers behind the building say it will be the largest passive-house building in the world once it is completed. The building will have 550 solar panels on the roof that will power the building. The dorms will be air-tight and will prevent any outside air of making its way in requiring more energy to be used. Special vents will be used to funnel and filter fresh into air into the dorms.
Cornell University has also gotten wind of further development in passive solar buildings. The university has seen designs that could make their next dormitories the most energy-efficient dorms in the world. The dorms will be a $115 million project and stand at 26-stories high. The passive solar design will ensure that the building uses 70 to 90 percent less energy than buildings of equal size. The engineers behind the building say it will be the largest passive-house building in the world once it is completed. The building will have 550 solar panels on the roof that will power the building. The dorms will be air-tight and will prevent any outside air of making its way in requiring more energy to be used. Special vents will be used to funnel and filter fresh into air into the dorms.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The time for getting your qualifications in engineering for oil and gas facilities has never been better. Kenya is ready to construct a 538-mile crude oil pipeline that will provide oil for a new port being built on the Indian Ocean coastline. This was confirmed by a government official on Thursday.
Pipeline engineers are now in a unique position because they can now apply to be considered to design the front-end engineering design of the pipeline.
 Ministry of Energy and Petroleum Principal Secretary Andrew Kamau, speaking to Bloomberg said: "Once we have the pipeline design, the engineering, procurement and construction contract would be awarded in first quarter 2018. It would take us that long as we need environmental impact assessment study conducted to international standards for the project to be able to attract international funding."
Ministry of Energy and Petroleum Principal Secretary Andrew Kamau, speaking to Bloomberg said: "Once we have the pipeline design, the engineering, procurement and construction contract would be awarded in first quarter 2018. It would take us that long as we need environmental impact assessment study conducted to international standards for the project to be able to attract international funding."
The east of Africa is seeing unprecedented successes in oil and gas. This week, a huge helium reserve was discovered in ancient rocks in Tanzania. Kenya is in the eight spot for the list of African countries with the biggest economy. They could jump up a few spots due to this refinery being its first refinery for the country. It will be delivering its first oil in June 2017. Africa Oil has said the South Lokichar basin will produce approximately 1.63 billion barrels of oil. The pipeline is estimated to cost $2.1 billion to build, which is a modest number based on other countries in Africa that have built bigger pipelines. Kenya seems to be playing catch up.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Rutgers University is New Jersey's own state university in the United States. The university's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering have shown off their new squishy robot. Yes, you read that right. To be more specific, the robot is considered to be a pneumatically driven elastomeric structure robot. The researchers have used the recent bendable robot technology to create a new robot that could have a host of applications in future industries where bendable, 'squishy' robots might be needed.

Bendable elements on robots are not a new innovation. They have been used in deep-sea coral expeditions for the purpose of handling coral with care, due to conventional robotic arms being too forceful. However, now the Rutgers researchers want to grow the innovation of soft robotics. The uses could range from sending the robots into rocky mountains or even driving the robots on different planets. The bendable, flexible material could be invaluable due to its ability to get through terrain that conventional robotics would not be able to do. See the video below to see how the robot navigates rocky terrain.
"If you build a robot or vehicle with hard components, you have to have many sophisticated joins so the whole body can handle complex or rocky terrain. For us, the whole design is very simple, but it works very well because the whole body is soft and can negotiate complex terrain," said Xiangyu Gong, an alumnus of Rutgers University in the mechanical engineering department.
The researchers used silicone rubber to build a wheel and axle assembly and used motors that are engineered to be devoid of metal. On top of that, the researchers had to assemble the vehicle to ensure its safety should it survive some sort of impact.
The team used 3D printers to print the rotors they used. As a result, the researchers were able to create 'squishy' pneumatic internal and external rotors. The external rotors were able to be used as wheels that the researchers used to design a four-wheeled rover robot.
"With no metal components and moisture-sensitive electronics on the vehicle itself, the vehicle is equipped with the actuators. [The rotors] function not only in a dry environment but also underwater as an amphibious vehicle," the researchers said. The researchers also showed that the robot could be dropped from eight times its height and survive the fall.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
A survey conducted by the Boston Consulting Group has revealed that Germany has shown more interest than the United States in industrial automation technologies. After receiving the opinions of 300 German and US manufacturing executives, the study showed that German executives were more ready for digital solutions in factories. However, only 17 percent of American and German manufacturers have adopted industrial automation. Business Insider confirms that 40 percent of German companies plan to update their factories with current automation technologies however only 25% of US factories feel the same way.
 The competition continues. 8% of U.S. manufacturers have autonomous robots and collaborative robots whereas Germans almost double that demand by having 14% of factories equipped with them. The US will want 20% more of those robots working in their factories in the next two years whereas Germans will want 39% more, of what they already have.
The competition continues. 8% of U.S. manufacturers have autonomous robots and collaborative robots whereas Germans almost double that demand by having 14% of factories equipped with them. The US will want 20% more of those robots working in their factories in the next two years whereas Germans will want 39% more, of what they already have.
The report also stated that worldwide spending on IoT connected factory automation technology reached $29 billion by the end of 2015 and will top $70 billion in 2020.
Germany's unique position on Industrie 4.0 has related to 47% of the companies surveyed saying that they have developed IoT strategies for the future of their companies. American companies say only 29% of them have strategies prepared.
"German companies' strong ambitions for Industry 4.0 reflect their need to overcome the challenges of significant factor costs that arise from high wages and a less flexible labor market. These factor costs encourage companies to strive for greater productivity and, thus, promote faster adoption of new technologies. The fast pace of adoption in Germany is also fueled by companies' advanced industrial-manufacturing capabilities. Companies can apply these capabilities to accelerate the introduction of new digital technologies, thereby reducing costs, increasing flexibility, and accelerating the speed of manufacturing," the researchers wrote.

"The early adopters have set a fast pace for implementation and are building capabilities that will enable them to increase their lead. To maintain their competitiveness, all companies will need to accelerate their efforts along the Industry 4.0 journey," the report concluded.
Source: Yibada
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
The world needs helium. We use it for many things, and then usually waste it by sucking it out of a balloon and putting on a cartoonish voice. Recent reports have indicated that the world is running low on helium due to the lack of new reserves. Thankfully, researchers in Tanzania have discovered a new reserve. Good news for balloon animals but also good news for MRI scanners and nuclear power plants. However, nuclear power plants need a special kind of helium, but the good news continues because the researchers in Tanzania say the new reserve is filled to the brim with "world-class" helium. The researchers have been working with a Norwegian company specializing in helium named Helium One. The researchers are from the University of Oxford and Durham University.
 "This researcher shows that volcanic activity provides the intense heat necessary to release the gas from ancient, helium-bearing rocks. Within the Tanzanian East African Rift Valley, volcanoes have released helium from ancient deep rocks and have trapped this helium in shallower gas fields," said the University of Oxford in a statement.
"This researcher shows that volcanic activity provides the intense heat necessary to release the gas from ancient, helium-bearing rocks. Within the Tanzanian East African Rift Valley, volcanoes have released helium from ancient deep rocks and have trapped this helium in shallower gas fields," said the University of Oxford in a statement.
The researchers use similar drilling techniques used in oil and gas discovery. Chris Ballentine, chief of geochemistry at Oxford who worked on the team that discovered the new helium, spoke to the Washington Post. He said: "We look for source rock, we look for a mechanism to release the gas from the source, and we look to understand how gases migrate and looking for trapping structures."
We also use helium in semiconductor manufacturing. Rodney Morgan, the vice president of procurement at the Semiconductor Industry Association said: "Although the semiconductor industry consumes only a small amount of the overall quantity of helium used today, it remains a critical, irreplaceable input into our manufacturing process."
Helium is also used to clean NASA's space shuttle engines. So, we imagine Elon Musk is probably doing the same. This means, we need a lot of helium in the world, without even considering what uses the most helium, which is, of course, helium balloons.
So, good thing we've found more, then. Diveena Danabalan of Durhan University's Department of Earth Sciences spoke to CNN, saying: "We are now working to identify the 'goldilocks-zone' between the ancient crust and the modern volcanoes where the balance between helium release and volcanic dilution is 'just right."
The researchers say that the new discovery could see more than a million MRI scanners being filled. Professors at Oxford say the discovery is a "game-changer" and will lead to more discoveries through the same methods soon, ensuring that society never runs out of helium. The researchers say the discovery comes at the right time, due to a helium price escalation of 500% in the last 15 years.
- Details
- Written by: Quintus Potgieter
Emissions testing company Emissions Analytics have written a report indicating that Diesel cars produce more emissions during winter. The group says that once the outside temperature reached below 18 degrees centigrade (65,4 Fahrenheit) cars began to release more emissions. The company reportedly tested 213 different models from 31 different auto engineering companies. The group found that cars built in the 2009-2011 bracket have produced the most emissions.
The tweaking of the engine in colder conditions has been proven to underreport the number of emissions the cars produce. Chief Executive of Emissions Analytics, Nick Molden, said: "If we were talking about higher emissions below zero, that would be more understandable and there are  reasons why the engine needs to be protected. But what we've got is this odd situation where the temperature threshold has been set far too high, and that is a surprise." The group found that the Euro 5 vehicles (manufactured between 2009-2011) produce 4.6 times the legal parameters for Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) when the outside temperature dropped.
reasons why the engine needs to be protected. But what we've got is this odd situation where the temperature threshold has been set far too high, and that is a surprise." The group found that the Euro 5 vehicles (manufactured between 2009-2011) produce 4.6 times the legal parameters for Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) when the outside temperature dropped.
The group did, however, say that the Euro 6 cars manufactured from September 2015 onwards reported better numbers, only reaching 2.9 times above the legal NOx limits.
Engineers say without the pollution controls partly switching off under colder temperatures, engines would undergo amounts of damage. The carmakers say it is a necessary method to ensuring that vehicles don't break down.
These revelations come at a time of an ongoing emissions scandal that has rocked the automotive engineering industry. Volkswagen has confirmed that they will use $15.3 billion to buy back vehicles from consumers. The carmaker admitted to developing software that underreported the amount of emissions their cars did.
VW will also be focusing on cleaner, more efficient technologies. According to Reuters, VW will be paying $2 billion over 10 years to a Californian company who specialize in electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
However, what are the automakers doing to shake off the pointing fingers, forcing their engineers to admit their years of underreporting? According to BBC:
- Vauxhall says that it is using diesel cleaning systems to prevent emissions
- Suzuki says it will be altering 3,200 cars' software to report more accurate emissions performance
- Renault has committed to buying back cars sold from September 2015 to July 2016. They will also change software to report accurate emissions
- Mercedes will tweak 26,000 A class and B class models in the UK to lower emission levels.
The Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders spoke to the BBC, saying: The temporary reduction or switching off of some emissions control systems under certain temperatures is allowed by law and necessary to avoid damage to vehicles’ engines.Without it, there could be a significant cost to the consumer for major repair work. In its recent report, government recognised the need for such technology and was satisfied with how vehicle manufacturers were using it. Manufacturers are investing billions of pounds in developing ever-more-advanced technology, and this along with new Real Driving Emissions regulation from next year will see significant lowering of emissions across a full range of driving conditions and temperatures."
